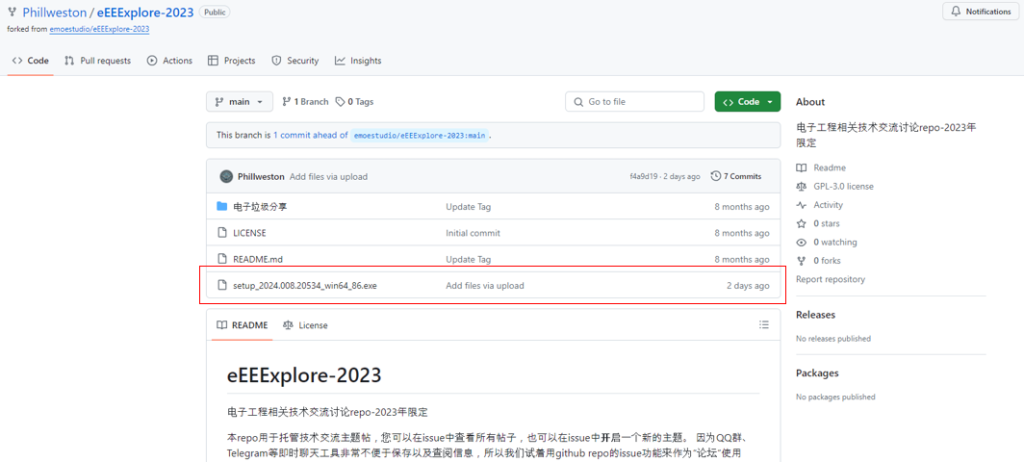
The malware uploaded on GitHub
Security experts at AhnLab Security Emergency Response Center (ASEC) have sounded the alarm on a widespread malware campaign employing the notorious StealC Infostealer. The malware is being distributed en masse, disguised as a legitimate program installer, and downloaded unwittingly through sources like Discord, GitHub, and Dropbox.
How the Attack Works

The attack begins with a lure – often a seemingly harmless installer for popular software. Malicious actors trick users into downloading these files, which redirect victims through a series of malicious web pages, ultimately leading to the disguised StealC download.

Upon execution, the malware employs a sophisticated web of techniques. It downloads an image file (.png) containing hidden malicious code and uses advanced injection methods like ntdll manual mapping and Heaven’s Gate to evade detection. This allows StealC to slip undetected into legitimate processes and steal a wide range of confidential information.
What StealC Targets
StealC is an Infostealer designed for maximum data theft. It targets:
- System Information: Hardware data, operating system details
- Browser Data: Saved passwords, autofill information, cookies
- Cryptocurrency Wallets: Keys and wallet information
- Messaging Apps: Discord, Telegram credentials
- Mail Clients: Account information and stored messages
Similarities to Past Campaigns
ASEC researchers have identified concerning similarities between this campaign and previous attacks involving the Vidar Infostealer. Both share overlapping distribution methods, injection techniques, and target data. The use of a common C2 (command-and-control server) further suggests a connection between the malware families or even the same threat actor.
High Risk of Infection
The recent surge in StealC distribution indicates it may be disguised as a program popular in Korea. Security experts advise extreme caution due to the risk of exposure.
How to Protect Yourself
- Download from Official Sources: Only download software from verified websites and app stores.
- Inspect Links: Scrutinize any links before clicking, especially shortened URLs or unexpected offers.
- Use Robust Security Software: Maintain up-to-date antivirus and anti-malware software on your devices.