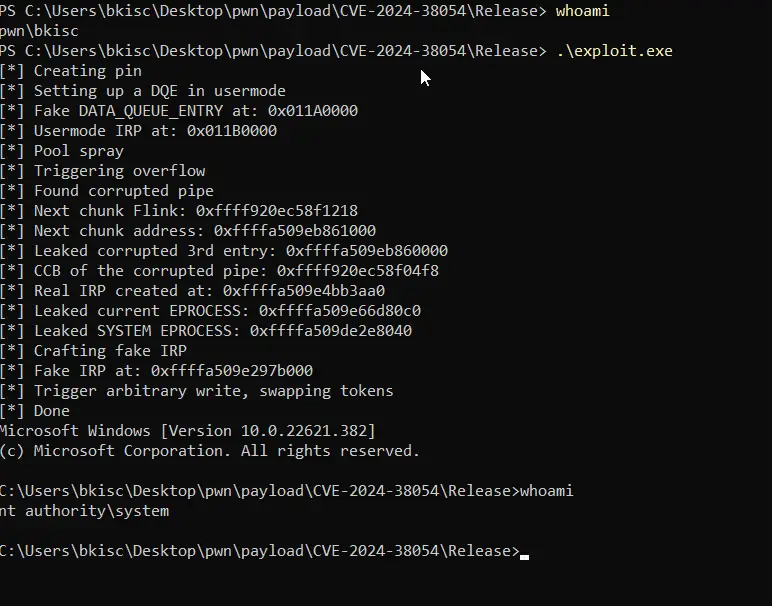
Security researcher ‘Frost’ has released proof-of-concept exploit code for the CVE-2024-38054 vulnerability, escalating concerns over a recently patched Windows security flaw. This high-severity vulnerability in the Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver could enable local attackers to escalate privileges to SYSTEM level by exploiting a heap-based buffer overflow.
CVE-2024-38054, carrying a CVSS score of 7.8, is classified as an Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerability. The vulnerability arises from a boundary error within the Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver, a component integral to managing multimedia streams in Windows environments. Specifically, the flaw allows a local user to pass specially crafted data to the application, triggering a heap-based buffer overflow. This overflow, in turn, can be exploited to escalate privileges, potentially giving the attacker SYSTEM-level access—the highest level of access within a Windows operating system.
Microsoft, recognizing the severity of this vulnerability, included a patch for CVE-2024-38054 in its July Patch Tuesday release. The vulnerability was reported by Angelboy (@scwuaptx) from DEVCORE, who was credited by Microsoft for finding this critical flaw. In its exploitability assessment, Microsoft labeled the flaw as “exploitation more likely,” suggesting that threat actors could develop reliable exploits to leverage this vulnerability in real-world attacks.
The release of the PoC by Frost underscores the urgency of applying the patch. With the exploit code now publicly available, the window for attackers to craft consistent and effective exploits has significantly narrowed. Organizations and individuals running vulnerable systems are at increased risk, particularly as threat actors may move quickly to weaponize the PoC in targeted attacks.
Frost’s GitHub repository not only contains the PoC exploit code for CVE-2024-38054 but also promises an upcoming in-depth vulnerability analysis. This analysis will likely provide further insights into the inner workings of the flaw and its exploitation, offering valuable information to both cybersecurity professionals and malicious actors alike.
Given the potential for this vulnerability to be exploited in the wild, system administrators and IT security teams must prioritize the deployment of the July Patch Tuesday updates. Ensuring that all systems are patched is the most effective way to mitigate the risk posed by CVE-2024-38054.
Related Posts:
- CISA & Microsoft Warn of 6 Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
- Cisco releases patch to fix three high security bugs
- MongoDB Patches High-Severity Windows Vulnerability (CVE-2024-7553) in Multiple Products
- North Korean Hackers Exploit VPN Vulnerabilities to Breach Networks