grap: define and match graph patterns within binaries
grap takes patterns and binary files, uses a Capstone-based disassembler to obtain the control flow graphs from the binaries, then matches the patterns against them.
Patterns are user-defined graphs with instruction conditions (“opcode is xor and arg1 is eax”) and repetition conditions (3 identical instructions, basic blocks…).
grap is available as a standalone tool with a disassembler and python bindings, and as an IDA plugin which takes advantage of the disassembly done by IDA and the reverser.
Match quick pattern:
Match full pattern:
Match on multiple files:
Create patterns interactively from IDA:
Changelog v1.3.1
Modifications:
- Various bugfix related to python3 migration
- New default patterns
- Added parser helper function “parse_first_address”
Usage
The tool can be launched by using the following command:
$ grap [options] pattern test_paths
Below are a few examples of supported options:
- grap -h: describes supported options
One can let grap infer a pattern from a string. Only a few options are supported but this is useful for prototyping:
- grap “opcode is xor and arg1 contains ‘[‘” (test.exe): look for a xor with a memory write
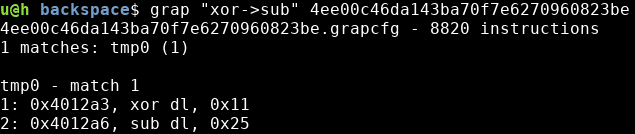
- grap -v “sub->xor->sub” (test.exe): -v will output the path of the inferred pattern
Choose how the binaries are disassembled:
- grap -od (pattern.grapp) samples/*: disassemble files in folder samples/ with no attempt at matching
- grap -f (pattern.grapp) (test.exe): force re-disassembling the binary, then matches it against pattern.grapp
- grap –raw (pattern.grapp) (test.bin): disassembling raw file (use –raw-64 for 64 bits binaries)
Control the verbosity of the output:
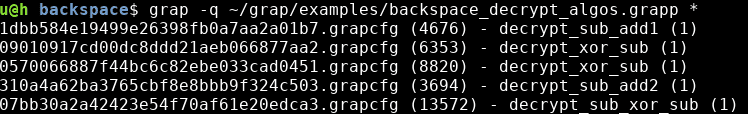
- grap -q -sa (pattern.grapp) (samples/*.grapcfg): match disassembled files, show matching, and non-matching files, one per line
- grap -m (pattern.grapp) (test.grapcfg): show all matched nodes
Choose where the disassembled file(s) (.grapcfg) are written; match multiple files against multiple patterns:
- grap patterns/basic_block_loop.grapp -o ls.grapcfg /bin/ls: disassemble ls into ls.grapp and looks for basic block loops
- grap (pattern1.grapp) -p (pattern2.grapp) (test.exe): match against multiple pattern files
- grap -r -q patterns/ /bin/ -o /tmp/ : disassemble all files from /bin/ into /tmp/ and matches them against all .grapp patterns from patterns/ (recursive option -r applies to /bin/, not to patterns/)
Pattern examples
The following pattern detects a decryption loop consisting of a xor followed by sub found in a Backspace sample:
Note that pattern files can contain multiple pattern graphs.
You may find additional pattern examples in two directories:
- patterns/ contains a few patterns that can be useful on any binary such as a pattern to detect short loops or to detect a loop on basic blocks,
- examples/ contains patterns used against the Backspace malware (see examples/backspace_samples.md to obtain the binary samples).
Download
Copyright (c) 2014 Inria
Copyright (c) 2015-2017 Cassidian CyberSecurity SAS
Copyright (c) 2018-2019 QuoScient GmbH
Copyright (c) 2020 QuoSec GmbH