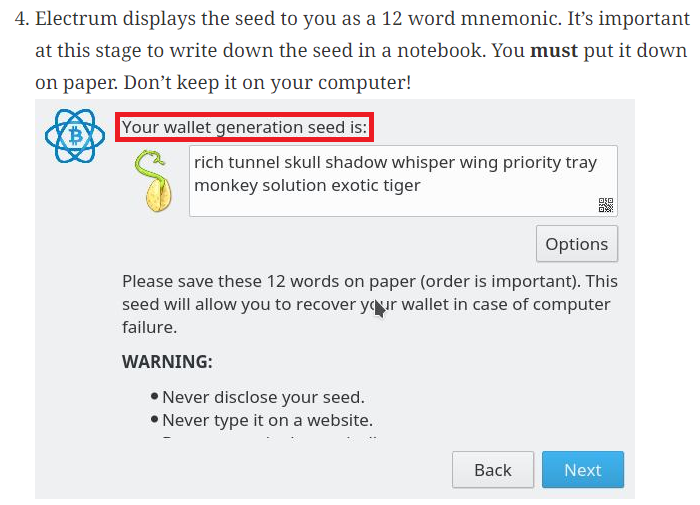
The seed input window when creating a cryptocurrency wallet
AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) has uncovered a new tactic employed by the notorious ViperSoftX malware. The latest analysis reveals that attackers are now utilizing Tesseract, an open-source Optical Character Recognition (OCR) engine, to exfiltrate sensitive information from users’ image files. This development underscores the evolving sophistication of ViperSoftX, a malware strain infamous for its ability to reside on infected systems and execute a variety of malicious commands, particularly those related to cryptocurrency theft.
ViperSoftX, first identified by Fortinet in 2020, has been a persistent threat, often distributed under the guise of software cracks or keygens. It is known for installing both Remote Access Trojans (RATs) and Infostealers designed to capture cryptocurrency wallet addresses. In 2022, Avast reported enhancements in ViperSoftX’s capabilities, including the use of PowerShell scripts and malicious browser extensions to expand its reach and functionality.

The latest iteration of ViperSoftX, however, marks a significant leap in its attack methodology. By integrating Tesseract, ViperSoftX can now extract text from images stored on infected systems. This deep learning-based tool scans for phrases related to passwords or cryptocurrency wallet addresses, exfiltrating any image files containing such sensitive information.
Upon infecting a system, ViperSoftX employs Tesseract to scan image files with extensions like .png, .jpg, and .jpeg, excluding those in the “editor” directory. The extracted text is then scrutinized for specific keywords associated with sensitive data, such as OTPs, recovery passwords, and cryptocurrency wallet phrases. If these strings are detected, the corresponding image files are sent to the attackers’ Command and Control (C&C) server.
This novel use of Tesseract is part of a broader strategy by ViperSoftX to install additional malware strains, including Quasar RAT and a new Infostealer dubbed TesseractStealer. Quasar RAT, an open-source malware developed with .NET, allows attackers to execute remote commands, steal user credentials, and take control of infected systems via a remote desktop feature. Recent observations indicate that Quasar RAT has been distributed extensively since March 2024, with some instances utilizing the Tor network for secure communication with C&C servers.
TesseractStealer, a new component in the ViperSoftX arsenal, leverages the Tesseract OCR engine to further the malware’s capabilities. It extracts texts from images using deep learning techniques and targets specific phrases that hint at cryptocurrency wallet seeds or recovery passwords. This meticulous approach enables attackers to restore wallets and steal cryptocurrencies with the captured seed phrases.
The surge in ViperSoftX’s activity and its advanced techniques highlight the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures. Users are advised to exercise extreme caution when downloading software from unverified sources, as ViperSoftX often masquerades as legitimate applications. It is crucial to download programs exclusively from official websites and to keep security software up to date to detect and mitigate such threats.