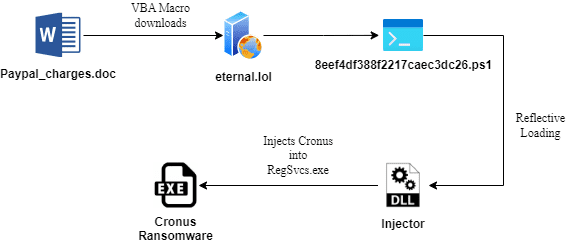
Infection Chain | Image: Seqrite Labs
In a recent report, the Seqrite Labs APT-Team has exposed a series of malicious campaigns employing fake PayPal documents to spread a new fileless ransomware variant known as Cronus. This sophisticated malware targets individuals worldwide and operates entirely in memory, leaving no trace of malicious content on the victim’s disk.
Technical Analysis Reveals Multi-Stage Attack
The Seqrite Labs team meticulously analyzed the campaign, uncovering a multi-stage attack chain. It all begins with a seemingly innocuous PayPal receipt document (paypal_charges.doc) that conceals a malicious VBA macro. This macro, heavily obfuscated to evade detection, downloads a PowerShell-based loader, which in turn deploys the Cronus ransomware using reflective DLL loading, a technique previously favored by ransomware groups like NETWALKER.
The PowerShell loader, disguised as a JPEG file, further obfuscates the malicious code, making analysis even more challenging. The final stage involves injecting malicious .NET assemblies responsible for the ransomware’s core functions, including file encryption, process termination, persistence establishment, and data manipulation.
Ransomware Functionality
- Self-Copy: The ransomware binary copies itself to the C:\Users<Username>\AppData\Local path, deleting itself if it already exists.
- Enumeration: The ransomware enumerates local disk drives and files, excluding specific folders in the \System\ directory.
- Encryption: Depending on the file size, the ransomware uses two encryption methods: FULL_ENCRYPT for files less than 512 KB and TRIPLE_ENCRYPT for larger files, both employing AES encryption.
- Process Termination: The ransomware terminates various processes by ending their main windows.
- Persistence: The binary abuses RunKeys for persistence, appending a new key named cronus to the registry hive to run RegSvcs.exe on startup.
- Data Manipulation: The ransomware manipulates Clipboard contents, replacing any found Bitcoin address with the threat actor’s BTC wallet address.
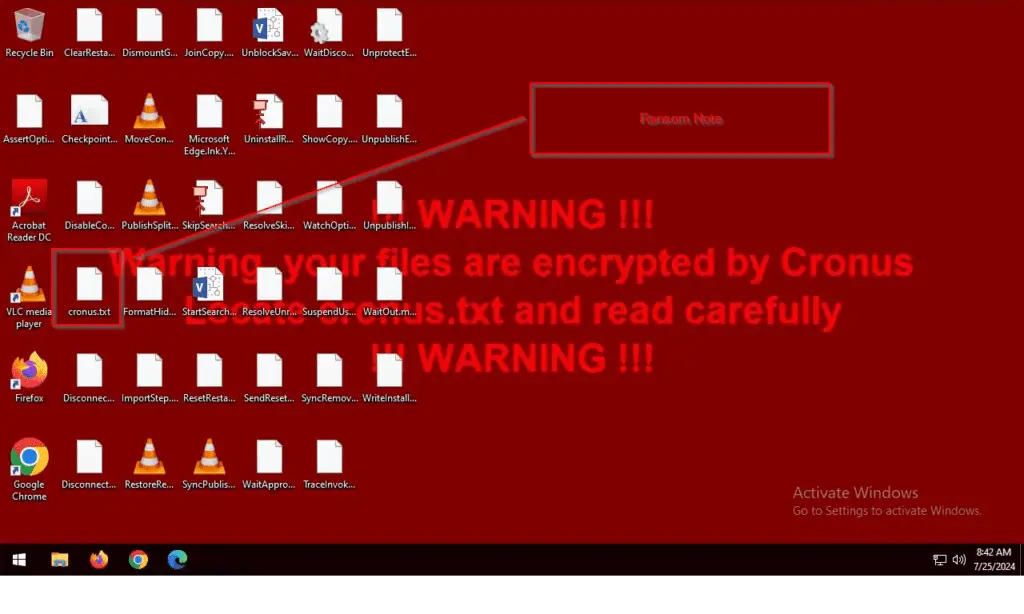
Cronus Ransomware: A New Threat in the Wild
Cronus is a relatively new ransomware variant, but it has already shown its ability to spread rapidly. Its fileless nature makes it particularly difficult to detect and remove, as it operates entirely in memory, leaving no traditional artifacts for security software to identify.
Code Overlaps with Other Fileless Malware
Interestingly, Seqrite Labs researchers discovered code overlaps between the PowerShell loader used in the Cronus campaign and other active fileless malware campaigns, such as Revenge RAT, Arrow RAT, Async RAT, Andromeda RAT, XWorm, and njRAT. This suggests a potential connection or shared codebase among these threats.
Protecting Yourself from Cronus and Similar Threats
To protect yourself from Cronus and similar fileless ransomware threats, it’s crucial to follow cybersecurity best practices:
- Be cautious of unsolicited emails and attachments: Avoid opening emails or attachments from unknown senders, especially if they appear suspicious or unexpected.
- Keep your software updated: Regularly update your operating system, antivirus software, and other applications to patch vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
- Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication: Protect your online accounts with strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Back up your data: Regularly back up your important files to an external drive or cloud storage service to ensure you can recover them in case of a ransomware attack.
- Educate yourself and your employees: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and educate your employees on how to recognize and avoid them.
Related Posts:
- From SideCopy to Transparent Tribe: Pakistan APTs Hit Indian Government With RATs
- Phishing for Secrets: Operation RusticWeb Casts Net on Indian Officials