Handle-Ripper
-
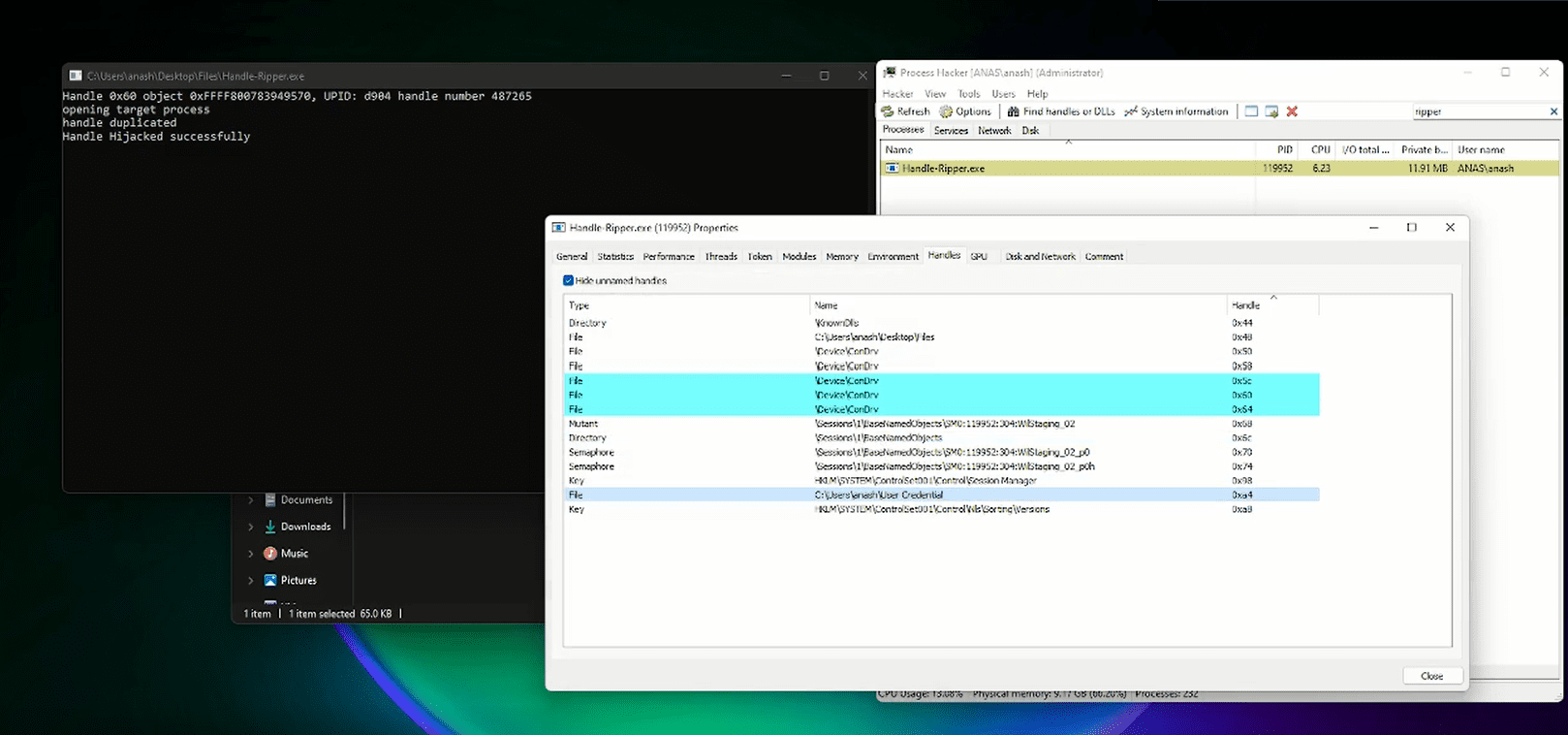
Handle hijacking is a technique used in Windows operating systems to gain access to resources and resources of a system without permission. It is a type of privilege escalation attack in which a malicious user takes control of an object handle, which is an identifier that is used to reference a system object, such as a file, a directory, a process, or an event. This allows the malicious user to gain access to resources that should be inaccessible to them.
-
Handle hijacking is a serious threat to system security as it allows a malicious user to access resources and data that should otherwise be protected. It can also be used to inject code into a vulnerable system, allowing the attacker to gain access to information and resources.
-
Handle hijacking techniques are becoming increasingly prevalent as hackers develop more sophisticated methods of exploiting vulnerabilities in Windows systems. As such, it is important that system administrators understand the risks associated with handle hijacking and take proactive measures to protect their systems.
DETAILS
-
To perform a handle hijacking attack, an attacker must first identify a handle that is being used by a legitimate process and that they want to access. This can be done using various techniques, such as scanning the handle table of a process, monitoring handle creation events, or using a tool that can enumerate handles on the system. Once the attacker has identified the handle they want to access, they can use the DuplicateHandle function to create a copy of the handle with their own process. This function takes the following parameters:
- hSourceProcessHandle: A handle to the process that contains the source handle.
- hSourceHandle: A handle to the object to duplicate.
- hTargetProcessHandle: A handle to the process that is to receive the duplicated handle.
- lpTargetHandle: A pointer to a variable that receives the handle value.
- dwDesiredAccess: The access rights for the duplicated handle.
- bInheritHandle: A value that specifies whether the handle is inheritable.
- dwOptions: Additional options for the handle duplication.
-
The DuplicateHandle function will create a new handle with the specified access rights and options, and return it in the lpTargetHandle parameter. The attacker can then use this handle to access the resource that it represents, allowing them to perform actions on the resource that they would not normally be able to do.