windapsearch: enumerate users, groups and computers from a Windows domain
windapsearch
windapsearch is a Python script to help enumerate users, groups, and computers from a Windows domain through LDAP queries. By default, Windows Domain Controllers support basic LDAP operations through port 389/tcp. With any valid domain account (regardless of privileges), it is possible to perform LDAP queries against a domain controller for any AD-related information.
You can always use a tool like ldapsearch to perform custom LDAP queries against a Domain Controller. I found myself running different LDAP commands over and over again, and it was difficult to memorize all the custom LDAP queries. So this tool was born to help automate some of the most useful LDAP queries a pentester would want to perform in an AD environment.
Installation
$ git clone https://github.com/ropnop/windapsearch.git
$ pip install python-ldap #or apt-get install python-ldap
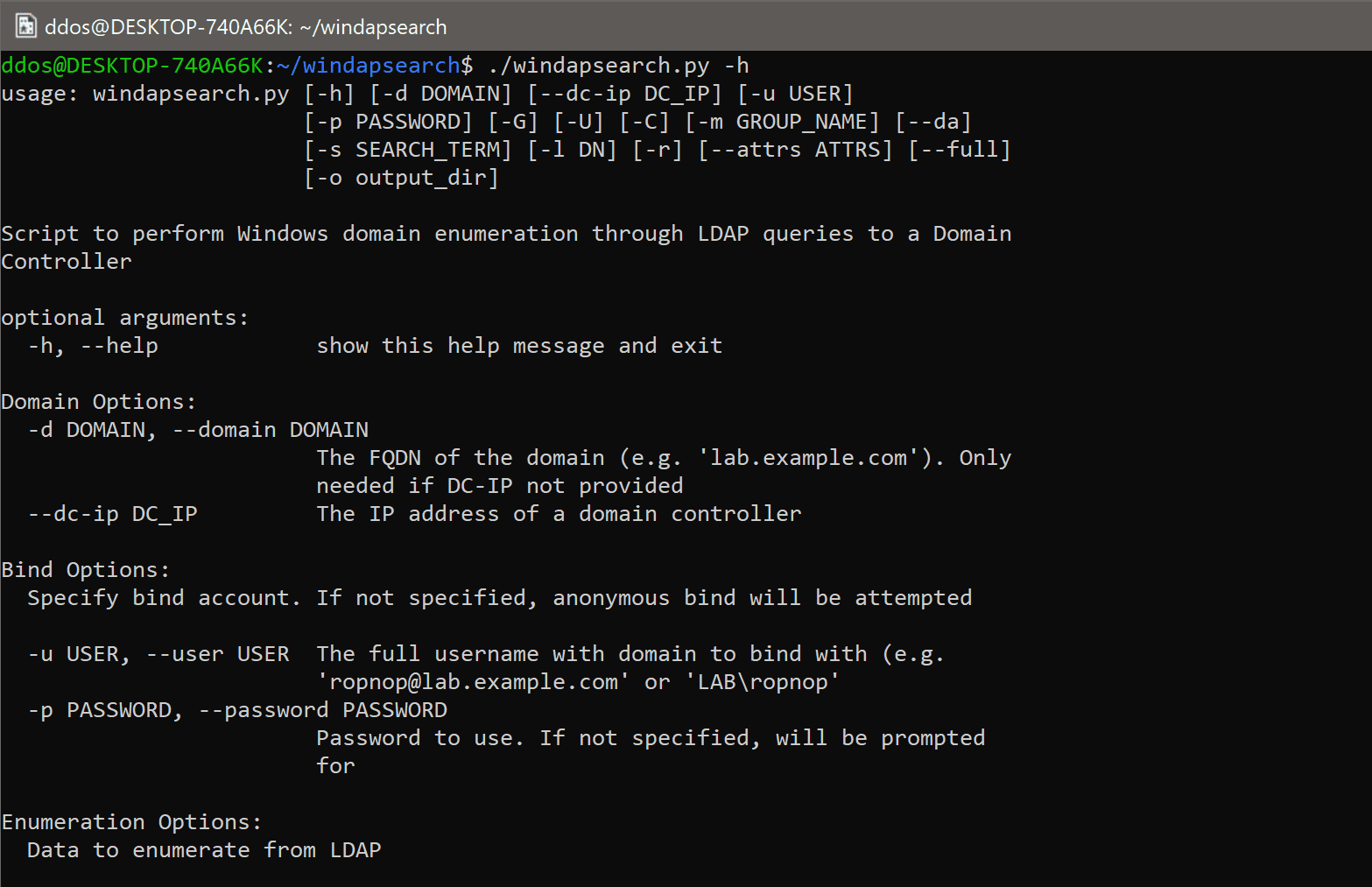
$ ./windapsearch.py
Usage
Specifying Domain and Account
To begin you need to specify a Domain Controller to connect to with --dc-ip, or a domain with -d. If no Domain Controller IP address is specified, the script will attempt to do a DNS host lookup on the domain and take the top result.
A valid domain username and password are required for most lookups. If none are specified the script will attempt an anonymous bind and enumerate the default namingContext, but most additional queries will fail. The username needs to include the full domain, e.g. ropnop@lap.example.com or EXAMPLE\ropnop
The password can be specified on the command line with -p or if left out it will be prompted for.
Enumerate Users
The -U option performs an LDAP search for all entries where objectCategory=user. By default, it will only display the commonName and the userPrincipalName. The --attrs option can be used to specify custom or additional attributes to display, or the --full option will display everything for all users.
Enumerate Groups and Group Memberships
Use the -G option to enumerate all entries where objectCategory=group. This will output the DN and CN of all groups.
To query group membership, use the -m option with either the DN or CN of the group you wish to query. The tool supports fuzzy search matching so even a partial CN will work. If it matches more than one group, the tool will specify which group to query.
Domain Admins
You can enumerate Domain Admins through two methods. One is to use -m with “Domain Admins”. This will query LDAP for the “Domain Admins” entry and display all the members.
The more thorough way is to do a lookup of all users and determine if they or a group they belong to are part of “Domain Admins”. This has the added benefit of discovering users who have inherited DA rights through nested group memberships. It’s much slower, however. See this link for more details on the technique used: https://labs.mwrinfosecurity.com/blog/active-directory-users-in-nested-groups-reconnaissance/ To do a recursive lookup for Domain Admins, you can use the “–da” option.
Enumerating Computers
LDAP queries can be used to enumerate domain-joined computers. This is very useful when trying to build a list of targets without running a portscan or ping sweep.
Use the -C option to list all matching entries where objectClass=Computer. By default, the attributes displayed are ‘cn’, ‘dNSHostName’, ‘operatingSystem’, ‘operatingSystemVersion’, and ‘operatingSystemServicePack’
If you specify the -r or --resolve option, the tool will perform a DNS lookup on every enumerated dNSHostName found and output the computer information, including IP address in CSV format. This can then be fed to other tools like nmap or CrackMapExec.
Copyright (C) ropnop
Source: https://github.com/ropnop/





