Security researchers published the technical details and proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code for a dangerous zero-day CVE-2024-21338 vulnerability that was recently exploited by the state-backed North Korean hacking group, Lazarus. This flaw resides in the Windows kernel itself, allowing attackers to gain deep system-level control and disable security tools.
The Lazarus Group exploited this vulnerability to create a read/write kernel primitive via an updated version of their FudModule rootkit, a malicious software previously noted for using a Dell driver in Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) attacks. This new exploitation method allowed them to bypass more detectable BYOVD techniques, achieving kernel-level access. This access was used to disable security tools, including prominent ones like Microsoft Defender and CrowdStrike Falcon, thus facilitating further malicious activities without detection.
Avast’s analysis revealed significant enhancements in the stealth and functionality of the new version of FudModule. The rootkit now includes capabilities to suspend processes protected by Protected Process Light (PPL) by manipulating handle table entries. It also features selective disruption strategies through DKOM and has improved methods to tamper with Driver Signature Enforcement and Secure Boot mechanisms.
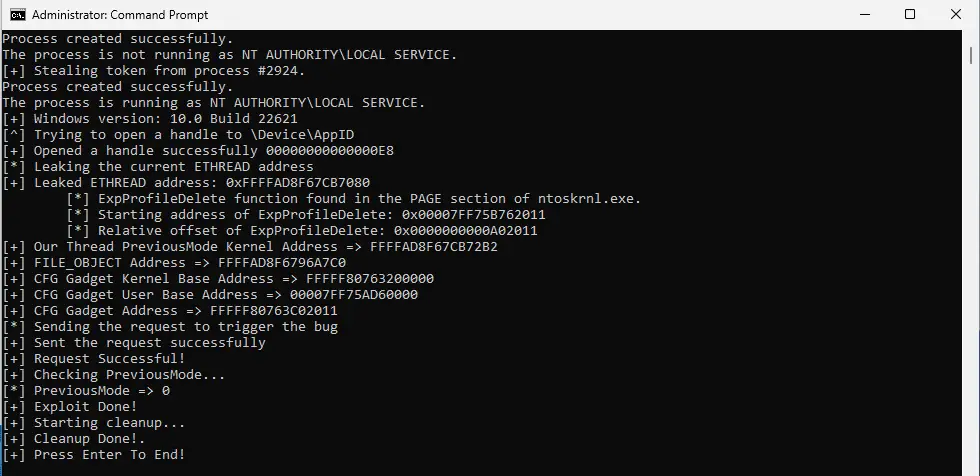
Following Avast’s initial analysis, researcher Nero22k released a PoC exploit code for the Windows Kernel vulnerability (CVE-2024-21338) last month. Rafael Felix of Hakai Security has since published technical details and a proof-of-concept for this flaw.

The exploit involves manipulating the Input and Output Control (IOCTL) dispatcher in the appid.sys driver to call an arbitrary pointer. This action deceives the kernel into executing unsafe code, effectively bypassing built-in security checks. Within this vulnerability’s scope, the FudModule rootkit conducts direct kernel object manipulation (DKOM) to disable security products, hide its activities, and ensure its persistence on the infected systems.
For organizations and individual users, the immediate and most effective defense against this exploit is to apply the updates released by Microsoft in the February 2024 Patch Tuesday. Ensuring that systems are up-to-date with these patches is crucial, as it closes the vulnerability window and prevents potential exploits of the same nature.