Image: CYFIRMA
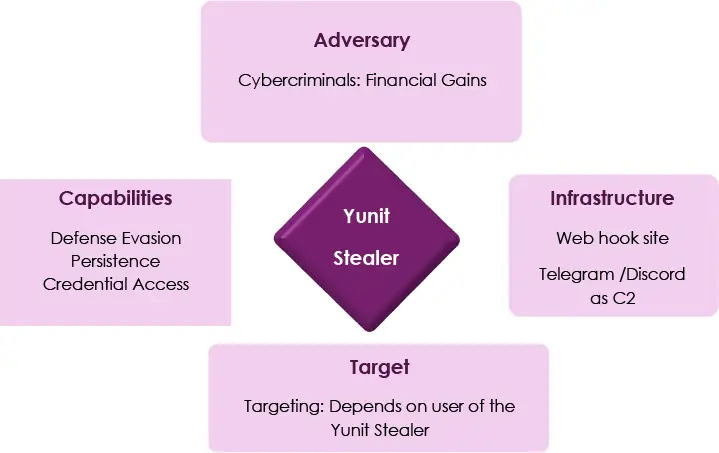
A new cybersecurity threat has emerged, named the “Yunit Stealer,” which is designed to collect a wide array of sensitive data from infected systems. Leveraging advanced JavaScript techniques, Yunit Stealer incorporates system utilities and cryptographic modules to extract personal information while evading detection.
According to a recent report by CYFIRMA, Yunit Stealer utilizes comprehensive data extraction techniques, focusing on user credentials stored in browsers like Chrome, Edge, and Opera. According to CYFIRMA, the malware can steal “passwords, cookies, autofill data, and cryptocurrency wallets“. It even uses PowerShell scripts to bypass antivirus defenses by exploiting system utilities.
The malware also employs persistence techniques to remain hidden on systems. It modifies Windows registry keys, adds exclusions to Windows Defender, and uses batch and VBScript files to maintain long-term control over the infected system. It even has geofencing capabilities that allow it to operate only in specific geographic locations, avoiding detection in non-targeted regions.
The report highlights strong evidence pointing to the Yunit Stealer’s developer being a French speaker with a background in malicious projects. The developer is believed to have connections to various platforms, including GitHub and YouTube, where they share their work and gaming interests. Interestingly, the malware’s name appears to be inspired by the computer game “Yunit,” further linking the developer to the gaming community.
What makes Yunit Stealer particularly dangerous is its ability to hide its tracks effectively. CYFIRMA’s analysis found that the malware “conceals windows during execution and obfuscates its command lines to avoid detection.” It also takes extra steps by “checking computer location settings” to selectively target specific regions, further complicating detection and prevention efforts.
In addition to stealing browser data, the malware also extracts credit card details stored in browsers and sends stolen information to pre-configured Discord webhooks or Telegram channels. This exfiltration technique ensures that sensitive data is transferred to the attackers while maintaining a high degree of anonymity.
Since its discovery, Yunit Stealer has been associated with active development on various platforms. The threat actor behind this malware, identified as “Freeboox,” has been selling related malicious projects on underground forums like CraxPro since October 2023. Additionally, CYFIRMA notes that the developer’s choice of Twitch and YouTube as outlets for their gaming interests may indicate that Yunit Stealer is part of a larger trend where cybercriminals in the gaming world seek financial gain through hacking.
Related Posts:
- Professional Goods & Services at Risk: Decoding CYFIRMA’s Cybersecurity Report
- Cybersecurity firm warns of actively exploited Windows IKE RCE (CVE-2022-34721) flaw
- Mekotio Trojan: A PowerShell-Based Threat Targeting Victims with Stealth and Persistence
- Transparent Tribe APT Group’s New Arsenal: Mythic Poseidon, Linux, and C2 Takedown
- Malware infections associated with online gaming