steady v3.1.15 releases: Discover, assess and mitigate known vulnerabilities in your Java and Python projects
Eclipse Steady (Incubator Project)
Discover, assess and mitigate known vulnerabilities in your Java and Python projects
Eclipse Steady supports software development organizations in regard to the secure use of open-source components during application development. The tool analyzes Java and Python applications in order to:
- detect whether they depend on open-source components with known vulnerabilities,
- collect evidence regarding the execution of vulnerable code in a given application context (through the combination of static and dynamic analysis techniques), and
- support developers in the mitigation of such dependencies.
As such, it addresses the OWASP Top 10 security risk A9, Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities, which is often the root cause of data breaches: snyk.io/blog/owasp-top-10-breaches
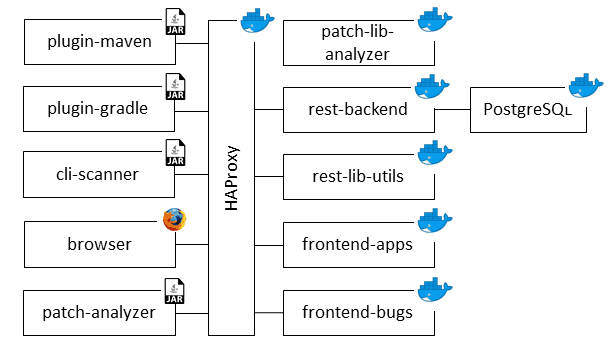
In comparison to other tools, the detection is code-centric and usage-based, which allows for more accurate detection and assessment than tools relying on meta-data. It is a collection of client-side scan tools, microservices and rich OpenUI5 Web frontends.

Features
- Detection of vulnerable code is realized by discovering method signatures in Java archives and comparing their source and byte code with the vulnerable and fixed version (as known from the fix commit). As such, the detection is more accurate than for approaches based on meta-data (less false-positives and false-negatives). In particular, it is robust against rebundling, a very common practice in the Java ecosystem.
- Assessment of vulnerable dependencies by application developers and security experts is supported by information about the potential and actual execution of vulnerable code. This information is based on call graph analysis and trace information collected during JUnit and integration tests. Going down to the granularity of single methods, application developers are presented with the potential and actual call stack from application code till vulnerable code.
- The addition of new vulnerabilities to the knowledge base does not require the re-scan of applications. In other words, right after an addition to the knowledge base, it is immediately known whether previously scanned applications are affected or not.
- Mitigation proposals consider the reachable share of dependencies, i.e., the set of methods that can be potentially reached from application code union the actual executions observed during tests. This information is used to compute several metrics aiming to let developers chose the best non-vulnerable replacement of a vulnerable dependency (best in regards to non-breaking and with least regression likelihood).
- Individual findings can be exempted if developers come to the conclusion that a vulnerability cannot be exploited in a given application-context. This information can be maintained in an auditable fashion (incl. timestamp and author information) and typically prevents build exceptions during CI/CD pipelines.
- Organization-internal CERTs can query for all applications affected by a given vulnerability. This feature supports, for instance, larger development organizations with many software applications developed by distributed and de-central development units.
Changelog v3.1.15
Bug fixes:
- Added manifest file entry
Multi-Releaseto all JAR artifacts (#437)
Install && Use
Copyright (c) 2018 SAP SE or an SAP affiliate company. All rights reserved.