
SonicWall’s Capture Labs threat research team warns that hackers are actively exploiting a severe security flaw in the popular Progress Kemp Loadmaster application delivery controller. The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-1212, (CVSS 10) allows for unauthenticated command injection, potentially giving attackers full control of affected systems.

What is the Vulnerability?
The unauthenticated command injection vulnerability lies within a specific API endpoint of the Loadmaster. Due to improper input sanitization, malicious actors can send specially crafted requests to the LoadMaster’s web interface, bypassing authentication, and inject arbitrary commands.
Who’s at Risk?
All LoadMaster versions after 7.2.48.1 are vulnerable. LoadMasters are widely used for load balancing and application delivery across hardware, cloud, and virtual environments. The sizeable user base makes this a particularly attractive target for attackers.
The Threat is Real
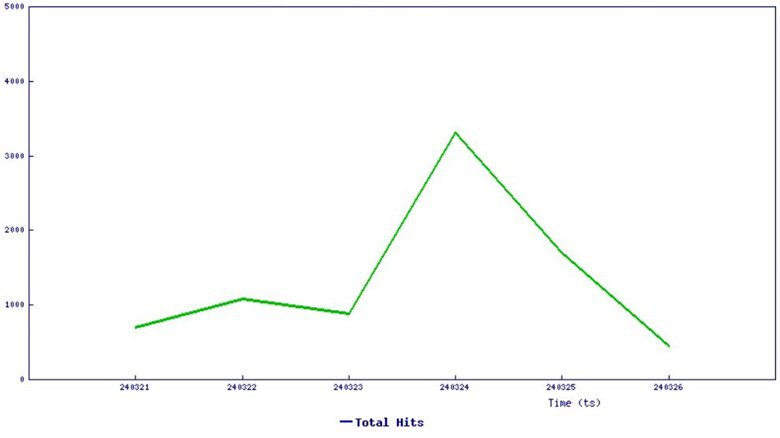
SonicWall sensors have already detected a rising number of active exploitation attempts targeting this vulnerability in recent weeks. This highlights the importance of immediate action.
“SonicWall sensors have confirmed active exploitation of these vulnerabilities. The graphs below indicate an increasing number of exploitation attempts over the last 40 days,” SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team confirms.
Consequences of Exploitation
If attackers successfully exploit this vulnerability, the consequences could be devastating:
- Complete System Compromise: Attackers could gain full administrative control of the LoadMaster.
- Data Exfiltration: Sensitive data could be stolen.
- Disruption of Services: Critical business operations that rely on the LoadMaster could be brought down.
- Further Attacks: The compromised LoadMaster could be used as a springboard for attacks on other systems within the network.
What Can You Do?
Kemp Technologies has released patches to address the vulnerability. LoadMaster users are strongly urged to prioritize upgrading to the latest patched versions. Failure to do so could leave organizations highly exposed to cyberattacks.