Google blogs have revealed that the Android P version has a built-in mitigation vulnerability that can defeat certain types of exploits.
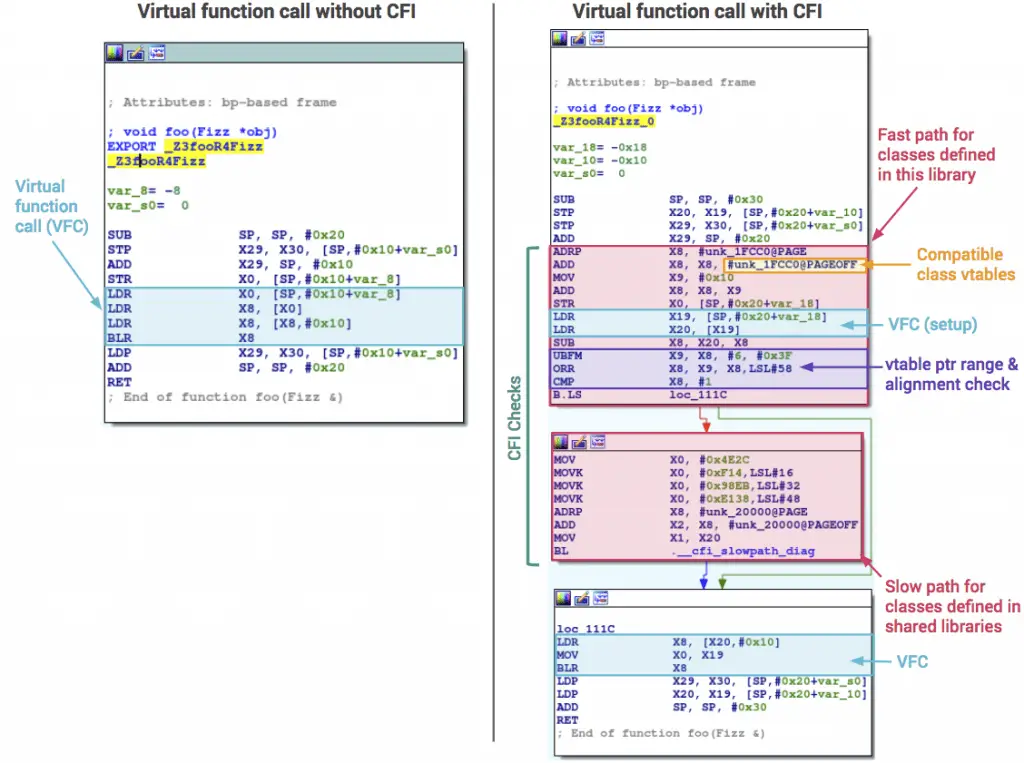
The mitigation scheme directly blocks the operation when the application has undefined behaviour to prevent re-use of the program code and data leakage issues. Google said that since the Android N version, the company has preset LLVM/Clang as a platform compiler to gain more depth security defences.

In common attack scenarios, hackers often control program flow by destroying functions or returning locations, and hackers use this executable code fragment to cause malicious purposes. The latest mitigation scheme is to use indirect jumps to prevent control flow operations, and eventually, the system will check for illegal functions by verifying the signature.
Also, the Google Media Services Framework, which often has vulnerabilities, is currently being expanded to use LLVM-based cleaners to remove unnecessary checks.
Google said that after testing, it found that the improved cleanup process would reduce the performance impact by 75%, and for some programs, it would improve the response speed.