
A severe security vulnerability has been identified in BentoML, a Python library used for building online serving systems optimized for AI applications and model inference. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-27520 (CVSS 9.8), allows for remote code execution (RCE) and poses a significant risk to systems utilizing the affected versions of the library.
The core issue lies in an insecure deserialization flaw within BentoML. According to the security advisory, “a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability caused by insecure deserialization has been identified in the latest version (v1.4.2) of BentoML. It allows any unauthenticated user to execute arbitrary code on the server.”
The report further elaborates on the vulnerable code segment found in serde.py:
Through data flow analysis, it was confirmed that the “payload content is sourced from an HTTP request, which can be fully manipulated by the attack.” The lack of proper validation means that “maliciously crafted serialized data can execute harmful actions during deserialization.”
The impact of this vulnerability is severe: remote code execution (RCE). Successful exploitation allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the server, potentially leading to:
- Complete system compromise
- Data theft
- Denial of service
- Installation of malware
A proof-of-concept exploit for CVE-2025-27520 is available, increasing the urgency for users to apply the patch.
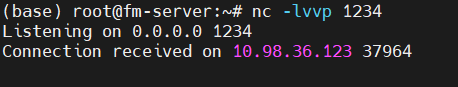
The following versions of BentoML are affected:
- =1.3.4, <1.4.3
Users are advised to upgrade to the patched version as soon as possible:
Given the critical nature of this RCE vulnerability and the availability of a proof-of-concept exploit, it is strongly recommended that all BentoML users upgrade to version 1.4.3 immediately. Failure to do so could leave systems vulnerable to complete takeover by malicious actors.