shellz v1.6 releases: track and control your ssh, telnet, web and custom shells
shellz is a small utility to track and control your ssh, telnet, web and custom shells.

Changelog v1.6
New Features
Fixes
- f951d8b fix: using more recent go versions
Misc
Installation
$ go get -u github.com/evilsocket/shellz/cmd/shellz
Use
The tool will use the ~/.shellz folder to load your identities and shells json files, running the command shellz the first time will create the folder and the idents and shells subfolders for you. Once both ~/.shellz/idents and ~/.shellz/shells folders have been created, you can start by creating your first identity json file, for instance, let’s create ~/.shellz/idents/default.json with the following contents:
As you can see my default identity is using my SSH private key to log in the evilsocket user, alternatively you can specify a “password” field instead of a “key”. Alternatively, you can set the “key” field to “@agent”, in which case shellz will ask the ssh-agent for authentication details to the remote host:
Now let’s create our first shell json file ( ~/.shellz/shells/media.json ) that will use the default identity we just created to connect to our home media server (called media.server in our example):
Shells can (optionally) be grouped (with a default all group containing all of them) and, by default, they are considered ssh, in which case you can also specify the cyphers your server supports:
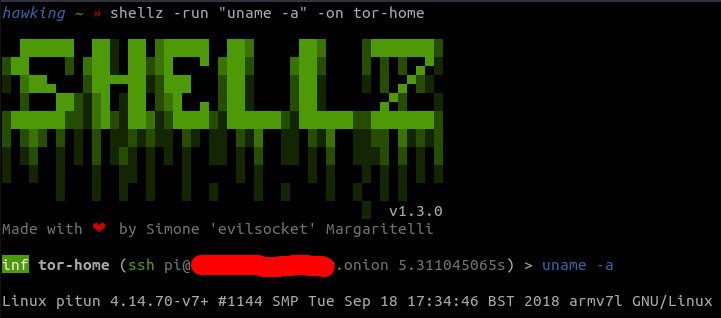
If you wish to use a SOCKS5 proxy (supported for the ssh session and custom shells), for instance, to reach a shell on a TOR hidden service, you can use the “proxy” configuration object:
Also, the telnet protocol is supported:
Examples
List available identities, plugins and shells:
shellz -list
List all available identities and shells of the group web:
shellz -list -on web
Enable the shells named machineA and machineB:
shellz -enable machineA, machineB
Enable shells of the group web:
shellz -enable web
Disable the shell named machineA (commands won’t be executed on it):
shellz -disable machineA
Test all shells and disable the not responding ones:
shellz -test
Test two shells and disable them if they don’t respond within 1 second:
shellz -test -on "machineA, machineB" -connection-timeout 1s
Run the command id on each shell ( with -to default to all):
shellz -run id
Run the command ‘id’ on each shell and print some statistics once finished:
shellz -run id -stats
Run the command id on a single shell named machineA:
shellz -run id -on machineA
Run the command id on machineA and machineB:
shellz -run id -on 'machineA, machineB'
Run the command id on shells of group web:
shellz -run id -on web
Run the command uptime on every shell and append all outputs to the all.txt file:
shellz -run uptime -to all.txt
Run the command uptime on every shell and save each output to a different file using per-shell data (every field referenced between {{ and }} will be replaced by the json field of the shell object):
shellz -run uptime -to "{{.Identity.Username}}_{{.Name}}.txt"
For a list of all available flags and some usage examples just type shellz without arguments.
Copyright (C) 2018 evilsocket
Source: https://github.com/evilsocket/