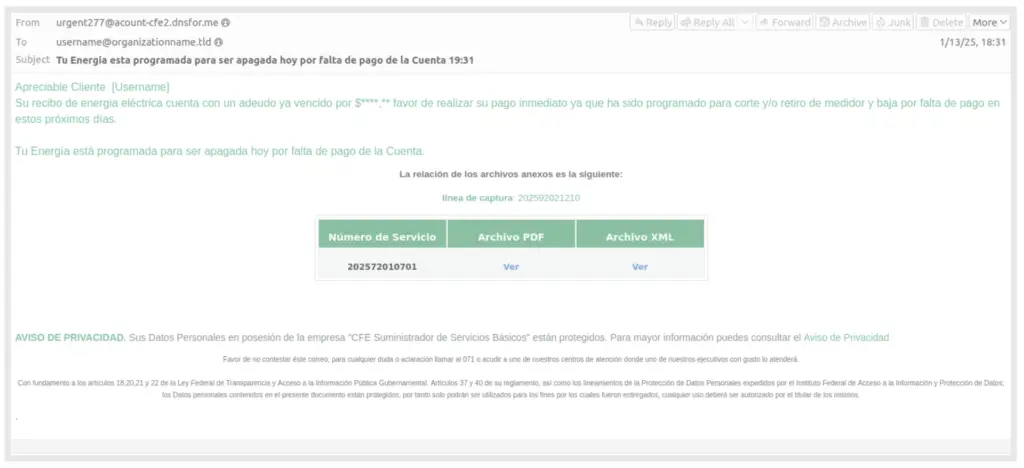
Spanish language TA2725 campaign observed on 14 January 2025 delivering ScreenConnect | Image: Proofpoint
Proofpoint researchers have released a report highlighting a concerning trend: the increasing use of legitimate Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools by cybercriminals to launch attacks. RMM software, typically used by IT administrators to manage computers remotely, is being leveraged as a first-stage payload in email campaigns, granting attackers initial access to victims’ systems.
“While threat actors have long used RMMs in campaigns and attack chains, their increased use as a first-stage payload in email data is notable,” the report states. This shift coincides with a decline in the use of traditional loaders and botnets, likely due to disruptions caused by law enforcement operations targeting cybercriminal infrastructure.
The Proofpoint report identifies several RMM tools being actively deployed in attacks, including ScreenConnect, Fleetdeck, and Atera. These tools offer attackers similar capabilities to Remote Access Trojans (RATs), enabling them to collect data, steal financial information, move laterally within a network, and install additional malware like ransomware.
One notable example is the threat actor TA583, which has been highly active in distributing ScreenConnect via email campaigns. TA583 employs various social engineering lures, often impersonating government agencies like the U.S. Social Security Administration, to trick users into installing the malicious RMM payload.
The report also highlights the use of RMM tools by other threat actors, such as TA2725, which has been observed delivering ScreenConnect in campaigns targeting organizations in Mexico.
The increasing popularity of RMM tools among attackers can be attributed to several factors. They are readily available, often legitimate software, and may bypass security defenses due to their signed installers. This makes them an attractive option for attackers seeking to gain a foothold in target networks.
Proofpoint recommends that organizations take proactive steps to mitigate the risks associated with RMM-based attacks. These include restricting the download and installation of unauthorized RMM tools, implementing network detections and endpoint protection, and training users to identify and report suspicious activity.
Related Posts:
- India announces to use artificial intelligence to develop weapon systems
- MuddyWater’s Sneaky New Tactic: Hijacking RMM Software for Espionage
- Threat Actors Continue to Exploit Legitimate RMM Tool ScreenConnect
- Critical Fortinet Vulnerability Exploited: Hackers Deploy Remote Control Tools and Backdoors
- CVE-2024-41779 (CVSS 9.8): IBM Rhapsody Model Manager Vulnerability Puts Systems at Risk