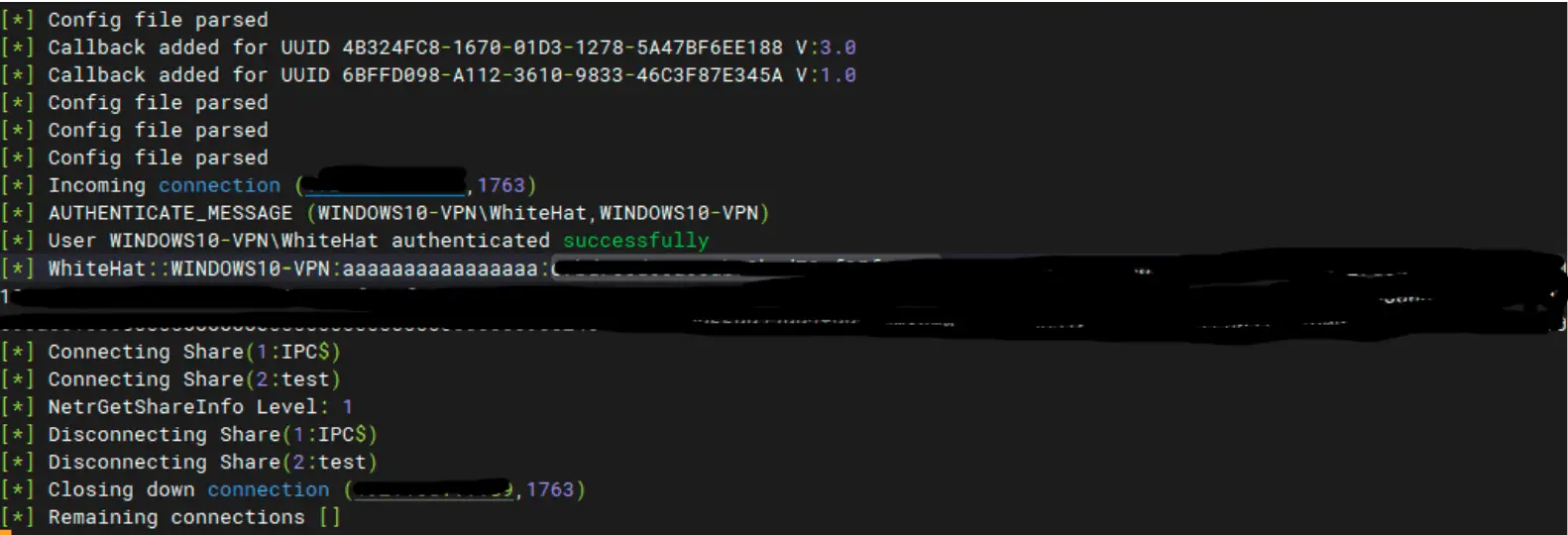
The login & hash of the person that clicked on the link
The pressure to update to the latest versions of Microsoft Outlook has hit boiling point with the release of proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code against a critical vulnerability (CVE-2024-21413), patched this week, and now in the public domain.
Discovered by Check Point vulnerability researcher Haifei Li and with a CVSS score of 9.8, the security flaw leads to remote code execution (RCE) when opening emails with malicious links employing a vulnerable Microsoft Outlook edition, among the family of affected Office products, comprising Microsoft Office LTSC 2021 and Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise, besides Microsoft Outlook 2016 and Microsoft Office 2019 (extended support).
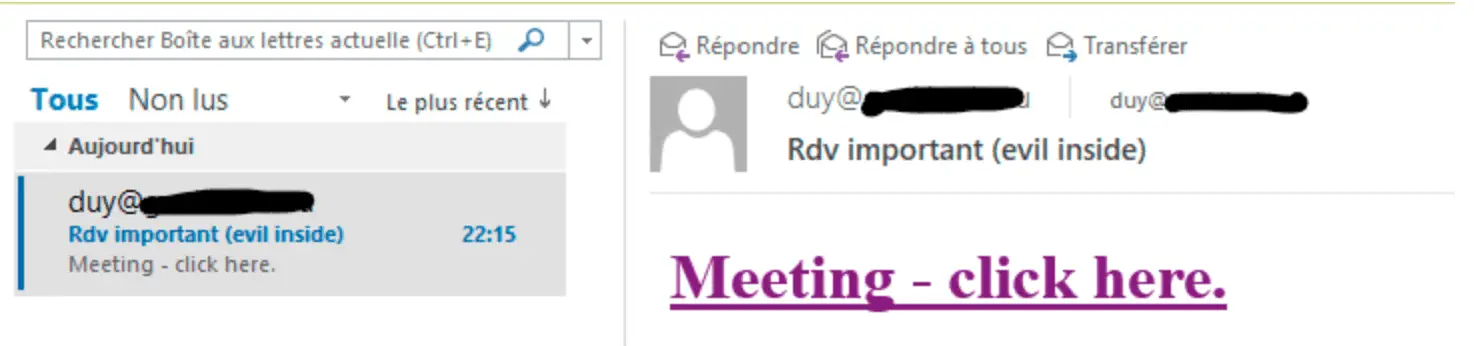
This bug happens because the vulnerability also allows attackers to circumvent the Protected View (which is designed to prevent suspicious content hidden in Office files from executing) and to open offending Office files in editing mode.
“Successful exploitation of this vulnerability would allow an attacker to bypass the Office Protected View and open in editing mode rather than protected mode,” explains Microsoft.
“An attacker could craft a malicious link that bypasses the Protected View Protocol, which leads to the leaking of local NTLM credential information and remote code execution (RCE).”
Within days after Microsoft announced patches for this and several other vulnerabilities, and after Check Point published a technical writeup on CVE-2024-21413, the PoC code targeting the critical issue was published on GitHub [1, 2], easing the way for its malicious exploitation.

This PoC code demonstrates how attackers can retrieve the login credentials and hash of individuals who click on the malicious link, all without triggering a warning prompt on the affected versions of Outlook. The existence of PoC code in the public domain makes this vulnerability a prime target for exploitation, increasing the risk of attacks on unpatched systems.
This flaw is a clear call to action for all Microsoft Outlook users. Users are advised to upgrade to Microsoft’s February 2024 Patch Tuesday to fix this bug.