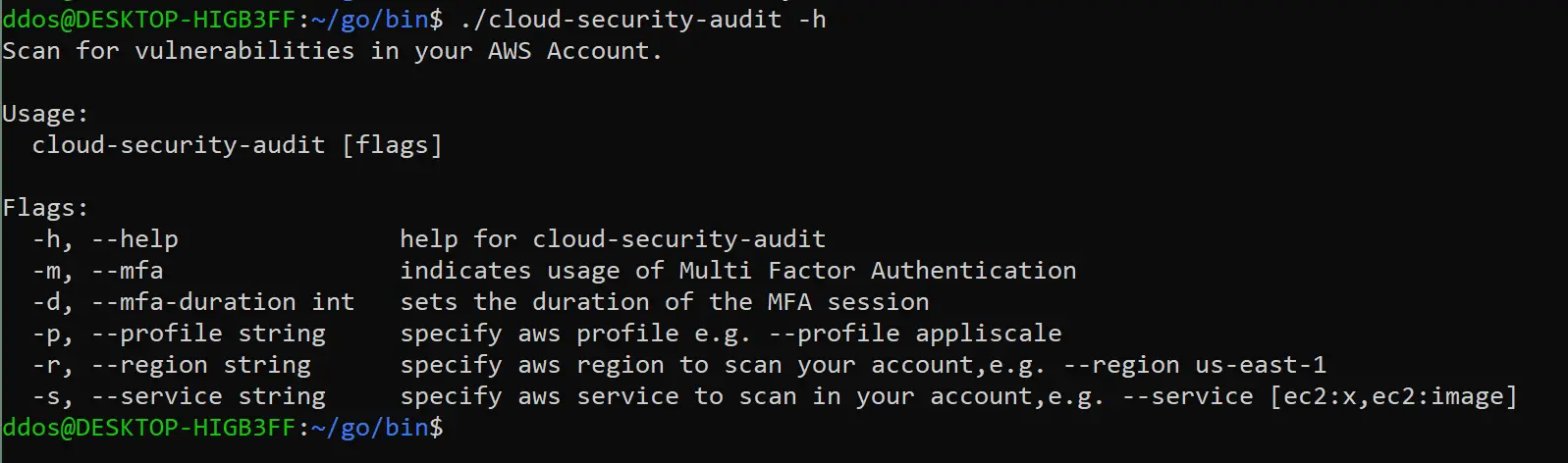
Cloud Security Audit
Cloud Security Audit is a command line tool that scans for vulnerabilities in your AWS Account. In an easy way, you will be able to identify unsecure parts of your infrastructure and prepare your AWS account for a security audit.
Install
$GOPATH $ go get github.com/Appliscale/cloud-security-audit
$GOPATH $ cd cloud-security-audit
cloud-security-audit $ make all
Use

Initialising Session
If you’re using MFA you need to tell Cloud Security Audit to authenticate you before trying to connect by using flag --mfa. Example:
$ cloud-security-audit --service s3 --mfa --mfa-duration 3600
EC2 Scan
How to use
To perform audit on all EC2 instances, type:
$ cloud-security-audit --service ec2
You can narrow the audit to a region, by using the flag -r or --region. Cloud Security Audit also supports AWS profiles – to specify profile use the flag -p or --profile.
Example output
How to read it
- First column
AVAILABILITY ZONEcontains information where the instance is placed - Second column
EC2contains instance ID. - Third column
Volumescontains IDs of attached volumes(virtual disks) to given EC2. Suffixes meaning:[NONE]– Volume not encrypted.[DKMS]– Volume encrypted using AWS Default KMS Key. More about KMS you can find here
- Fourth column
Security Groupscontains IDs of security groups that have too open permissions. e.g. CIDR block is equal to0.0.0.0/0(open to the whole world). - Fifth column
EC2 TAGScontains tags of a given EC2 instance to help you identify purpose of this instance.
Docs
You can find more information about encryption in the following documentation:
S3 Scan
How to use
To perform audit on all S3 buckets, type:
$ cloud-security-audit --service s3
Cloud Security Audit supports AWS profiles – to specify profile use the flag -p or --profile.
Example output
How to read it
- First column
BUCKET NAMEcontains names of the s3 buckets. - Second column
DEFAULT SSEgives you information on which default type of server side encryption was used in your S3 bucket:
NONE– Default SSE not enabled.DKMS– Default SSE enabled, AWS KMS Key used to encrypt data.AES256– Default SSE enabled, AES256.
- Third column
LOGGING ENABLEDcontains information if Server access logging was enabled for a given S3 bucket. This provides detailed records for the requests that are made to an S3 bucket. More information about Server Access Logging can be found here - Fourth column
ACL IS PUBLICprovides information if ACL (Access Control List) contains permissions, that make the bucket public (allow read/writes for anyone). More information about ACLs here - Fifth column
POLICY IS PUBLICcontains information if bucket’s policy allows any action (read/write) for an anonymous user. More about bucket policies here R, W and D letters describe what type of action is available for everyone.
Docs
You can find more about securing your S3’s in the following documentations:
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/serv-side-encryption.html
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/ServerLogs.html
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/user-guide/server-access-logging.html
Copyright 2018 Appliscale
Source: https://github.com/Appliscale/