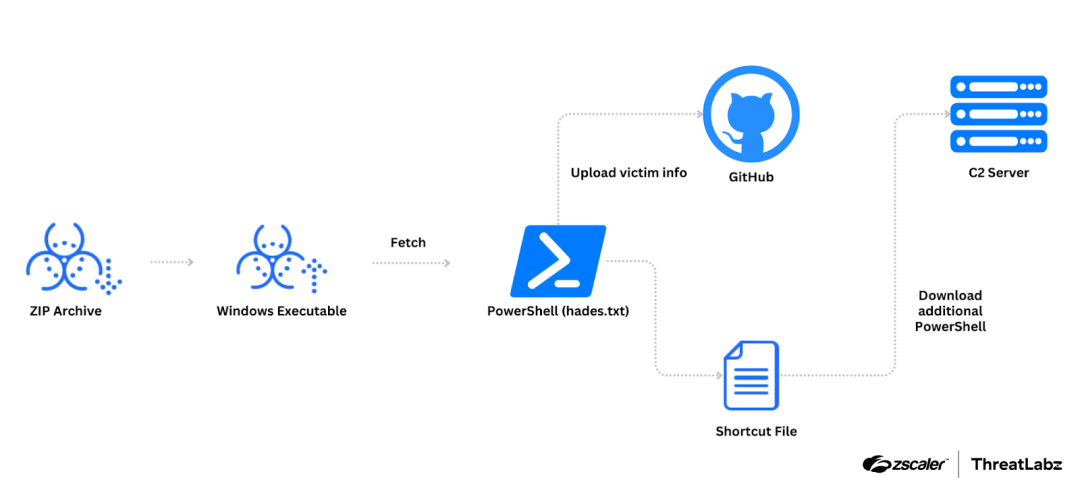
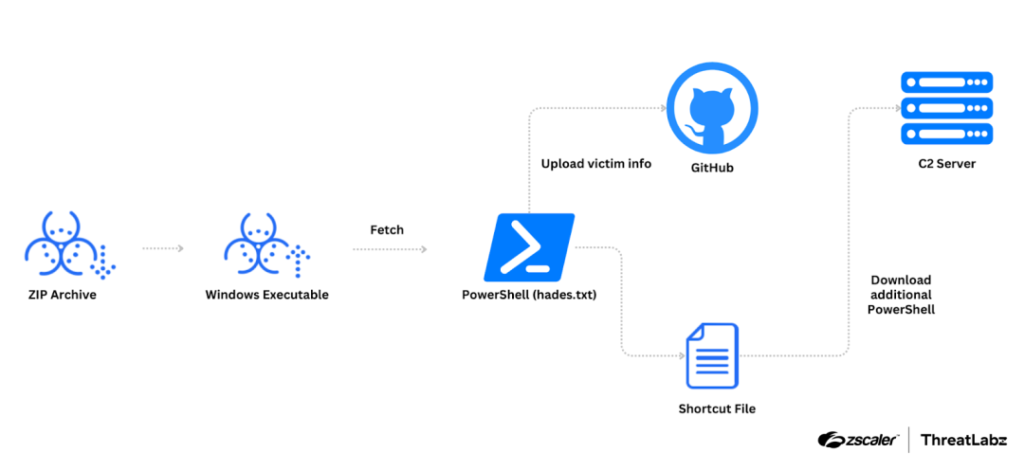
Example Kimsuky infection chain
Zscaler ThreatLabz, a leading cybersecurity research team, has uncovered a new cyber espionage campaign by the North Korean state-sponsored hacking group Kimsuky. The group is deploying a malicious Google Chrome extension called “TRANSLATEXT” to steal sensitive information from South Korean academics, particularly those researching political issues related to North Korea.
The TRANSLATEXT extension, uploaded as “GoogleTranslate.crx” to GitHub, contained four malicious JavaScript files designed to bypass security measures like Gmail, Naver, and Kakao, steal credentials, cookies, and capture browser screenshots. It requested excessive permissions, allowing it to inject scripts into web pages, modify content, and interact with page elements, facilitating the exfiltration of stolen data.
The researchers believe that Kimsuky is using a multi-stage attack to deliver TRANSLATEXT, starting with a malicious archive file disguised as a research paper on Korean military history. Once the victim opens the file, it triggers a chain of events that ultimately leads to the installation of the extension.
The data stolen included browser login credentials and cookies, with at least one known victim from the South Korean education sector. This information suggests that academic researchers specializing in geopolitical matters involving the Korean peninsula are among the primary targets. The campaign underscores Kimsuky’s ongoing efforts to collect intelligence on South Korea.
“The group appears to be targeting academia in South Korea as part of an ongoing intelligence collection campaign. To mitigate the risk from active North Korea-affiliated threat actors like Kimsuky, it is imperative to stay informed about their latest tactics,” said Seongsu Park, a senior researcher at Zscaler ThreatLabz.
Zscaler’s findings highlight the ongoing cyber espionage threat posed by North Korea, particularly against South Korean targets. The company urges users to be vigilant about the extensions they install in their browsers and to keep their software updated to protect against such threats.