Details have emerged about a now-patched security flaw in Windows TCP/IP that could be exploited by an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the system.
The bug has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2022-34718 (CVSS score: 9.8) and was addressed by Microsoft as part of its September Patch Tuesday updates.
“An unauthenticated attacker could send a specially crafted IPv6 packet to a Windows node where IPSec is enabled, which could enable a remote code execution exploitation on that machine,” Microsoft noted in its advisory.
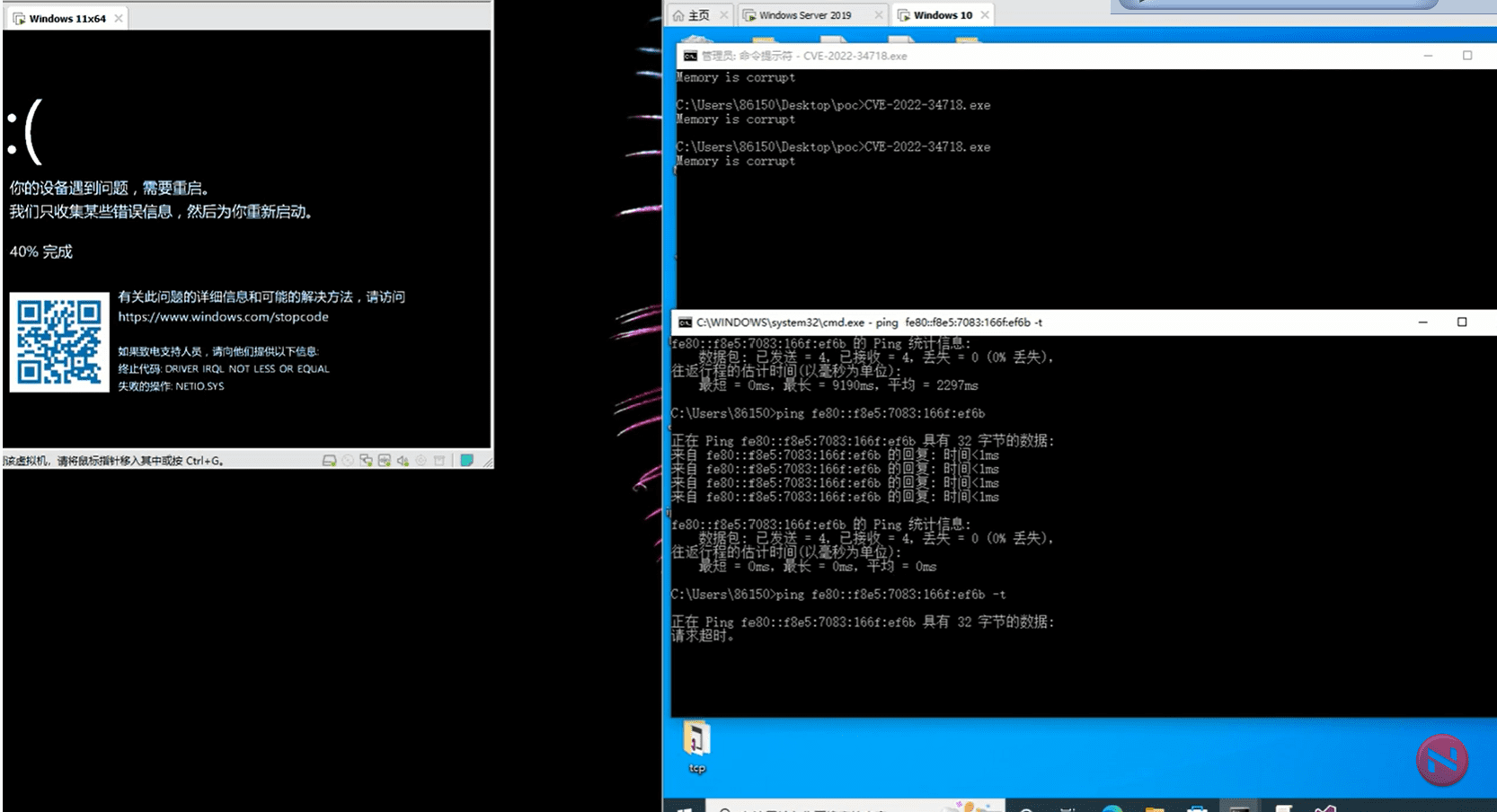
Numen’s security research team conducted an in-depth analysis of the vulnerability and publicly disclosed TCP/IP Vulnerability CVE-2022-34718 PoC through patch comparison.

The cybersecurity firm wrote: “When comparing the August and September patch of the tcpip.sys, we found that there are two functions that needed to be patched, as follows:
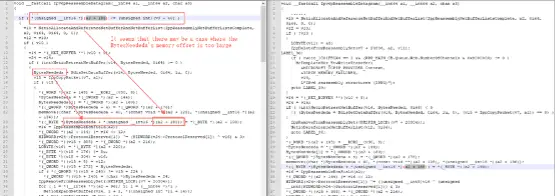
The repair method of the first function indicates that there seems to be an error in that the memory offset is larger than expected when reassembling the IPv6 fragmented data.
Second patched function:
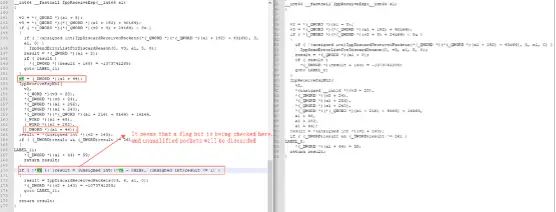
This function patch is not very intuitive. We only know that during the process of receiving IPsec ESP packets, if its flag bits do not meet the patch conditions, the packets will be discarded.“
If an attacker can construct an IPv6 fragmented data that meets the patching conditions in the Ipv6pReassembleDatagram function, an attacker is able to trigger an error (larger than expected) offset in the memory.
“The current POC code can cause a byte in the content of the NetIo protocol header object (an arbitrary offset address greater than 0x38) to be overwritten to an arbitrary value (0x2C here). The 0x2c mentioned here is not the first IPv6 extension header type flag carried in the ESP. It is the IPv6 extension header flag next to the partition header carried in the ESP. This can be set arbitrarily,” the cybersecurity firm said in an analysis.
Numen has further made available proof-of-concept (PoC) instructions to trigger the CVE-2022-34718 security flaw, making it essential that users of Windows upgrade to the latest version to mitigate potential threats.