Honeyscanner – A vulnerability analyzer for Honeypots
Honeyscanner – A vulnerability analyzer for Honeypots
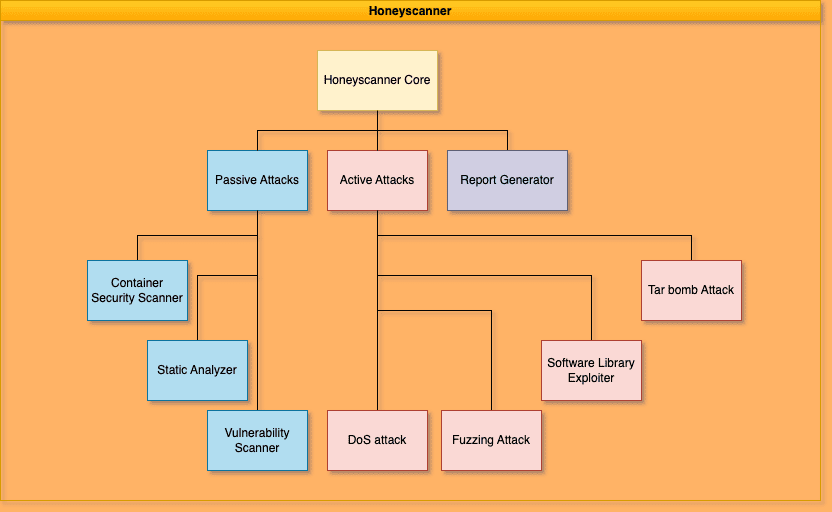
Honeyscanner is a vulnerability analyzer for honeypots designed to automatically attack a given honeypot, in order to determine if the honeypot is vulnerable to specific types of cyber attacks. It uses a variety of attacks, ranging from exploiting vulnerable software libraries to DoS, and fuzzing attacks. The analyzer then provides an evaluation report to the honeypot administrator, offering advice on how to enhance the security of the honeypot. Targeted toward security enthusiasts, open-source communities, and companies, Honeyscanner provides a much-needed safety check for various honeypots.
This project was presented at BlackHat Europe 2023 in London. For more information about Honeyscanner in BlackHat Europe click here.
Architecture

Install
Requirements
- Python v3.9.12 – Required to run the project
- Pipenv v2023.7.9 – Required to install Python dependencies
- Git – Used to download the source code
-
Download the Honeyscanner source code from GitHub. Open a terminal and introduce the following command.
git clone https://github.com/honeynet/honeyscanner.git
-
Navigate to the Honeyscanner’s folder, install the required Python packages, and activate the virtual environment.
cd Honeyscanner/honeyscanner
pipenv install
pipenv shell
NOTE FOR PIPENV: To exit the virtual environment, you just need to enter the command “exit” in the terminal.
Configuration
-
Before you run Honeyscanner, you need to control or own a Honeypot instance. For testing purposes, this guide assumes that the targeted Honeypot runs on a Docker container on the local machine, where Honeyscanner runs.
-
To test Honeyscanner against the latest Cowrie version, you can use the official Docker Image here, pull it locally, and run a Docker container with it.
-
If you prefer to test Honeyscanner against Kippo, you can use the following Docker Image in DockerHub here.
-
For testing Honeyscanner against Dionaea, use the following Docker Image in DockerHub here.
-
For testing Honeyscanner against Conpot, use the following Docker Image in DockerHub here.
-
After running a Honeypot using Docker containers locally, you will be able to specify the following parameters: –target_ip 127.0.0.1 –port 2222 when running the Honeyscanner.
NOTE: NEVER RUN Honeyscanner AGAINST HONEYPOTS YOU DO NOT OWN, OR YOU DO NOT HAVE EXPLICIT PERMISSION TO TEST.
NOTE: Currently Honeyscanner can actively attack the Dionaea and the Conpot honeypots only by using the DoS attack module. The way it works is that initially Honeyscanner uses nmap to find the open ports on the targeted honeypot, then tries to DoS all ports simultaneously. In order to run the nmap scanner, run Honeyscanner with root privileges for scanning Dionaea and Conpot. This provides nmap with deeper view of the services that run behind each port on the honeypot.
NOTE: For Dionaea only version 0.11.0 is supported at this stage of Honeyscanner. For Conpot, all versions up to 0.6.0 are supported.
Use
Use the following examples as a reference for how to runHoneyscanner :
python3 main.py –honeypot cowrie –honeypot_version 2.5.0 –target_ip 127.0.0.1 –port 2222 –username root –password 1234
python3 main.py –honeypot kippo –honeypot_version 0.9 –target_ip 127.0.0.1 –port 2222
sudo python3 main.py –honeypot dionaea –honeypot_version 0.11.0 –target_ip 127.0.0.1 –port 2323
sudo python3 main.py –honeypot conpot –honeypot_version 0.6.0 –target_ip 127.0.0.1 –port 2323
Copyright (c) 2023 Aristofanis Chionis Koufakos