Poisoned model leads to intellectual property exfiltration | Image: Palo Alto Networks
In a recent report, Palo Alto Networks researchers disclosed two critical vulnerabilities within Google’s Vertex AI platform that could expose organizations to serious security risks. Known as ModeLeak, these vulnerabilities enable privilege escalation and model exfiltration, potentially allowing attackers to access sensitive machine learning (ML) and large language model (LLM) data within Vertex AI environments.
The first vulnerability revolves around privilege escalation via custom jobs in Vertex AI. By exploiting custom job permissions within Vertex AI Pipelines, attackers could access data across the entire project. “By manipulating the custom job pipeline,” the report notes, “we discovered a privilege escalation path that allowed us to access resources far beyond the intended scope”. This access includes the ability to list, read, and export data from Google Cloud Storage and BigQuery datasets—actions that typically require a higher level of authorization.
Through custom code injection, researchers demonstrated how an attacker could inject commands to open a reverse shell, essentially creating a backdoor within the environment. This vulnerability stems from the default permissions granted to service agents, which researchers found to be excessively broad. “With the service agent’s identity, we could list, read and even export data from buckets and datasets we should never have been able to access.”
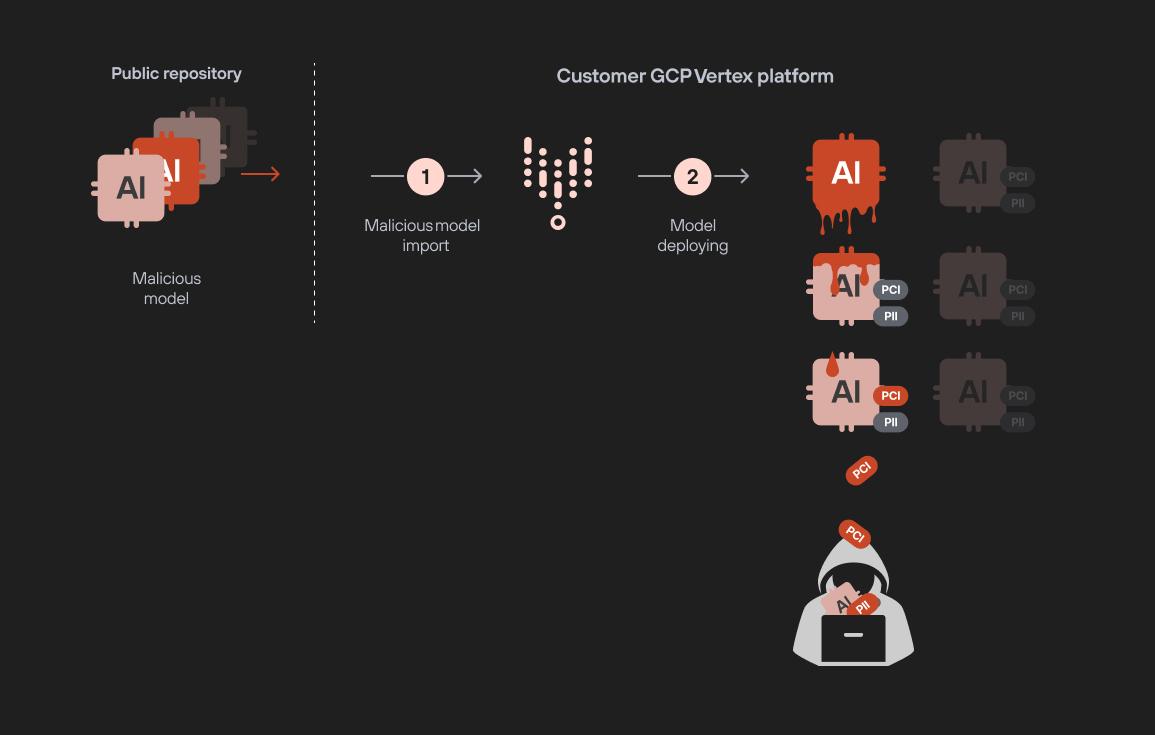
The second vulnerability presents an even more insidious threat: model exfiltration via malicious models. A malicious actor could upload a poisoned model to a public repository, which, once deployed, could infiltrate other sensitive models in the environment. “Imagine a malicious actor uploading a poisoned model to a public model repository,” the report explains. “Once deployed, the malicious model can exfiltrate every other ML and LLM model in the project, including sensitive fine-tuned models”. This scenario creates a model-to-model infection pathway, where proprietary information embedded in fine-tuned adapters could be replicated and exfiltrated by attackers.
Palo Alto Networks has since shared these findings with Google, which has deployed fixes to secure Vertex AI on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). To defend against similar threats, Palo Alto Networks recommends that organizations implement strict access controls and monitor model deployment processes closely. The report warns that these vulnerabilities could have widespread consequences if exploited by threat actors, particularly in environments where sensitive data drives model training and tuning.
Related Posts:
- Microsoft will focus on building AI and cloud platforms in the future instead of Windows
- Chrome 131 Rolls Out with Security Fixes and Performance Enhancements
- CISA Adds Five Actively Exploited Vulnerabilities to KEV Catalog