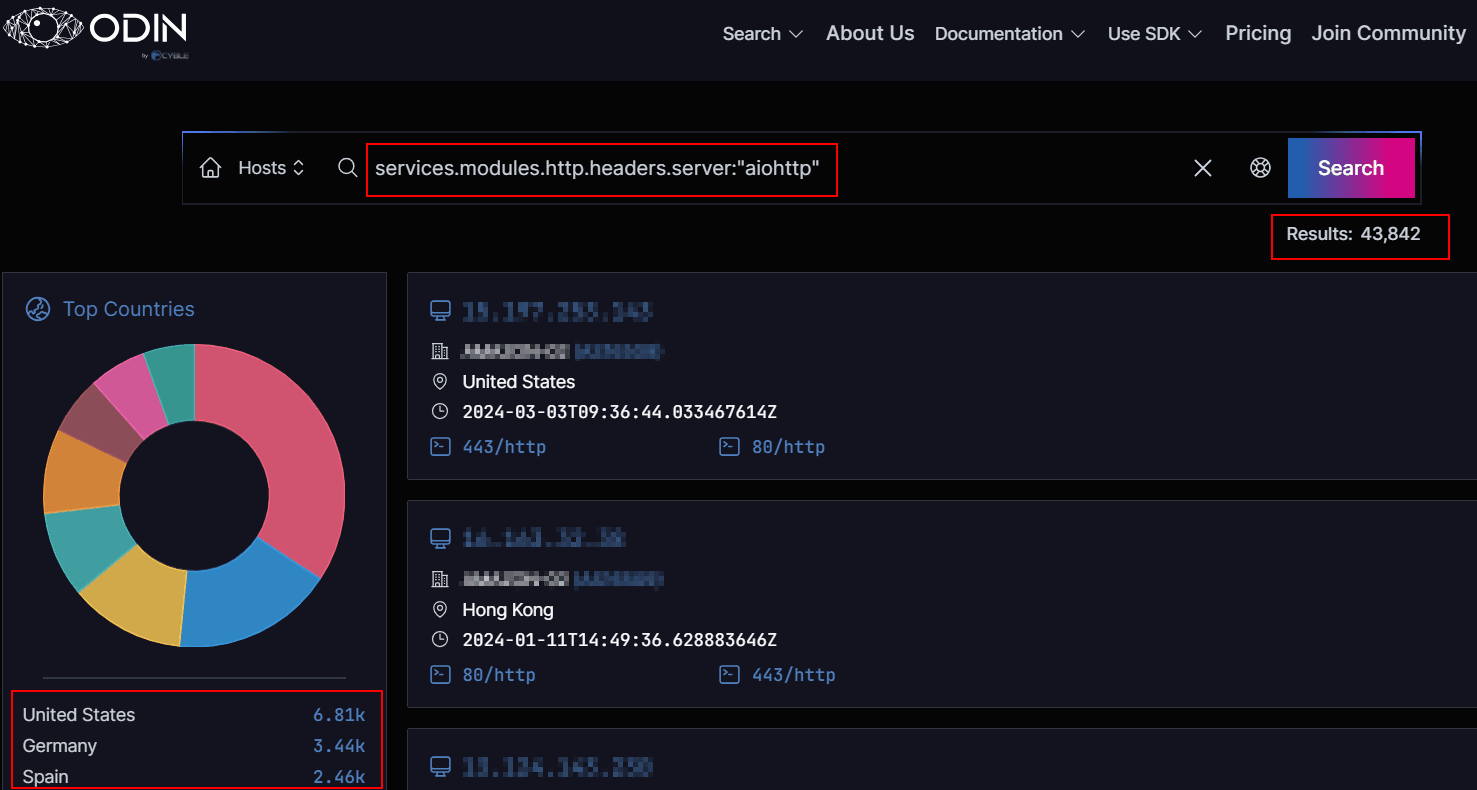
Exposure of aiohttp instances
A recently patched vulnerability in the popular Python web framework aiohttp has swiftly landed on the radar of notorious ransomware operators, according to a report from Cyble Global Sensor Intelligence (CGSI). The flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-23334 (CVSS 7.5), could give attackers unfettered access to sensitive files on servers running older versions of aiohttp.
The Vulnerability: A Doorway for Hackers
At its core, the vulnerability lies in how aiohttp handles file paths. If not carefully configured, attackers could trick the server into divulging files well outside intended directories, potentially exposing everything from passwords to private company data.
Exploit in the Wild
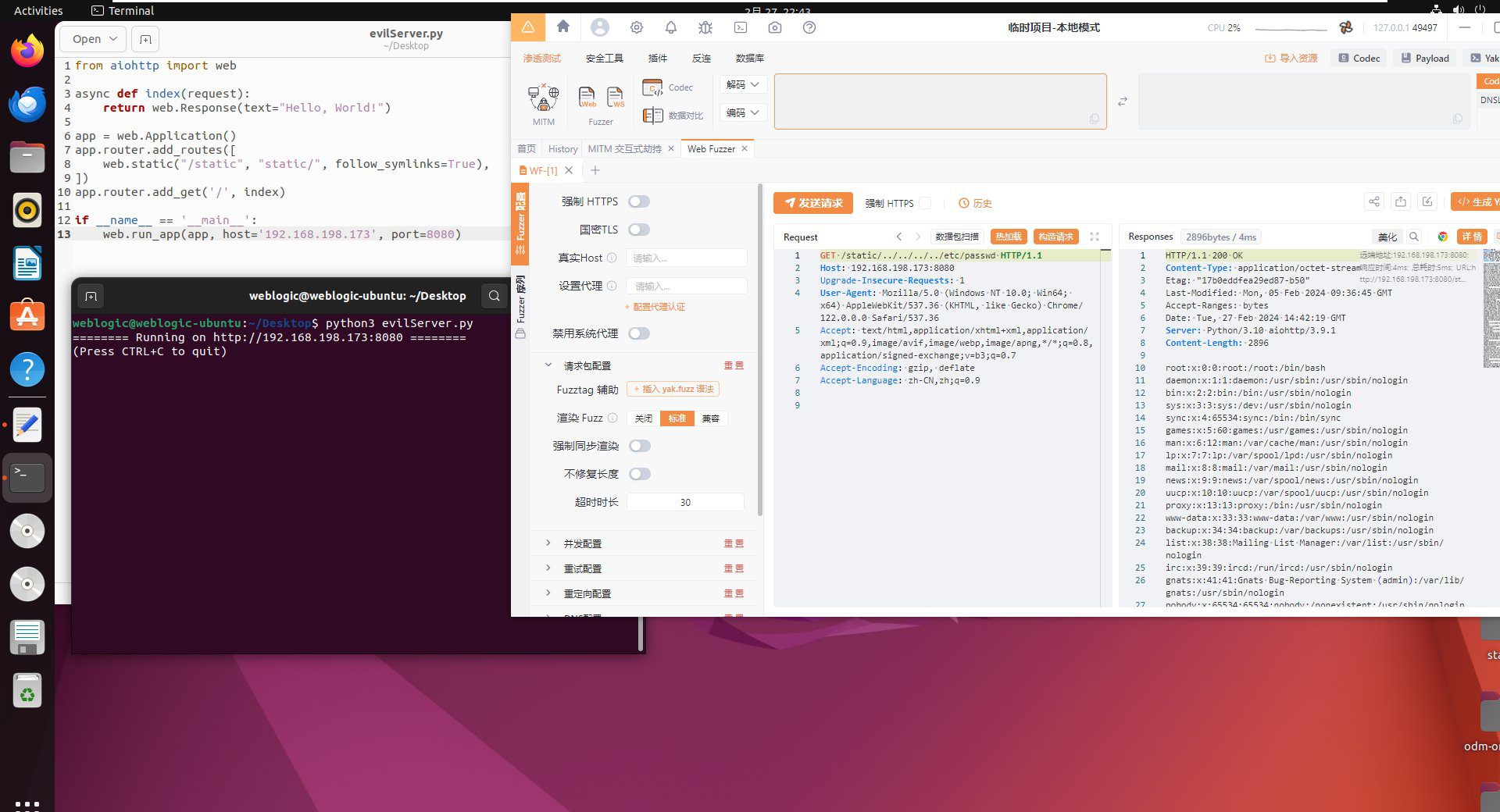
Worryingly, the CGSI report reveals that just days after a proof-of-concept exploit became public, scanning activity targeting the vulnerability spiked. The threat group ShadowSyndicate, infamous for its ransomware campaigns, is implicated in these scans.
Swift Patching is Key

With over 43,000 internet-exposed aiohttp servers identified worldwide, the potential attack surface is massive. Organizations utilizing the framework are urged to immediately update to aiohttp version 3.9.2 or later, where the flaw has been fixed.
ShadowSyndicate: A Ransomware Powerhouse
ShadowSyndicate has quickly solidified its position as a formidable ransomware player. Linked to numerous attacks involving strains like Quantum, Nokoyawa, and ALPHV, the group shows no signs of slowing its relentless pursuit of vulnerable targets.
The Takeaway
The aiohttp vulnerability highlights the breakneck speed with which threat actors move to exploit new flaws. This incident underscores the criticality of staying ahead of the curve – patch early, patch often. Failure to do so leaves the door wide open for groups like ShadowSyndicate to inflict costly damage.