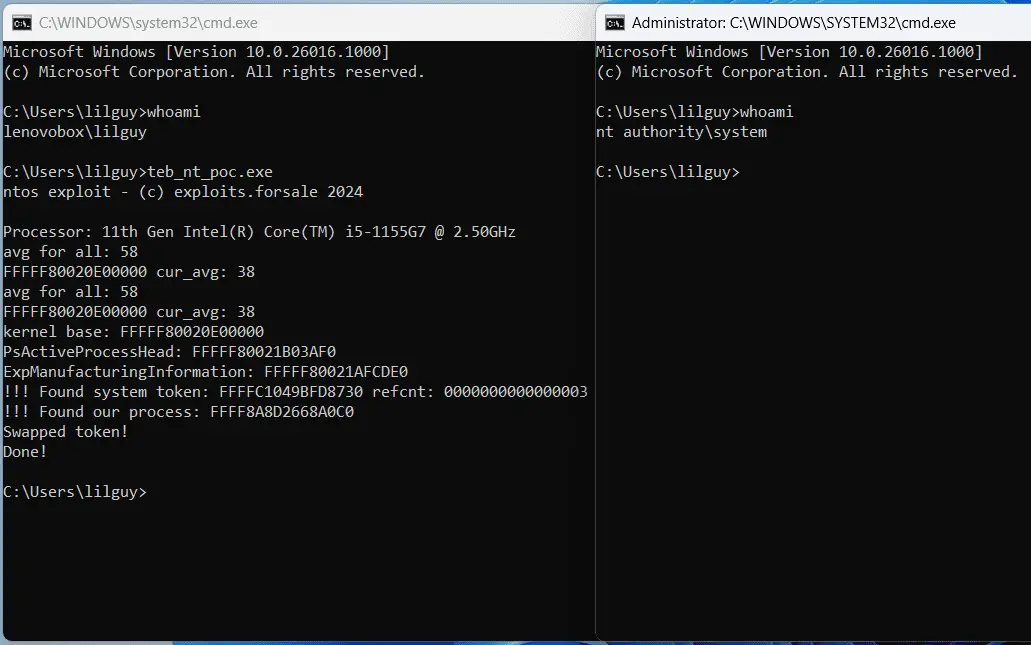
Security researcher Gabe Kirkpatrick has released proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code for CVE-2024-21345, a high-severity Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege vulnerability. This exploit allows authenticated attackers to escalate privileges to the SYSTEM level, granting them full control over affected systems.
CVE-2024-21345 is a complex vulnerability that involves the manipulation of the Windows kernel’s memory handling operations. It specifically exploits a double-fetching issue in the NtQueryInformationThread syscall, a part of the system responsible for handling requests to retrieve information about thread execution environments. Here’s how the vulnerability works:

- Triggering the Flaw: An authenticated user can run a specially crafted application that manipulates how the kernel fetches length fields during data copy operations between user mode and kernel mode.
- Exploiting the Double-fetch: The flaw arises from the kernel performing a double-fetch of a length field from a user-provided address. Typically, this should be fetched once and verified. However, by changing the fetched data between these fetches, the verification can be bypassed.
- Bypassing Safety Checks: Using the ProbeForWrite function, which checks if a memory address can be written to, the exploit circumvents safety measures by setting the data size to zero, which the function does not validate, allowing an arbitrary kernel address to be written to.
- Execution and Control: The final move involves writing controlled data to this address, which can include the thread’s Thread Environment Block (TEB), allowing the attacker to manipulate kernel memory and potentially gain SYSTEM privileges.
The exploitation of this vulnerability could allow attackers to escape contained execution environments and take control over the system at the kernel level. This sort of elevation of privilege is particularly concerning because it provides the attacker with the highest level of access, akin to that of the system’s own operations.
CVE-2024-21345, which carries a high-severity score of 8.8, has been patched, but the subsequent release of a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code on GitHub by researcher Gabe Kirkpatrick has put the spotlight back on its potential risks.
Microsoft addressed this flaw in the February 2024 Patch Tuesday updates. Immediate installation of these updates is the only effective mitigation at this time.
Vulnerabilities with publicly available exploits pose an immediate and heightened risk. Organizations and individuals must treat this situation with utmost urgency to secure their Windows environments.