The SonicWall Capture Labs Threat Research Team has published an in-depth analysis of CVE-2024-38812, a critical heap-overflow vulnerability found in VMware vCenter Server. This vulnerability affects VMware vCenter Server version 8.0 U3a and has been patched in version 8.0 U3d, addressing an issue in the DCERPC protocol that could allow remote code execution (RCE).
CVE-2024-38812, classified under CWE-122 (Heap-based Buffer Overflow), enables attackers to exploit improper memory handling within the vCenter Server’s implementation of the DCERPC protocol. By sending specially crafted network packets, an attacker could overwrite memory in the heap, potentially leading to arbitrary code execution or even full system compromise. The severity of this vulnerability is underscored by its CVSS score of 9.8, marking it as a high-risk exploit for organizations using unpatched VMware vCenter versions.
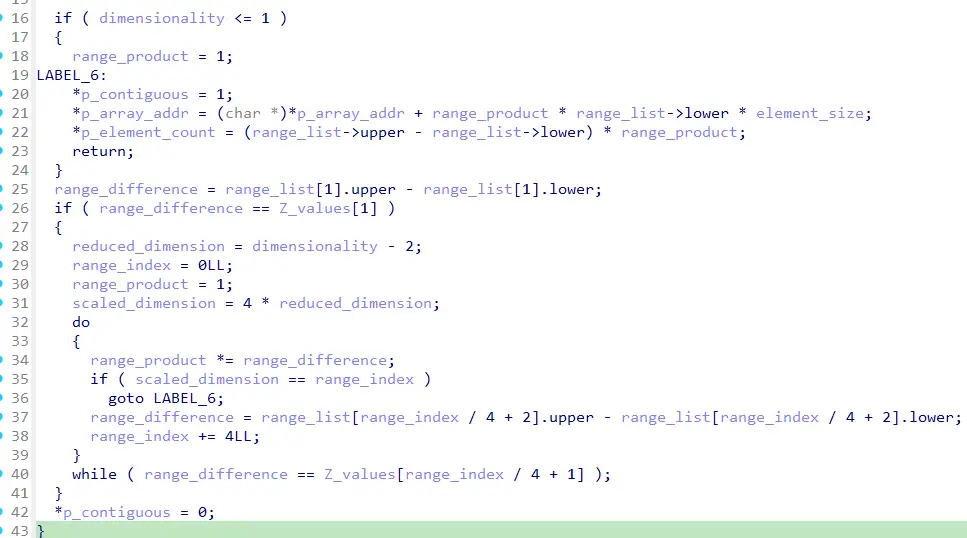
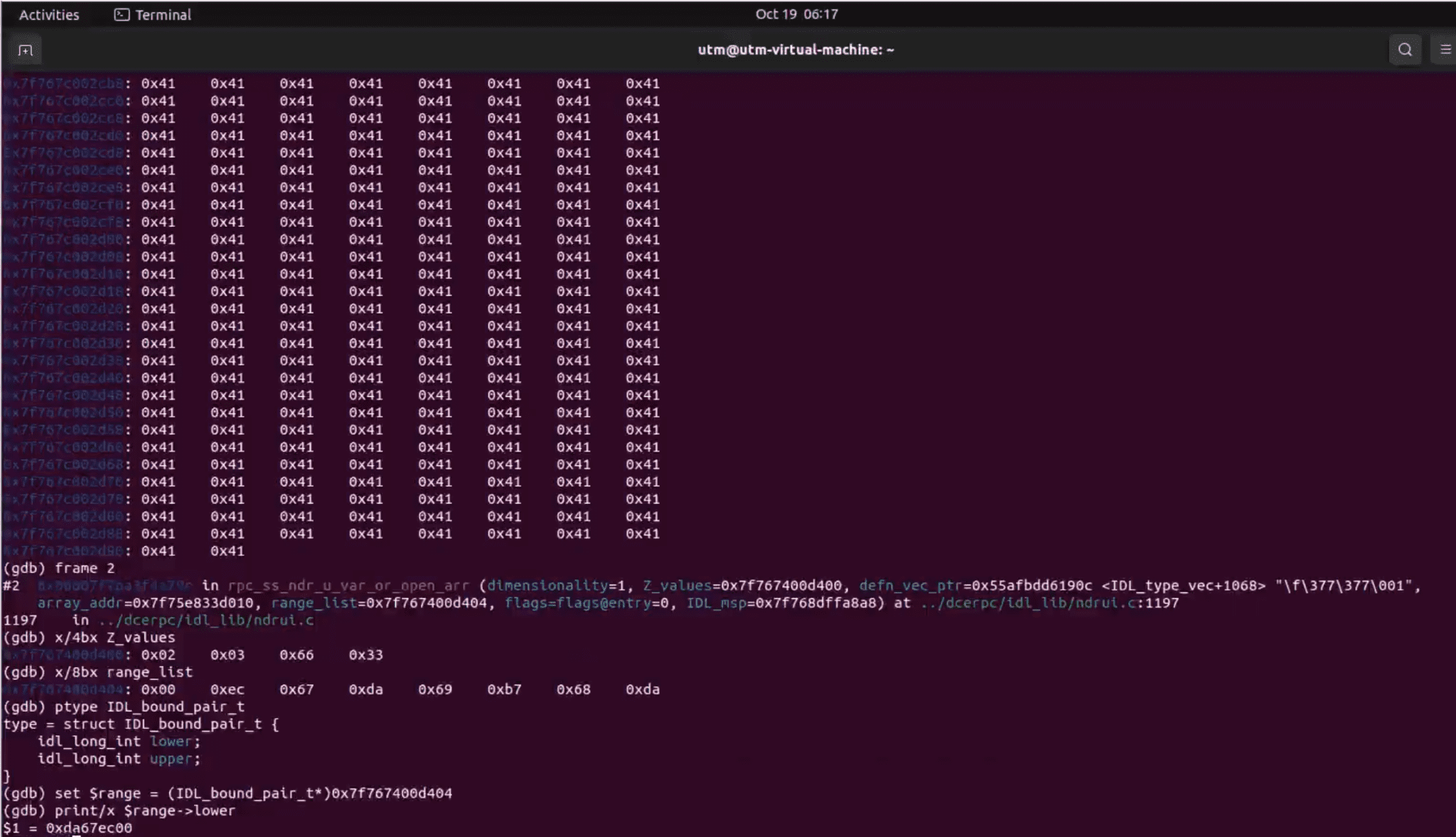
The root cause of CVE-2024-38812 lies in how the rpc_ss_ndr_contiguous_elt() function handles the range_list->lower value, a parameter controlled by user input. Attackers can exploit this flaw by sending specially crafted network packets that manipulate memory offsets. The vulnerability occurs when the range_list value is improperly used to modify a base memory address. This can lead to arbitrary memory access, potentially allowing attackers to overwrite critical system memory, leading to remote code execution.
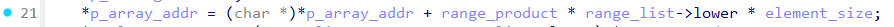
In a detailed analysis by the SonicWall Capture Labs Threat Research Team, they explain, “Once an attacker controls the range_list->lower value, they effectively control the memory address to which p_array_addr points“. This gives attackers significant control over the memory allocation process, increasing the likelihood of exploiting the vulnerability.
To trigger this heap-overflow vulnerability, an attacker must carefully craft input parameters, such as the parameter count and type index, which govern how memory is allocated during the RPC process. By manipulating these values, an attacker can cause memory to be allocated beyond normal bounds. “If the offset is large enough, it can push the array’s address into memory regions that the attacker can control,” highlights the analysis.
The vulnerability is particularly dangerous because the attacker can control both the destination memory address and the amount of data being copied. For instance, in the rpc_ss_ndr_unmar_by_copying() function, the length of the data to be copied is attacker-controlled, making it possible for malicious actors to overwrite critical memory areas using crafted input.
VMware addressed the issue with the release of vCenter Server version 8.0 U3d, which introduces more stringent checks to prevent unbounded pointer arithmetic. According to SonicWall’s analysis, “The patch… introduces a significant fix focusing on how the calculation involving the range list is handled, particularly in the verification of range_list->lower.” These changes effectively prevent attackers from leveraging this vulnerability by ensuring memory pointers remain within safe bounds.
Organizations using vCenter Server 8.0U3a or earlier are strongly advised to upgrade to version 8.0 U3d to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
Related Posts:
- CVE-2024-38812: VMware’s 9.8 Severity Security Nightmare
- Critical VMware vCenter Server Flaw Allows Remote Code Execution
- VMware Confirms CVE-2023-34048 RCE Flaw in vCenter Exploited in the Wild
- Broadcom Security Alert: VMware Vulnerabilities Expose Data, Enable Attacks