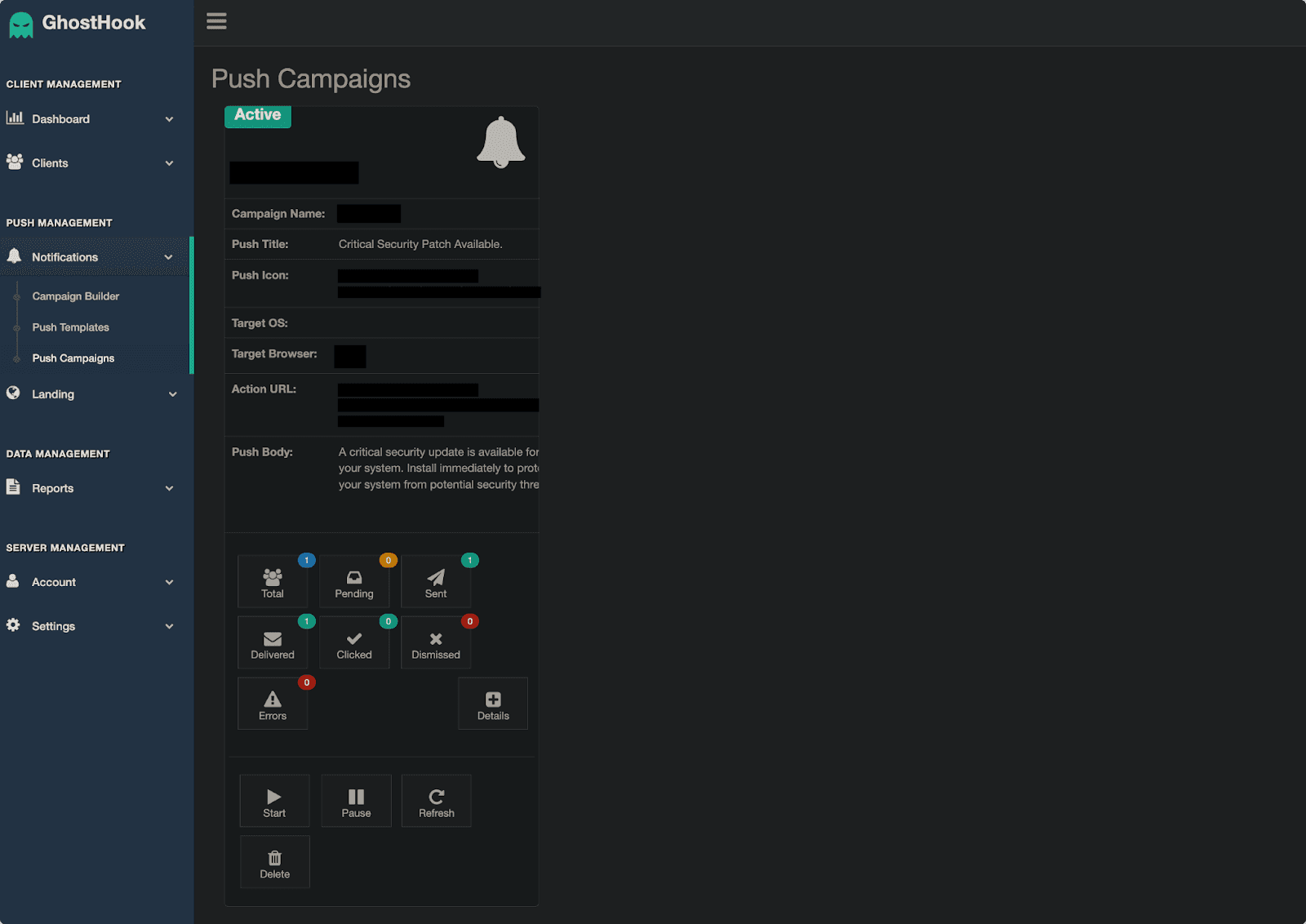
Security researchers from iVerify have recently detected a sophisticated fileless malware-spreading framework named GhostHook, which is currently being circulated across various cybercrime forums and networks. Designed for disseminating malware and other malicious payloads, GhostHook leverages numerous distribution methods, such as malicious push popups, making it an invaluable tool for cybercriminals.
GhostHook employs a multi-stage attack chain, initiating with the distribution of seemingly innocuous URLs through social media, forums, emails, or messaging platforms. Upon clicking, a hidden script embedded in the webpage seizes control of the victim’s browser, transforming it into a “slave browser.” This compromised browser is then exploited to deliver push notifications masquerading as legitimate system alerts. These deceptive notifications often prompt victims to download and install malicious payloads disguised as software updates or security patches.
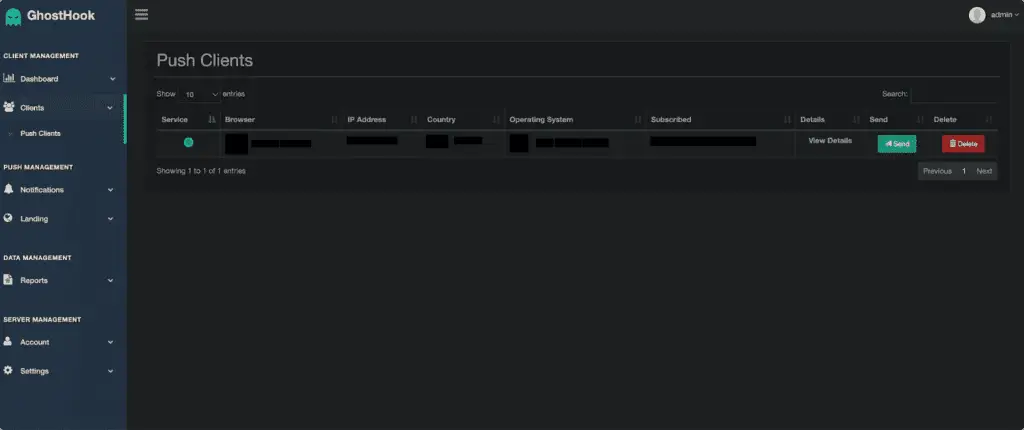
GhostHook stands out due to its compatibility with multiple operating systems and browsers, broadening its reach and impact. The framework supports Windows, Android, Linux, and macOS, while being compatible with major browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Opera Browser, and Microsoft Edge. This cross-platform and cross-browser functionality enhances its utility for attackers aiming to target a diverse range of systems.
To counter the threat posed by GhostHook and similar fileless malware, organizations and individuals must remain vigilant and adopt a multi-layered security approach. This includes exercising caution when interacting with unsolicited links, maintaining updated software and security patches, and enabling two-factor authentication where available.
Related Posts:
- Non-Malware (or Fileless) Attack: five knowledge points
- Turla APT Group Unleashes Sophisticated Fileless Backdoor via Compromised Site