DDoS Attacks by Vectors
2023 was a year of marked transformation in the world of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Qrator Labs’ extensive report exposed several alarming developments: the strategic weaponization of DDoS as a commercial tool, a relentless rise in attacks aimed at e-commerce platforms, and an increasingly complex threat landscape demanding adaptive defense strategies.

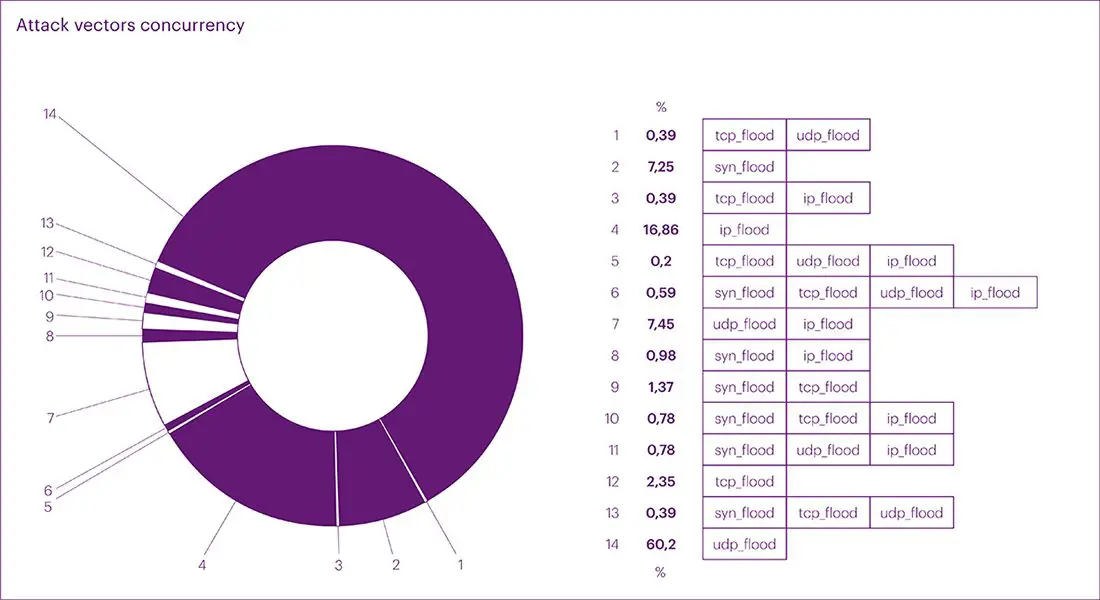
The year saw a pronounced rise in UDP flood attacks, dominating the attack vectors by a significant margin. This surge can be attributed to the shift in business infrastructures towards UDP with DTLS protocol for enhanced performance, the expansion of internet channels due to remote work setups, and the adaptation of malicious actors to more cost-effective and manageable attack methodologies. The report underscores the dominance of UDP flood attacks, constituting a staggering 60.20% of mixed attacks, with SYN flood and IP flood trailing behind at 7.26% and 16.86%, respectively. Notably, the report documents an increasing trend in commercial DDoS attacks, signaling a shift in the threat landscape that organizations must navigate.
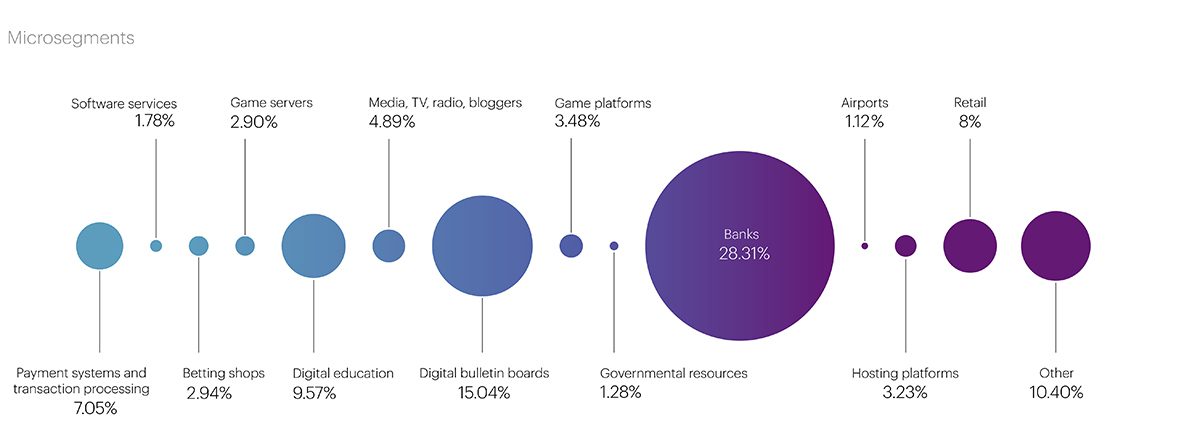
E-commerce and financial sectors bore the brunt of the attacks, reflecting a strategic choice by attackers to disrupt businesses during peak seasons. The educational technology sector also found itself in the crosshairs, underlining the broad spectrum of targets and the need for robust defense mechanisms across industries.
UDP floods remained the weapon of choice for attackers in 2023, with some striking record intensities as high as 690.24 Gbps. However, other vectors like TCP, SYN, and IP Flood, as well as mixed-vector strategies, present persistent threats that require robust defenses.
Qrator Labs uncovered alarming examples of sustained attack campaigns. Continuous assaults lasting days on end were particularly evident in the Transport and Logistics sector. Intermittent, strategic attack bursts against gaming platforms and cloud hosting represent growing sophistication, with potential implications for businesses relying on uninterrupted cloud services.
The report unveils a surge in bot activity, with online retail emerging as a prime target, witnessing a meteoric rise from 16% to nearly 30% of total bot activity. E-commerce giants faced a particular onslaught, suggesting these platforms harbor valuable data or assets prized by bot operators.
Qrator observed L7 attacks becoming more calculated. In addition to service disruptions, these attacks sometimes deliberately cause resource consumption with direct financial damage to the target. Businesses relying on cloud systems with usage-based cost models may find themselves particularly vulnerable.
The persistence of Route Leaks and BGP Hijacking tactics remains a concerning area. Although numbers remained relatively stable, these occurrences underscore the potential for large-scale disruptions of traffic routing, which can lead to a wide range of security problems.
The threat landscape exposed by Qrator Labs demands serious attention. Businesses across sectors, but particularly those heavily reliant on e-commerce, need agile defensive strategies.