A high-severity vulnerability has been discovered in the Common Log File System (CLFS) driver in Windows 11, enabling local users to escalate their privileges. CLFS is responsible for efficiently managing system and application logs for event tracking and error recovery.
The vulnerability resides in the function CClfsBaseFilePersisted::WriteMetadataBlock and is linked to an unchecked return value in ClfsDecodeBlock. This oversight can result in data corruption within the CLFS structure, creating a pathway for privilege escalation.
The exploit also allows attackers to reveal the kernel address within the memory pool, aiding in circumventing upcoming security measures planned for Windows 11 version 24H2. However, this aspect was not utilized in the proof-of-concept (PoC) presented at the TyphoonPWN 2024 event, as testing was conducted on Windows 11 version 23H2.
The vulnerability is exploited by manipulating the CLFS log structure. During the attack, a log file is created, its data modified, and core system structures disrupted, enabling control at the kernel level. The lack of Supervisor Mode Access Prevention (SMAP) in Windows simplifies kernel memory manipulation, allowing attackers to alter process tokens for privilege escalation.
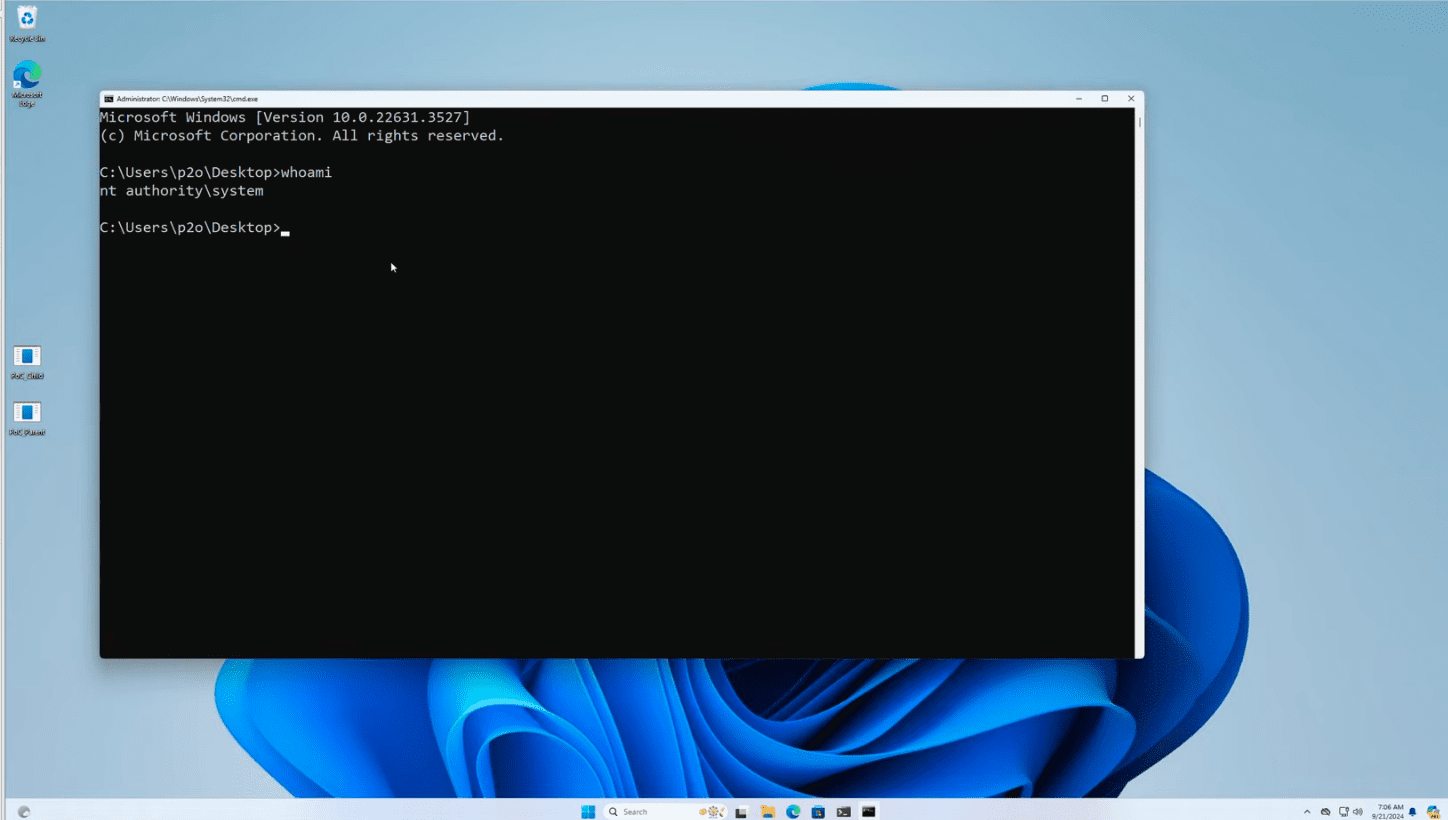
The exploit demonstrated at TyphoonPWN 2024 showcased the launch of a command line with SYSTEM privileges, underscoring the severity of the threat.
The researcher who identified the issue at the competition secured first place. Although Microsoft reported this vulnerability as a duplicate and claimed it was patched, tests on the latest version of Windows 11 indicate that the issue remains unresolved. A CVE identifier or patch information has yet to be published.
“The vendor has told us that the vulnerability is a duplicate and has been already fixed, though at the time of trying this on Windows 11 latest version the vulnerability still worked. We were never provided with a CVE number or Patch information,” reads the security advisory.
Related Posts:
- Researchers release the technical analysis & PoC for Windows 0-Day CVE-2022-37969 Flaw
- MongoDB Patches High-Severity Windows Vulnerability (CVE-2024-7553) in Multiple Products
- Microsoft Introduces New Publish API to Enhance Security of Edge Extensions