headerpwn
A fuzzer for finding anomalies and analyzing how servers respond to different HTTP headers.
Install
go install github.com/devanshbatham/headerpwn@v0.0.3
Use
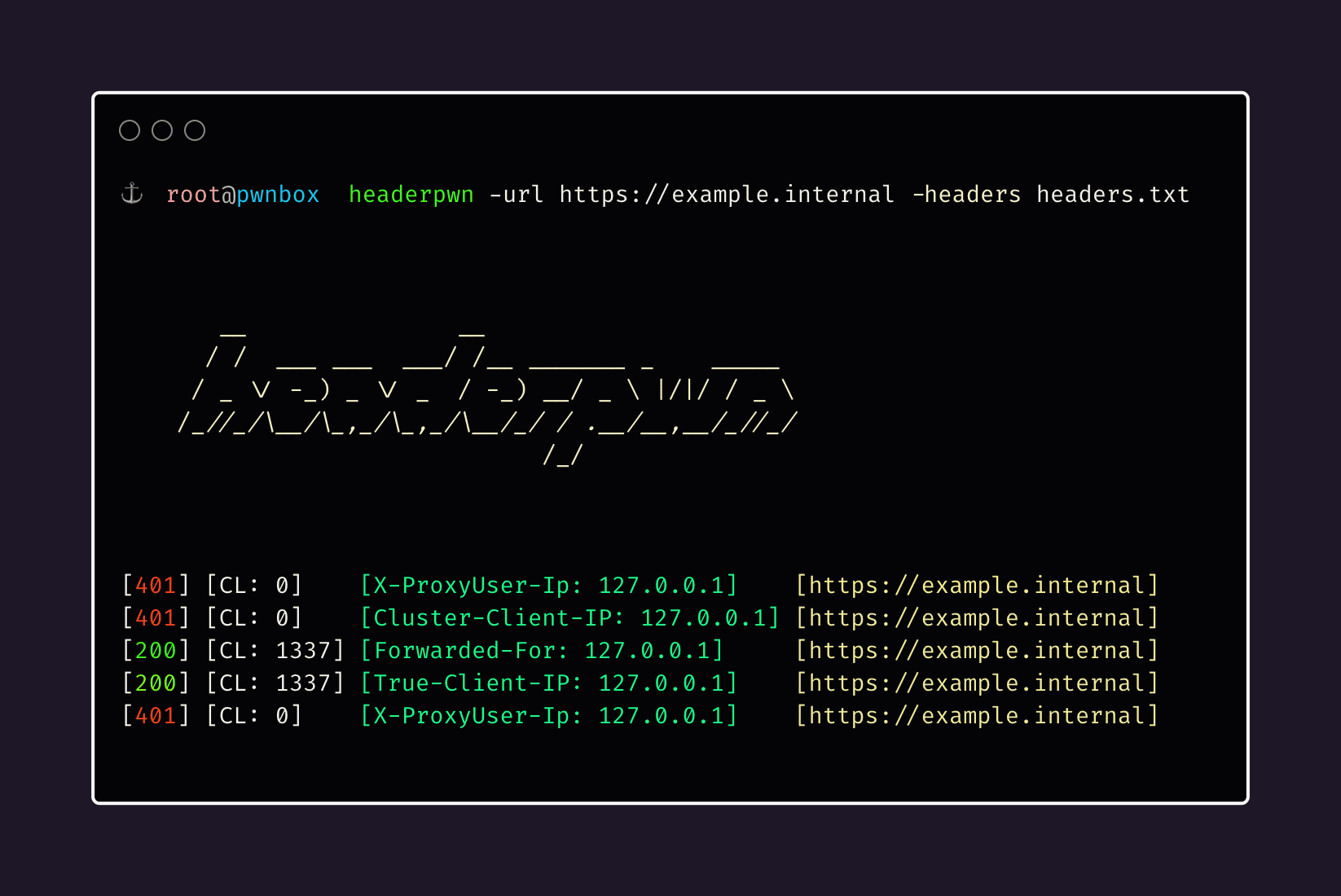
headerpwn allows you to test various headers on a target URL and analyze the responses. Here’s how to use the tool:
- Provide the target URL using the -url flag.
- Create a file containing the headers you want to test, one header per line. Use the -headers flag to specify the path to this file.
Example usage:
headerpwn -url https://example.com -headers my_headers.txt
- Format of my_headers.txt should be like the below:
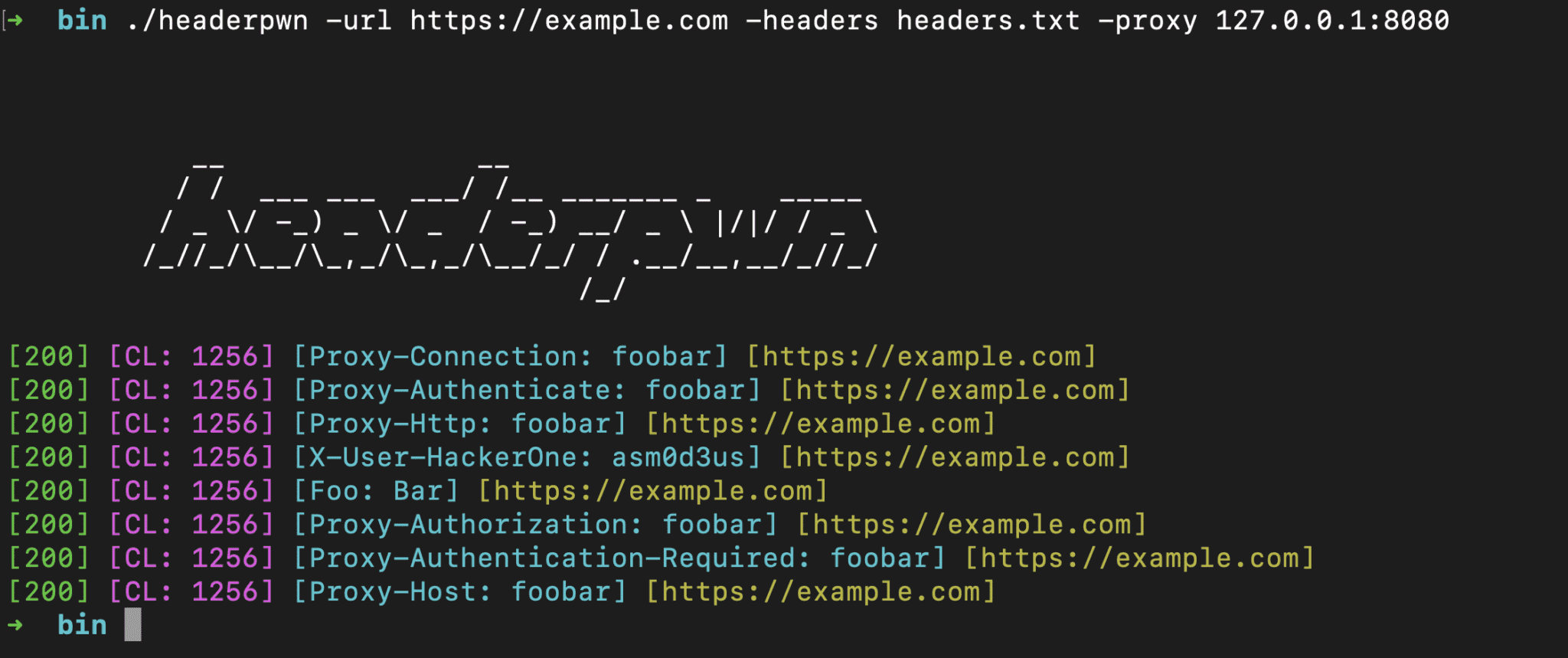
Proxying requests through Burp Suite:
Follow the following steps to proxy requests through Burp Suite:
-
Export Burp’s Certificate:
- In Burp Suite, go to the “Proxy” tab.
- Under the “Proxy Listeners” section, select the listener that is configured for
127.0.0.1:8080 - Click on the “Import/ Export CA Certificate” button.
- In the certificate window, click “Export Certificate” and save the certificate file (e.g., burp.der).
-
Install Burp’s Certificate:
- Install the exported certificate as a trusted certificate on your system. How you do this depends on your operating system.
- On Windows, you can double-click the .cer file and follow the prompts to install it in the “Trusted Root Certification Authorities” store.
- On macOS, you can double-click the .cer file and add it to the “Keychain Access” application in the “System” keychain.
- On Linux, you might need to copy the certificate to a trusted certificate location and configure your system to trust it.
You should be all set:
headerpwn -url https://example.com -headers my_headers.txt -proxy 127.0.0.1:8080

Copyright (c) 2023 Devansh Batham
Source: https://github.com/devanshbatham/