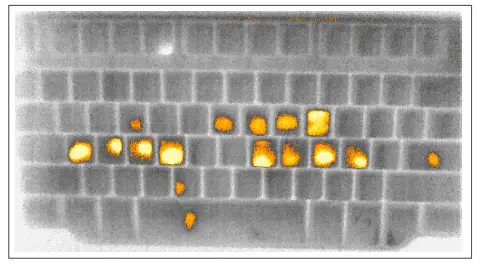
Researchers at the University of California, Irvine, have published new papers on how to measure keyboard temperature to steal passwords with thermal imaging cameras.
The principle of this kind of attack is mainly to use the residual temperature left by the finger on the keyboard. Based on the heat loss, the button information can usually only be collected within a few minutes.
For example, if you have a tap record, if you leave the computer, the thermal imaging camera can collect the record. The temperature difference determines the crucial specific sequence.

Image: uci
The specific attack scenarios are naturally not suitable for daily attacks. This type of attack is more in line with social engineering for stealing in the business environment.
The researchers tested in real-life environments, allowing 30 users to enter ten groups of long and short passwords on four well-known keyboards and then compare them.
The actual experimental results show that the untrained user can fully record the password within 30 seconds after entering the password for the first time, and collect some of the passwords within 60 seconds.
The thermal imaging camera used is also a medium-sized camera chicken sold in the market, so even a thermal imaging camera not explicitly used for social workers can complete the collection.
Interestingly, the researchers revealed that this method of stealing is particularly useful for people with two-finger input. The two-finger method uses two fingers to type the keyboard.
The researchers also revealed that this method of attack must be able to fully see the keyboard and mount the thermal imaging camera around the victim, so the actual limit is much.
But even users, especially business users, should be wary of this type of attack. The solution is to use a few keyboards or use a virtual keyboard.
Suggest Reading
Thermanator: Thermal Residue-Based Post Factum Attacks On Keyboard Password Entry