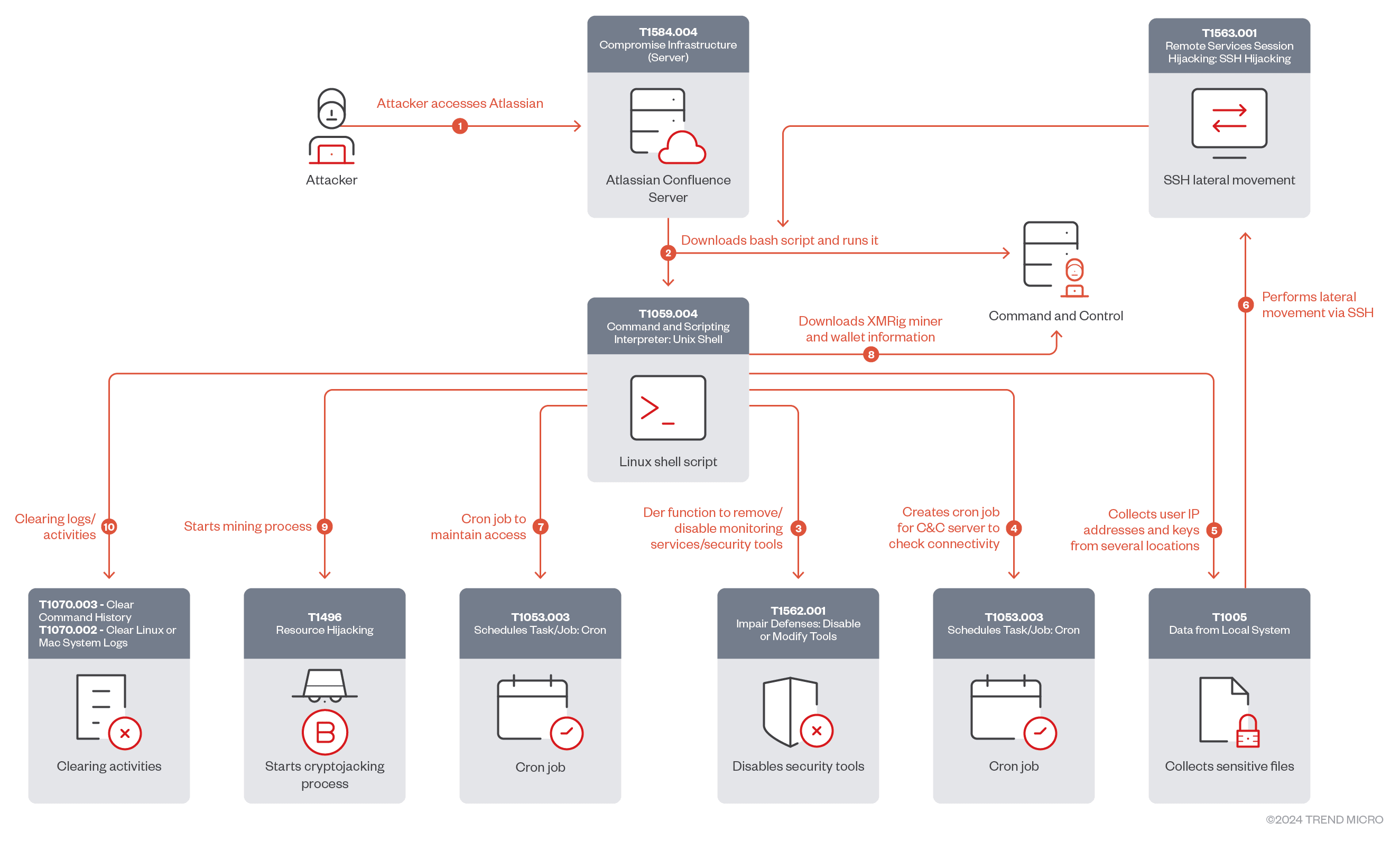
Attack chain used in the second attack vector
Trend Micro researchers have uncovered a widespread cryptojacking campaign leveraging a critical vulnerability (CVE-2023-22527) in the Atlassian Confluence Data Center and Server. Attackers are exploiting this flaw to install cryptocurrency mining malware, hijacking computing resources, and generating illicit profits.
On January 16, 2024, Atlassian issued a security advisory for CVE-2023-22527, a severe vulnerability with a perfect CVSS score of 10. This flaw impacts older versions of Confluence Data Center and Server, platforms widely used by organizations to collaborate and manage content. The vulnerability stems from a template injection flaw that allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute remote code on the affected systems, potentially giving them full control over the server.
Since mid-June 2024, Trend Micro observed a significant uptick in exploitation attempts targeting this vulnerability. The attacks have been traced to three main threat actors, each employing distinct methods to capitalize on the vulnerability for cryptomining.
- Threat Actor 1: This actor leverages an ELF file payload to deploy the XMRig miner directly on compromised systems, using the vulnerability to execute the cryptomining operations.
- Threat Actor 2: Utilizing a more sophisticated approach, this attacker employs a shell script executed over Secure Shell (SSH) to infiltrate accessible endpoints within the victim’s environment. The script is designed to eliminate competing cryptomining processes, disable cloud security services like Alibaba Cloud Shield and Tencent Cloud mirrors, and gather critical information such as IP addresses and SSH keys to spread the cryptomining operation to other hosts. This actor focuses on maintaining persistent access to the compromised server by creating multiple cron jobs under various aliases. These cron jobs not only ensure the continuity of the mining operations but also systematically disable any security tools that might detect or interrupt the process.
In each case, once the cryptomining setup is complete, the attackers deploy the XMRig miner to begin harvesting cryptocurrency. To cover their tracks, they meticulously clear logs and bash history, leaving minimal evidence of their activities.
The continued exploitation of CVE-2023-22527 underscores the importance of timely patching. Administrators should immediately update their Confluence instances to the latest version to mitigate this risk.
Additionally, organizations should implement robust security measures, including:
- Network segmentation to limit lateral movement
- Endpoint detection and response solutions to identify and block suspicious activity
- Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments
Related Posts:
- CVE-2023-22527 (CVSS 10): Critical RCE Flaw in Confluence Data Center and Server
- Researchers Published Technical Details for Atlassian Confluence RCE (CVE-2023-22527)
- Evolving Cryptojacking Campaign Targets Misconfigured Kubernetes Clusters
- Hackers use Youtube server ads hijack the computer to dig Monero
- C3RB3R Ransomware Strikes Again: Exploiting the Confluence Vulnerability