Network Security Toolkit (NST) is a bootable ISO image (Live DVD/USB Flash Drive) based on Fedora 28 providing easy access to best-of-breed Open Source Network Security Applications and should run on most x86_64 systems.
The main intent of developing this toolkit was to provide the security professional and network administrator with a comprehensive set of Open Source Network Security Tools. The majority of tools published in the article: Top 125 Security Tools by INSECURE.ORG are available in the toolkit. An advanced Web User Interface (WUI) is provided for system/network administration, navigation, automation, network monitoring, host geolocation, network analysis, and configuration of many network and security applications found within the NST distribution. In the virtual world, NST can be used as a network security analysis, validation, and monitoring tool on virtual enterprise servers hosting virtual machines.

Features
- Multi-Tap Network Packet Capture
- Web-Based Network Security Tools Management
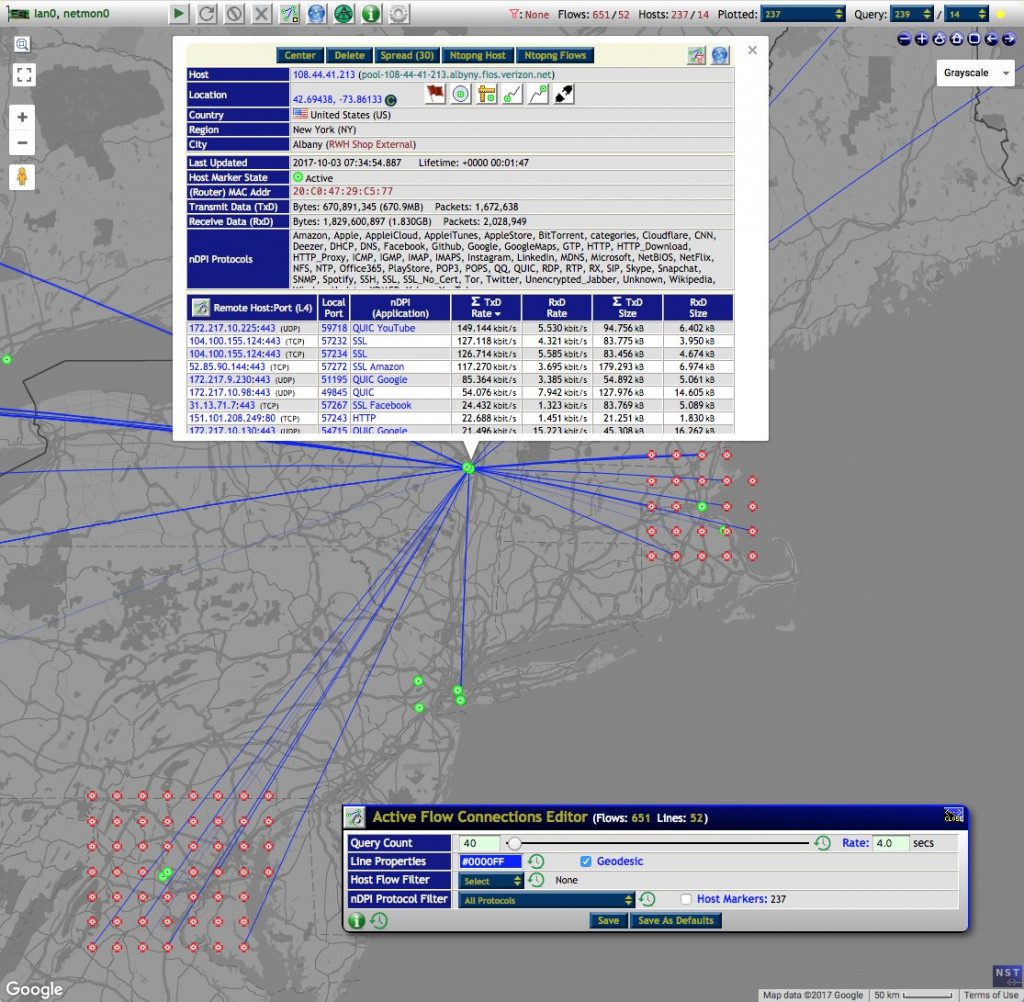
- Host/IPv4 Address Geolocation
- Network/System Monitoring
- Network Intrusion Detection
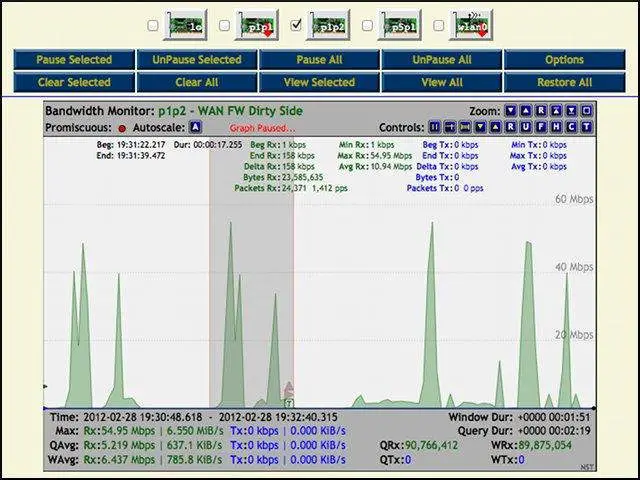
- Network Interface Bandwidth Monitor
- Web-based Snort IDS Integration
- Active Connections Monitor
- Network Segment ARP Scanner
- Network Packet Capture CloudShark Upload Support
- Multi-Port Terminal Server
- VNC / RDP Desktop Session Management
Changelog version 38-13644
- Access to the Open Vulnerability Assessment Scanner (OpenVAS) and Greenbone Vulnerability Management (Greenbone GVM) has been refactored to run as a docker container providing the full-featured vulnerability scanner. The latest Greenbone Community Edition container is used.
- An acceleration overlay and control was added to the geolocation of Dash Cam videos. See the graphic: NST Map Data Layer – Dash Cam Track With Acceleration Overlay.
- The NST WUI ARP Scan has been enhanced to support the configured Name Service (NS) switch hosts resolver. An article on NST WUI ARP Scan usage can be found here.
- As always, the networking and security applications included have been updated to their latest version which can be found in the manifest.
- For more details related to the code changes for this release, refer to the “Change Log” page or review the change log for an individual RPM package.