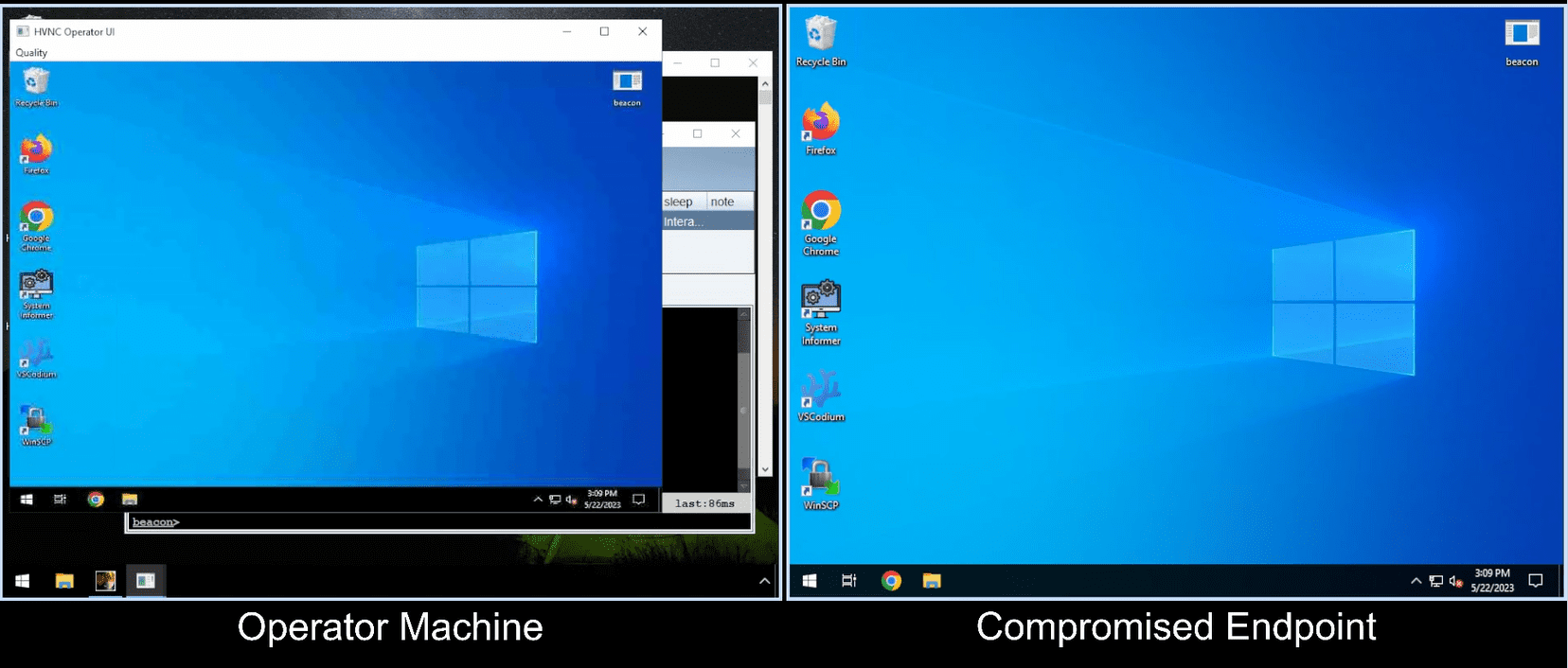
Hidden Desktop BOF
Hidden Desktop (often referred to as HVNC) is a tool that allows operators to interact with a remote desktop session without the user knowing. The VNC protocol is not involved, but the result is a similar experience. This Cobalt Strike BOF implementation was created as an alternative to TinyNuke/forks that are written in C++.

There are four components of Hidden Desktop:
-
BOF initializer: Small program responsible for injecting the HVNC code into the Beacon process.
-
HVNC shellcode: PIC implementation of TinyNuke HVNC.
-
Server and operator UI: Server that listens for connections from the HVNC shellcode and a UI that allows the operator to interact with the remote desktop. Currently only supports Windows.
-
Application launcher BOFs: Set of Beacon Object Files that execute applications in the new desktop.
Implementation Details
- The Aggressor script generates random pipe and desktop names. These are passed to the BOF initializer as arguments. The desktop name is stored in CS preferences at execution and is used by the application launcher BOFs. HVNC traffic is forwarded back to the team server using
rportfwd. Status updates are sent back to Beacon through a named pipe. - The BOF initializer starts by resolving the required modules and functions. Arguments from the Aggressor script are resolved. A pointer to a structure containing the arguments and function addresses is passed to the
InputHandlerfunction in the HVNC shellcode. It usesBeaconInjectProcessto execute the shellcode, meaning the behavior can be customized in a Malleable C2 profile or with process injection BOFs. You could modify Hidden Desktop to target remote processes, but this is not currently supported. This is done so the BOF can exit and the HVNC shellcode can continue running. InputHandlercreates a new named pipe for Beacon to connect to. Once a connection has been established, the specified desktop is opened (OpenDesktopA) or created (CreateDesktopA). A new socket is established through a reverse port forward (rportfwd) to the HVNC server. The input handler creates a new thread for theDesktopHandlerfunction described below. This thread will receive mouse and keyboard input from the HVNC server and forward it to the desktop.DesktopHandlerestablishes an additional socket connection to the HVNC server through the reverse port forward. This thread will monitor windows for changes and forward them to the HVNC server.
Use
Copyright (c) 2023 White Knight Labs