LetsMapYourNetwork v2.0 releases: visualise your physical network in form of graph
LET’S MAP [YOUR] NETWORK (v2.0)
It is utmost important for any security engineer to understand their network first before securing it and it becomes a daunting task to have a ‘true’ understanding of a widespread network. In a mid to large level organization’s network having a network architecture diagram doesn’t provide the complete understanding and manual verification is a nightmare. Hence in order to secure the entire network, it is important to have a complete picture of all the systems which are connected to your network, irrespective of their type, function, technology, etc.
BOTTOM LINE – YOU CAN’T SECURE WHAT YOU ARE NOT AWARE OF.
Let’s Map Your Network (LMYN) aims to provide an easy to use interface to security engineer and network administrator to have their network in graphical form with zero manual error, where a node represents a system and relationship between nodes represent the connection.
LMYN does it in two phases:
- Learning: In this phase, LMYN ‘learns’ the network by performing the network commands and querying the APIs and then builds the graph database leveraging the responses. User can perform any of the learning activities at any point of time and LMYN will incorporate the results in an existing database.
- Monitoring: This is a continuous process, where LMYN monitors the ‘in-scope’ network for any changes, compare it with existing information and update the graph database accordingly.
Below technologies have been used in the tool:
- Django Python
- Neo4j DB
- Sigma JS
- Celery and RabbitMQ
WHY IT IS
- Visualizing infrastructure network in the form of the graph makes it more ‘visible’ and it becomes significantly easy to perform the analysis and identify the key areas of concern for a security engineer and network administrator
- Also, Let’s Map Your Network formulates the graph entirely based-on either network actions performed from ‘seed’ system which will be part of the actual network or querying the APIs. Hence there is no chance of manual-error in the mapping of network
WHERE TO USE IT
- Network Architecture ‘Validation’
- Troubleshooting for network administrator
- Internal Network vulnerability assessment and penetration testing
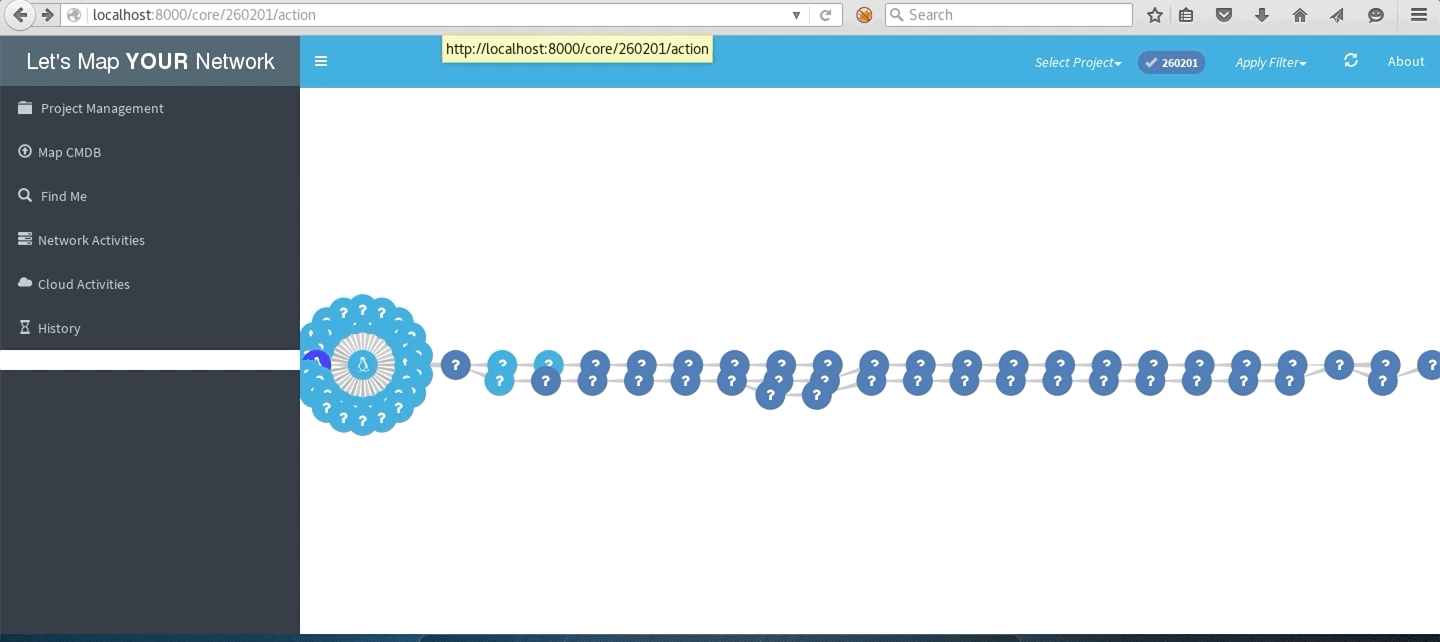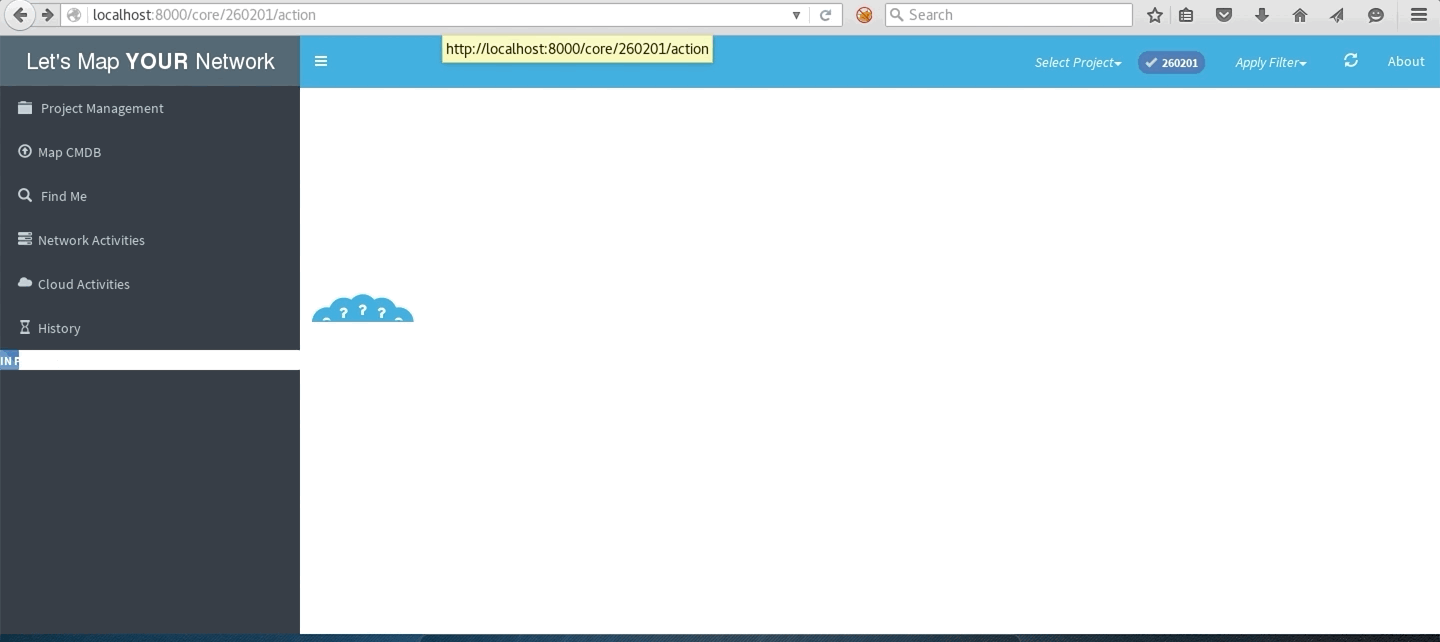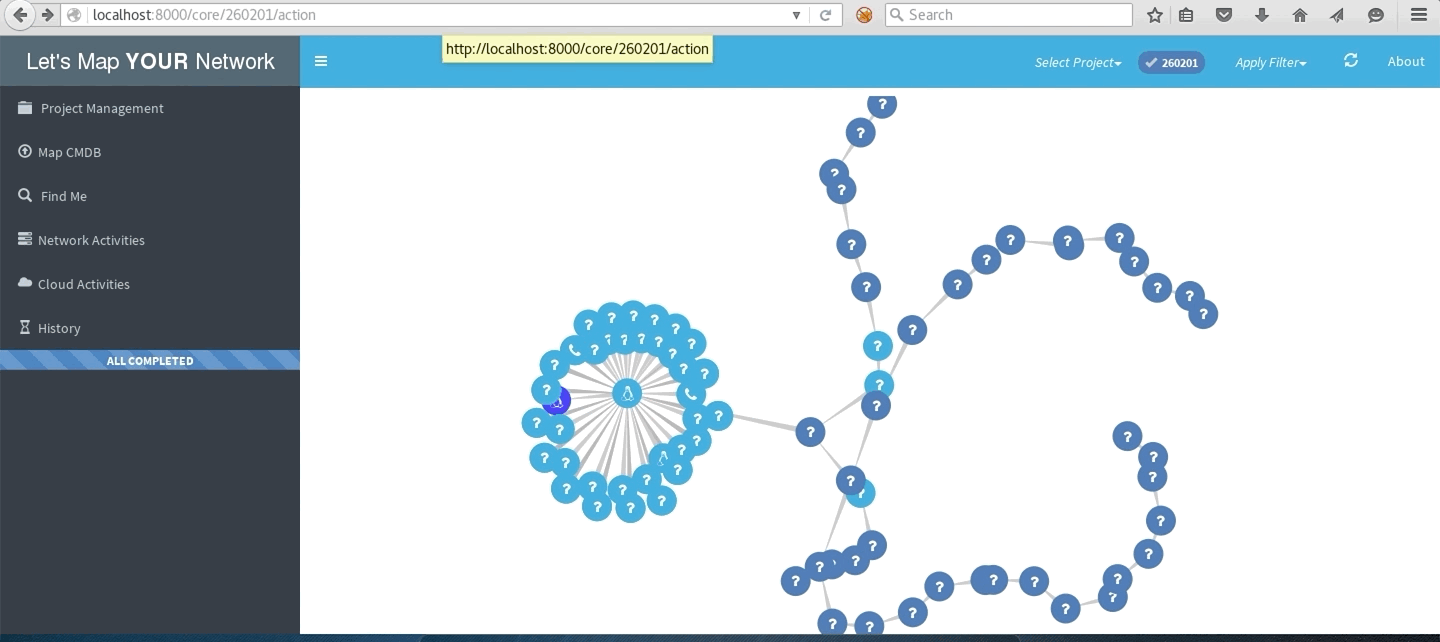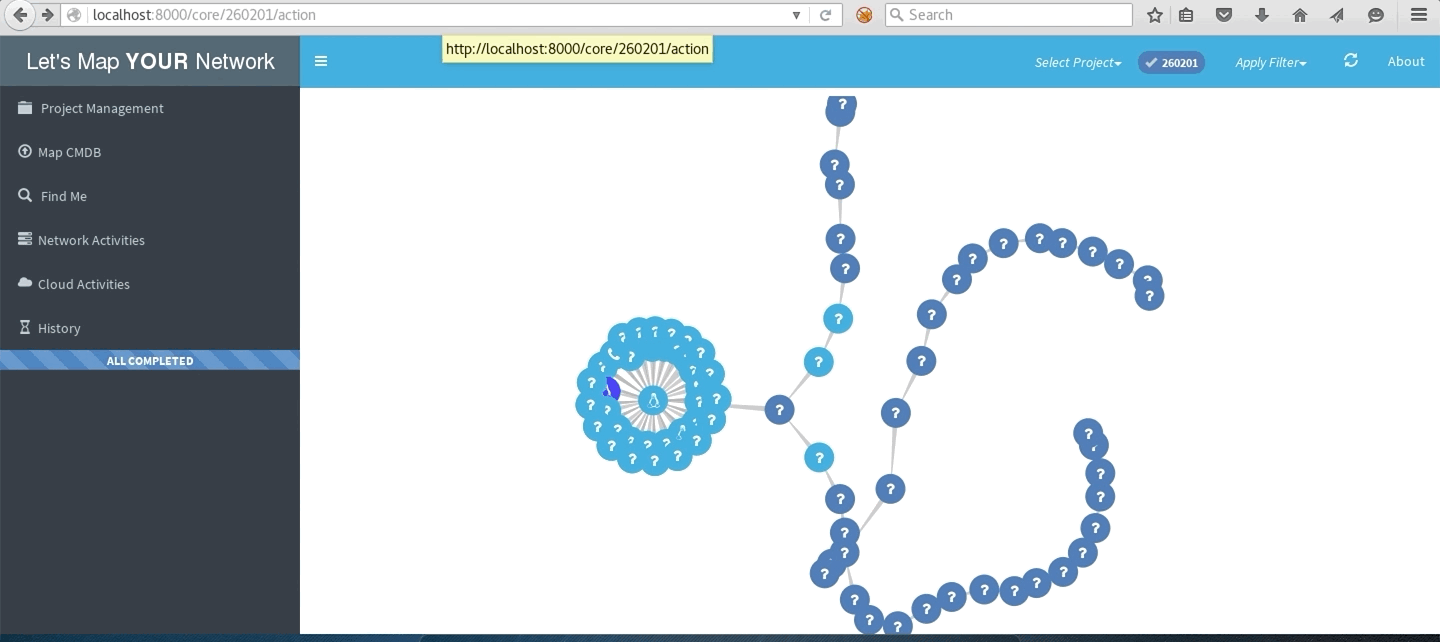
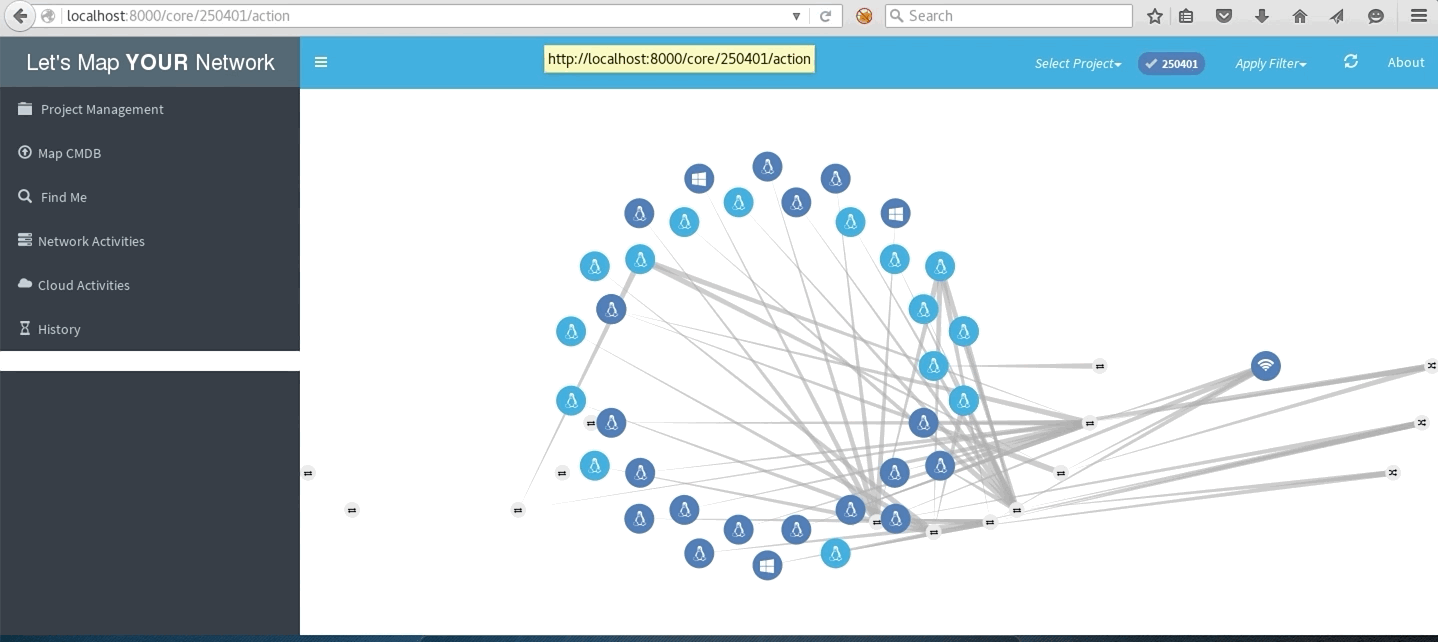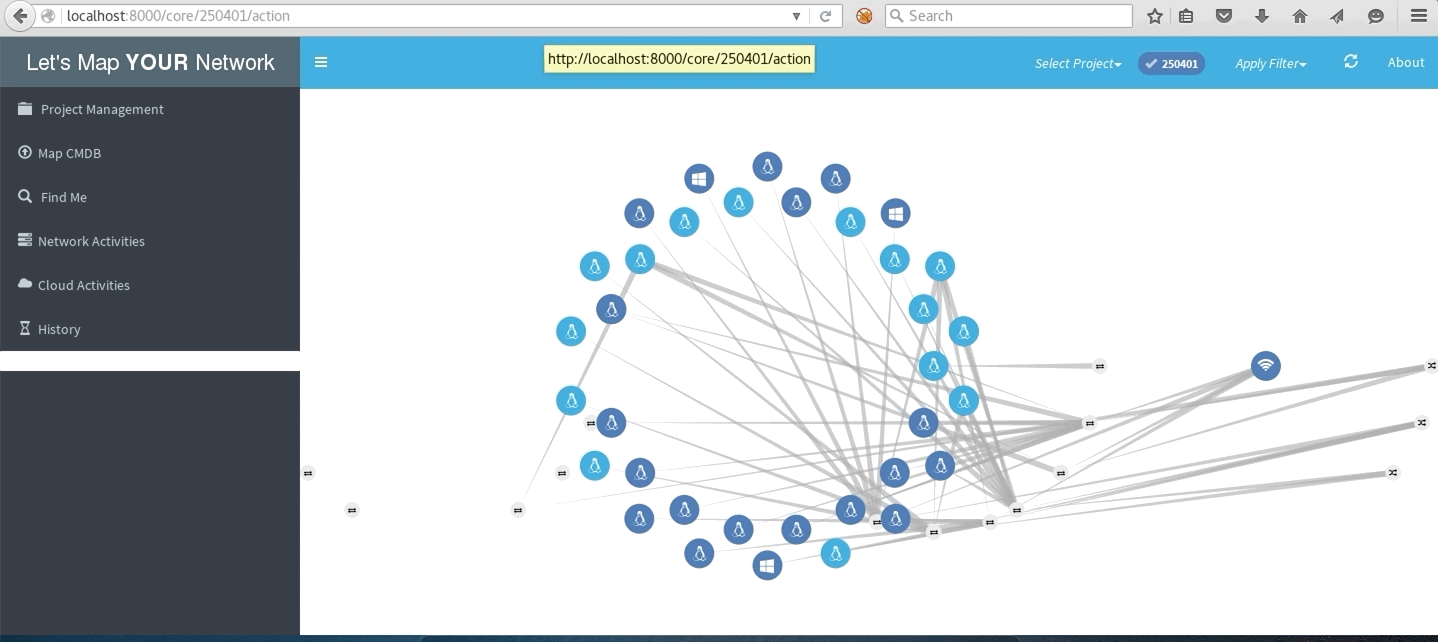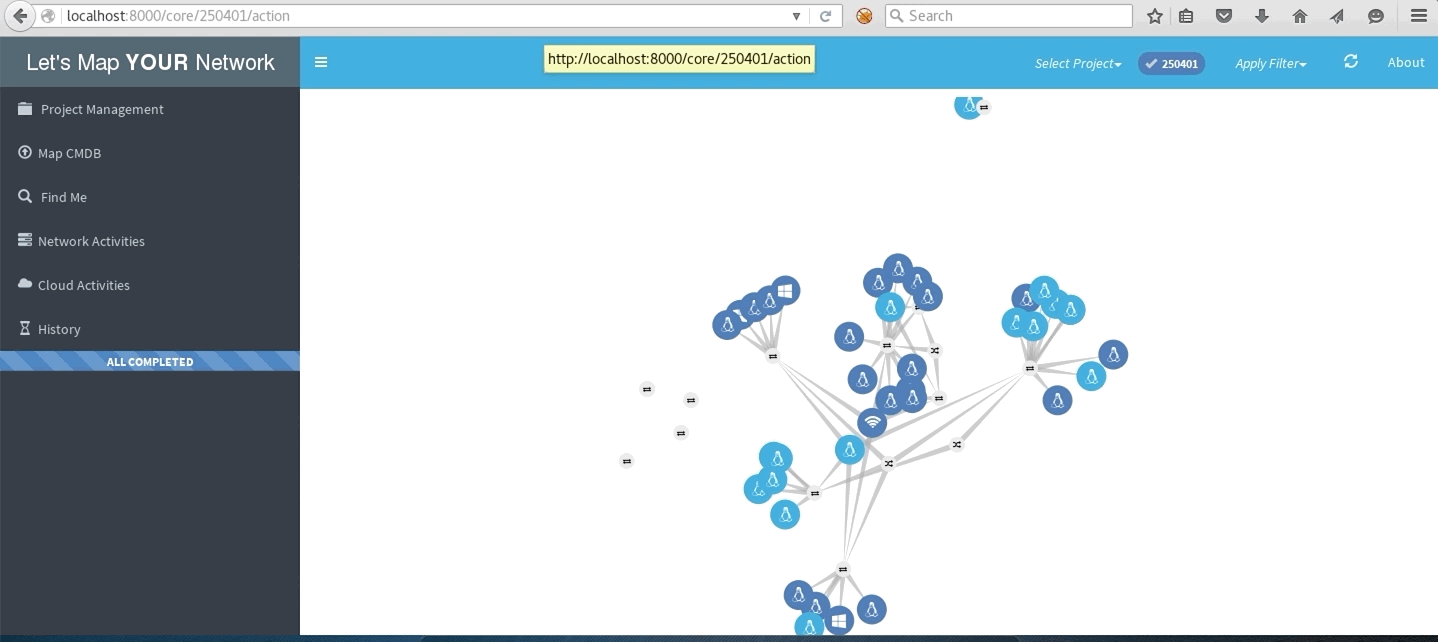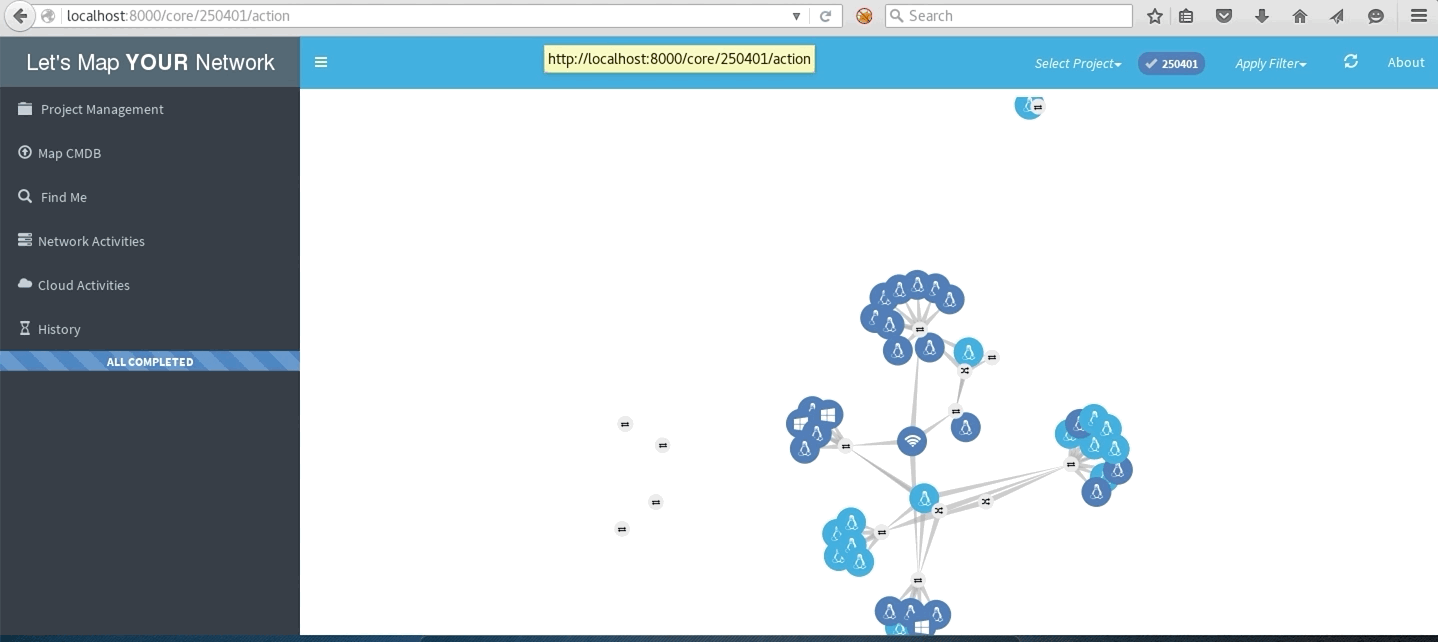
LMYN In Action
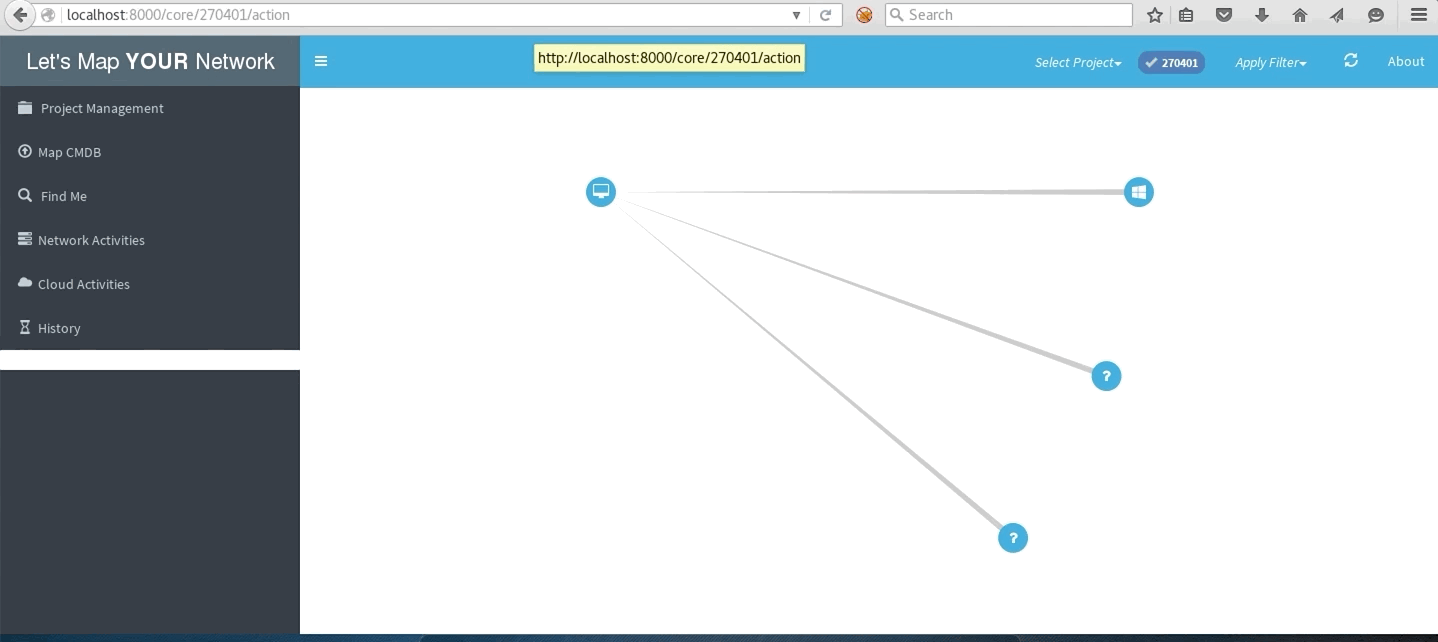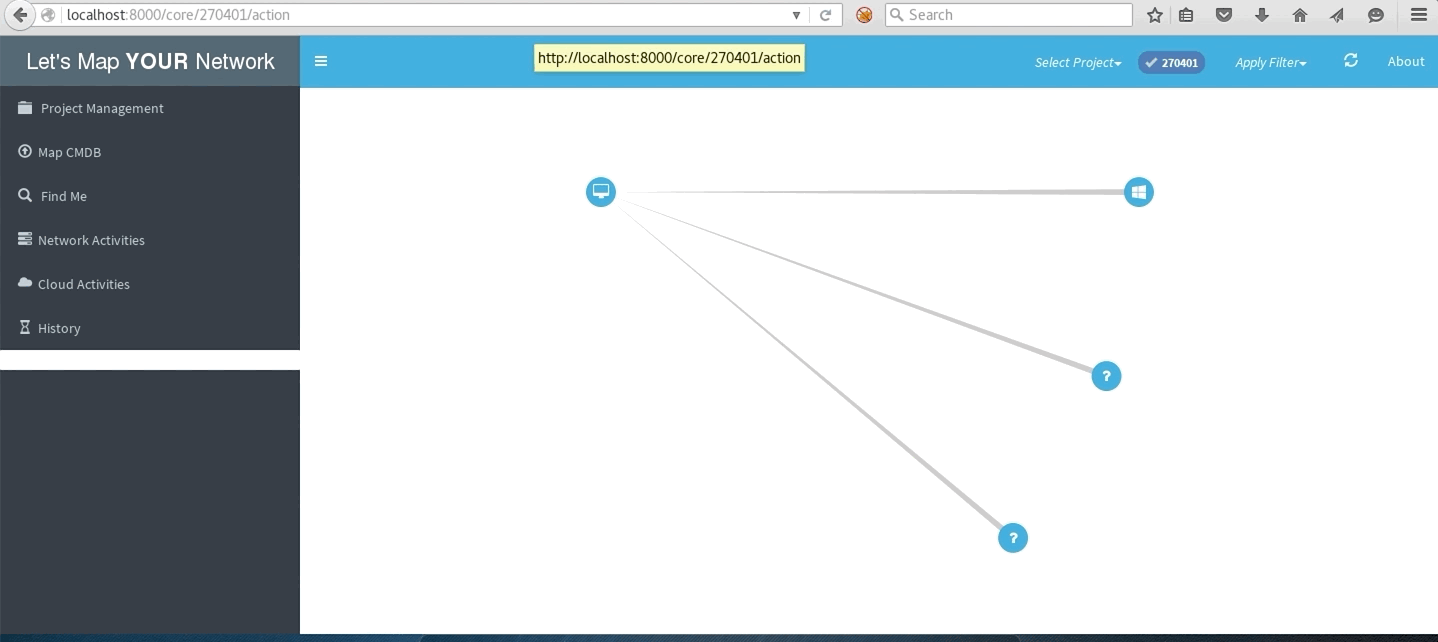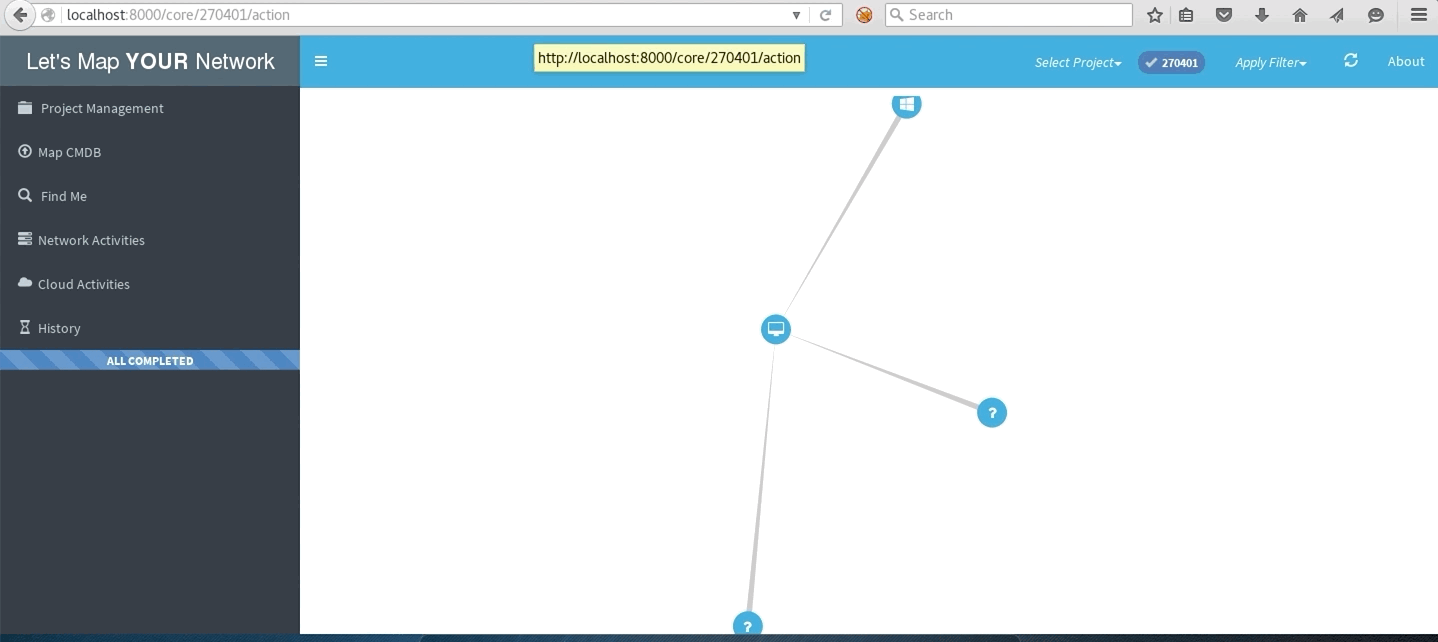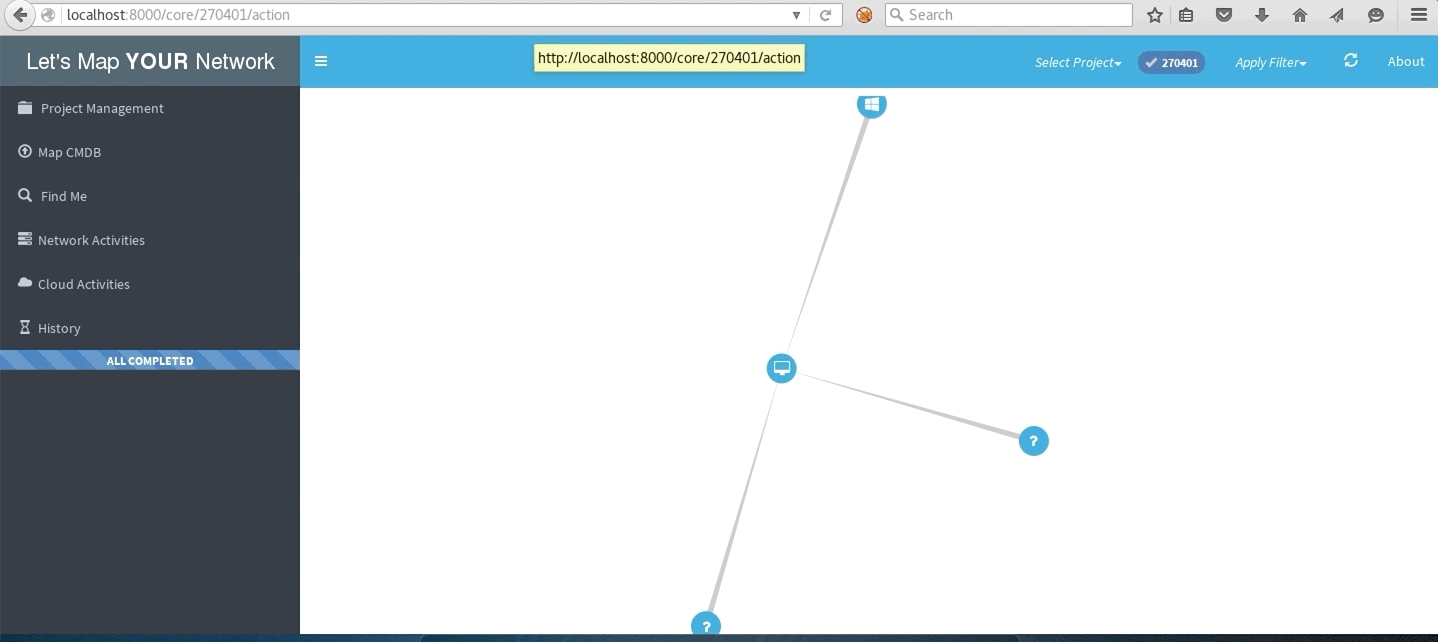
Local subnet network
Network with traceroute to multiple destinations
Cloud network
Features
- Project management
- User can create and delete multiple projects to view same network from different perspective and/or to analyze mulitple networks at same time
- Within a single project, result of all learning activities performed will be collated into a single view and thus provides a holistic perspective of network
- Bulk load of existing CMDB
- User can upload their existing CMDB file into the LMYN and it will provide the ‘delta’ with the actual network
- So LMYN will provide the segregation between what’s in their CMDB and not in network and vice-versa for user to take actions on rogue system
- It uses different color-code scheme for different type of systems for e.g. systems which are live in network and not presented in CMDB will be shown as RED node
- Ability to perform on-demand network activities
- Other than uploading the CMDB file, user can perform below network activities to any project:
- Traceroute to any destination host
- Network scan to any IP and/or range (all well-known format of IP is accepted)
- LMYN will incorporate the result of above actions into same project to build the network
- Other than uploading the CMDB file, user can perform below network activities to any project:
- Cloud (AWS) support
- LMYN fetches the topology information such as VPC, Subnets, Peering, Internet Gateway etc. from AWS APIs and represent it in form of graph
- LMYN makes logical segregation of AWS network as “Regions > VPCs > Subnets > Instances” and groups them accordingly
- Enumeration
- LMYN performs multiple enumeration probes to identify the operating system and type of device, as and when network is built
- For AWS, LMYN queries the AWS API to fetch the information of instances such as Platform, State, VPC, Subnet etc.
- If enumeration is successful, then LMYN assigns a relevant icon for each node
- LMYN performs multiple enumeration probes to identify the operating system and type of device, as and when network is built
- Ability to analyse ‘interesting’ network only
- Now, once user builds the network using multiple activities (CMDB upload, ad-hoc network activities, cloud scan, enumeration), then the user can filter only ‘interesting’ network out of the entire database on UI section
- This filtering process can be performed on the basis of actions (for e.g. IP range, destination host) or enumeration details (Linux, Windows, Router, VPC, Subnet, State, etc.)
- Filtering process allows to perform ‘AND’ and ‘OR’ kind of operation for e.g. ‘all IP in range 192.168.1.1/24 and Windows’
- Filtering process gives the ability to users to feed all the information in the database but at the same time not overwhelming with the information in UI and make a run-time decision on what user wants to see
- Continuous monitoring
- Also, LMYN gives the ability to monitor any existing network over the period of time
- User can identify, in graph-form, that how their network is changing (which systems are disconnecting and connecting to the network)
- LMYN again utilizes color-coded scheme to segregate the different type of systems in the network for e.g. all nodes which are not life will be shown as GREY
- Segregation of backend activities and UI
- LMYN segregates functionally of backend activities with UI
- LMYN have an implementation of Celery and RabbitMQ; thus, the user has a seamless UI irrespective of background activities
- LMYN keeps track of the status of all background activities and updates UI periodically
- Docker support
- All of these you can have in docker 🙂
Install && Use
Copyright (C) 2018 varchashva