Shed v2.0 releases: .NET runtime inspector
Shed is an application that allows inspecting the .NET runtime of a program in order to extract useful information. It can be used to inspect malicious applications in order to have a first general overview of which information are stored once that the malware is executed.
Shed is able to:
- Extract all objects stored in the managed heap
- Print strings stored in memory
- Save the snapshot of the heap in a JSON format for post-processing
- Dump all modules that are loaded into memory
Changelog v2.0.
- Improved dumping code
- Improved reporting
- Added capability to inject managed Assembly
Download
- Source code
- Download binary
Use
Inspecting an already running application
In order to inspect an already running process, you have to pass the pid to Shed. Example:
Shed.exe --pid 2356
Inspecting a binary
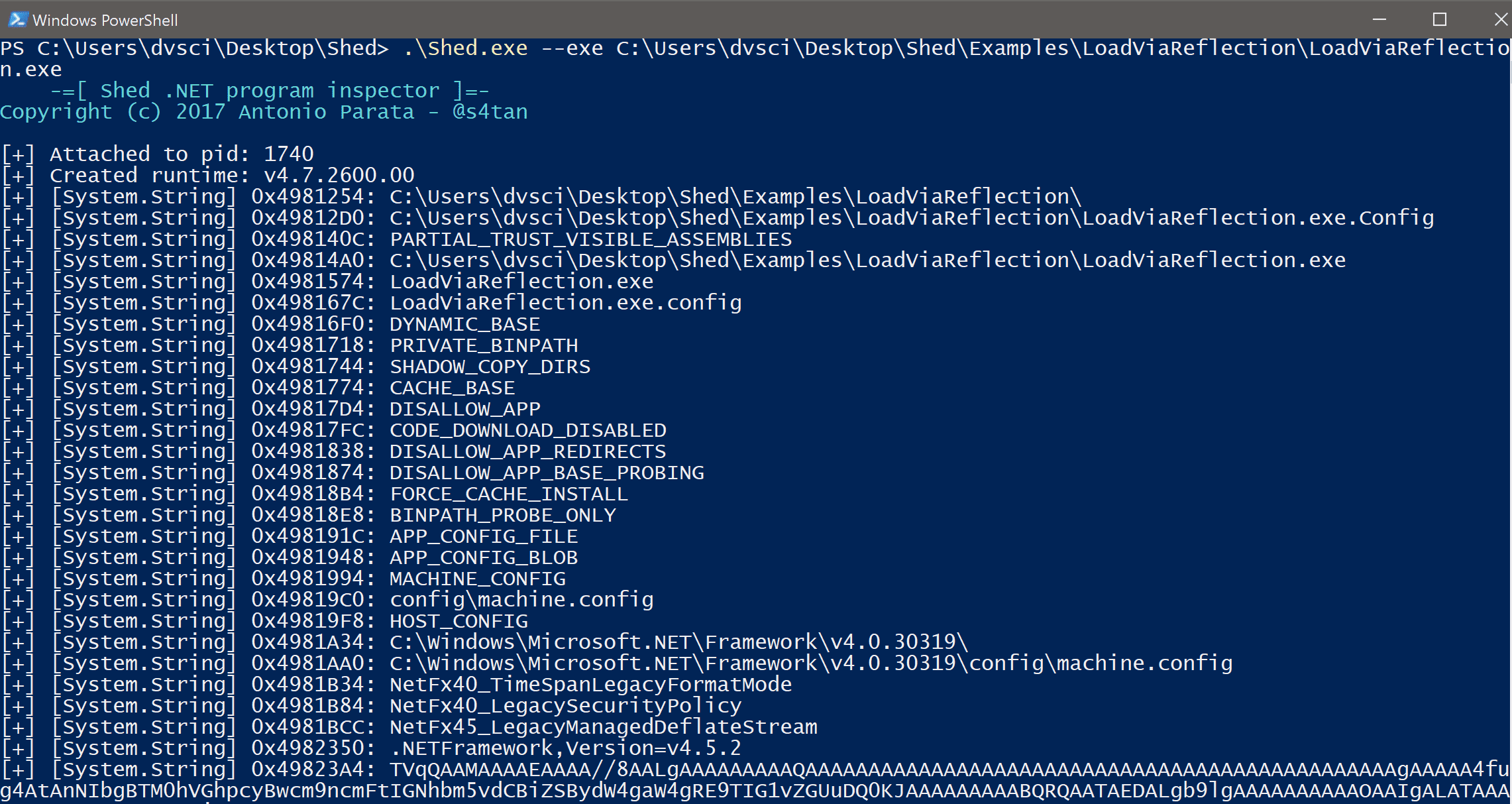
In order to inspect a binary, Shed needs to execute it and to attach to it in order to inspect the runtime. Example:
Shed.exe --exe malware.exe
You can also specify the amount of time (in milliseconds) to wait before to suspend the process. This will allow the program to have the time to initialize its properties. Example:
Shed.exe --timeout 2000 --exe malware.exe
Dumping options
By default Shed dump both the heap and the modules. If you want only one of that specifies the –dump-heap option to dump only the objects in the heap or the –dump-modules to dump only the modules.
Dumping the heap can produce a lot of information which are not strictly used for the analysis. You can filter it by using two files:
blacklist.txt this file contains the type names prefix that must not be logged
whitelist.txt this file contains the type names prefix that must be logged even if blacklisted
For example, if you want to filter all the System.IO namespace but you are interested in logging System.IO.MemoryStream, you can add the first value to blacklist.txt and the second one to whitelist.txt.
Examples
In the Examples folder, you will find three different projects that you can use in order to test Shed. Example:
Shed.exe –exe ..\Examples\ConfigurationSample\ConfigurationSample.exe
When the analysis is completed, Shed will print where you can find the result, as shown below:
[+] Result saved to C:\Shed\Result\7800
Build Shed
If you have installed Visual Studio, just run the build.bat batch file, it will create a zip file inside the build folder.
Copyright (C) 2017 Antonio Parata – @s4tan
Source: https://github.com/enkomio/