Image Credit: Drweb
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, Doctor Web’s November 2023 virus activity review offers an intriguing glimpse into the shifting nature of digital threats. This comprehensive analysis reveals a notable decrease in the overall number of detected threats, alongside a slight reduction in unique threats. The most prevalent dangers include pervasive adware programs, adware trojans, and malicious apps, intricately designed to elude detection. Interestingly, the cyber realm witnessed a surge in phishing documents, particularly through email traffic. These devious tactics are accompanied by malicious scripts and various downloaders, all aimed at surreptitiously installing malware on target computers.

In November 2023, Doctor Web‘s virus activity review revealed an 18.09% decrease in overall threats compared to October, with unique threats also diminishing by 13.79%. The prevalent threats included adware programs, adware trojans, and malicious apps, often accompanied by other threats to evade detection. Email traffic was primarily dominated by phishing documents, along with malicious scripts and downloaders for additional malware.
Encoder trojans continued to challenge users, with a 6.98% increase in decryption requests. Trojan.Encoder.3953 led these incidents, followed by Trojan.Encoder.26996 and Trojan.Encoder.35534.
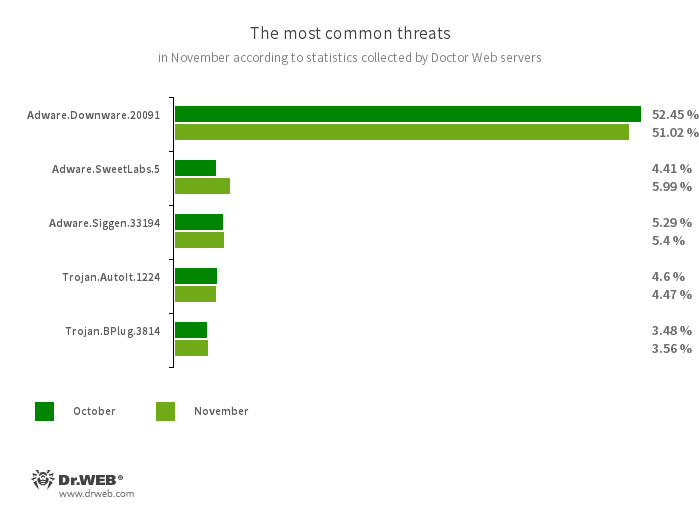
Notably, new malicious programs surfaced on Google Play, including over 20 fake apps involved in fraud and a trojan subscribing users to paid services. The most common threats identified were Adware.Downware.20091, Adware.SweetLabs.5, Adware.Siggen.33194, Trojan.AutoIt.1224, and Trojan.BPlug.3814.
Doctor Web’s analysis also highlighted the persistence of dangerous websites, primarily fraudulent investment sites and lottery scams. The mobile landscape saw a decrease in adware-trojan activity and fewer encounters with banking trojans and spyware, although new threats on Google Play emerged.
Further, the mobile world wasn’t spared, with new malicious programs surfacing on Google Play, including fraudulent apps and a trojan subscribing users to paid services without consent. This review underlines the critical need for vigilant cybersecurity practices in the face of these evolving threats.