Public Exploit Released for Cisco IMC Flaw – Update Immediately to Halt Takeover Attacks
Cisco customers are facing an increased risk of attack as publicly accessible exploit code has emerged for CVE-2024-20356, a critical vulnerability in Cisco’s Integrated Management Controller (IMC). This vulnerability could allow authenticated attackers with administrator privileges to inject commands and escalate to root-level control.
The Vulnerability Explained
CVE-2024-20356 stems from inadequate validation of user input within Cisco IMC’s web-based interface. A skilled attacker could exploit this flaw by sending specially crafted commands, ultimately allowing them to seize full administrative control of the affected system.
“A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco Integrated Management Controller (IMC) could allow an authenticated, remote attacker with Administrator-level privileges to perform command injection attacks on an affected system and elevate their privileges to root,” Cisco wrote.
Affected Systems
A wide range of Cisco enterprise devices are impacted, including:
- 5000 Series ENCS
- Catalyst 8300 Series Edge uCPE
- UCS C-Series M5, M6, and M7 Rack Servers (standalone mode)
- UCS E-Series Servers
- UCS S-Series Storage Servers (standalone mode)
- Appliances based on preconfigured versions of Cisco UCS C-Series servers exposing the IMC UI
“CISCown” Exploit Tool and DOOM Demonstration
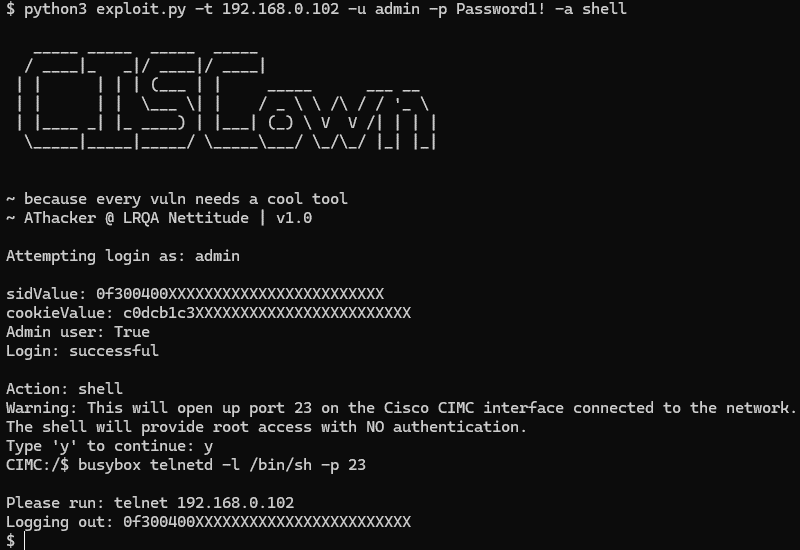
Security researcher Aaron Thacker (LRQA Nettitude), who discovered the CVE-2024-20356 vulnerability, has published both technical details and a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit. Thacker further developed a tool named “CISCown” to automate the exploitation process, including opening a root shell.

Image: Nettitude
In a chilling demonstration, researchers showed how this vulnerability could be chained with others to fully compromise a Cisco appliance and even run the classic game DOOM on the device.
Call to Action
Cisco has released patches to address CVE-2024-20356. Administrators are urged to take the following steps immediately:
- Update Firmware: Apply available firmware updates that patch this vulnerability for all affected devices.
- Strong Passwords: Enforce a robust password policy and change default credentials on Cisco IMC systems.
- Limit Access: If possible, restrict access to the IMC interface, minimizing the attack surface.





