Security researcher Dhmos Funk has released a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2025-0411 (CVSS 7.0), a high-severity vulnerability in the 7-Zip file archiver that enables attackers to bypass the Windows Mark of the Web (MotW) security feature and execute code on users’ systems when extracting malicious files from nested archives.
7-Zip, in an effort to enhance security, introduced support for MotW in 2022. This feature adds a special flag to files extracted from downloaded archives, alerting the operating system and other applications that the files may be untrusted. This warning prompts users to exercise caution when opening or running such files.
However, the security researcher Peter Girnus discovered a flaw in 7-Zip’s handling of archived files. When extracting files from a crafted archive that bears the MotW, 7-Zip fails to propagate the MotW to the extracted files. This allows attackers to create malicious archives that appear to be safe due to the MotW flag, but upon extraction, the files become unprotected and can be executed without any warnings.
“The specific flaw exists within the handling of archived files. When extracting files from a crafted archive that bears the Mark-of-the-Web, 7-Zip does not propagate the Mark-of-the-Web to the extracted files. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user,” Trend Micro explains.
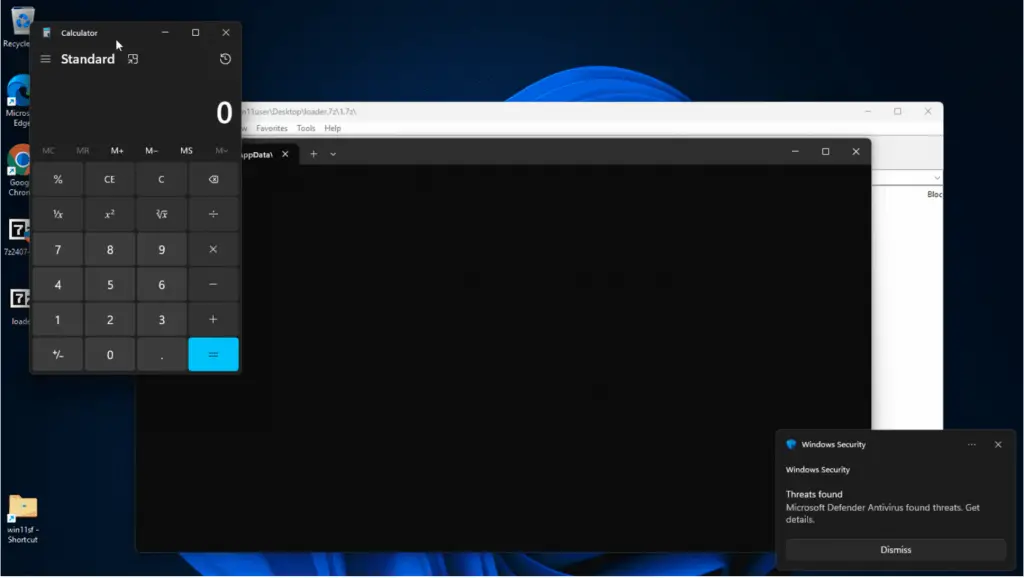
Security researcher Dhmos Funk recently published a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit demonstrating how CVE-2025-0411 can be weaponized. The attack follows these key steps:
- Crafting the Payload: The attacker creates a specially designed double-compressed archive containing malicious files.
- Delivery Mechanism: The archive is uploaded to a file-sharing platform, such as MediaFire, and distributed via phishing emails.
- Execution: When a victim downloads and extracts the file using a vulnerable version of 7-Zip, the MotW flag is bypassed, allowing the malicious payload to execute without triggering Windows security warnings.
The PoC leverages shellcode injection to execute the payload, which in this case launches a benign program (calc.exe) to demonstrate the exploit. However, this technique could easily be used to deliver more dangerous malware.
The vulnerability affects all versions of 7-Zip prior to 24.09. Users are strongly urged to update to the latest patched version as soon as possible to mitigate the risk.
In the meantime, as a temporary mitigation measure, users should exercise extreme caution when opening files from unknown or suspicious sources, especially compressed archives. Additionally, ensuring that their operating systems and security software are up-to-date and configured to detect and block malicious files can further enhance protection.
Related Posts:
- CVE-2025-0411: 7-Zip Security Vulnerability Enables Code Execution – Update Now
- CVE-2024-11477: 7-Zip Vulnerability Allows Remote Code Execution, Update Now!
- 7-Zip Remote Code Execution Vulnerability