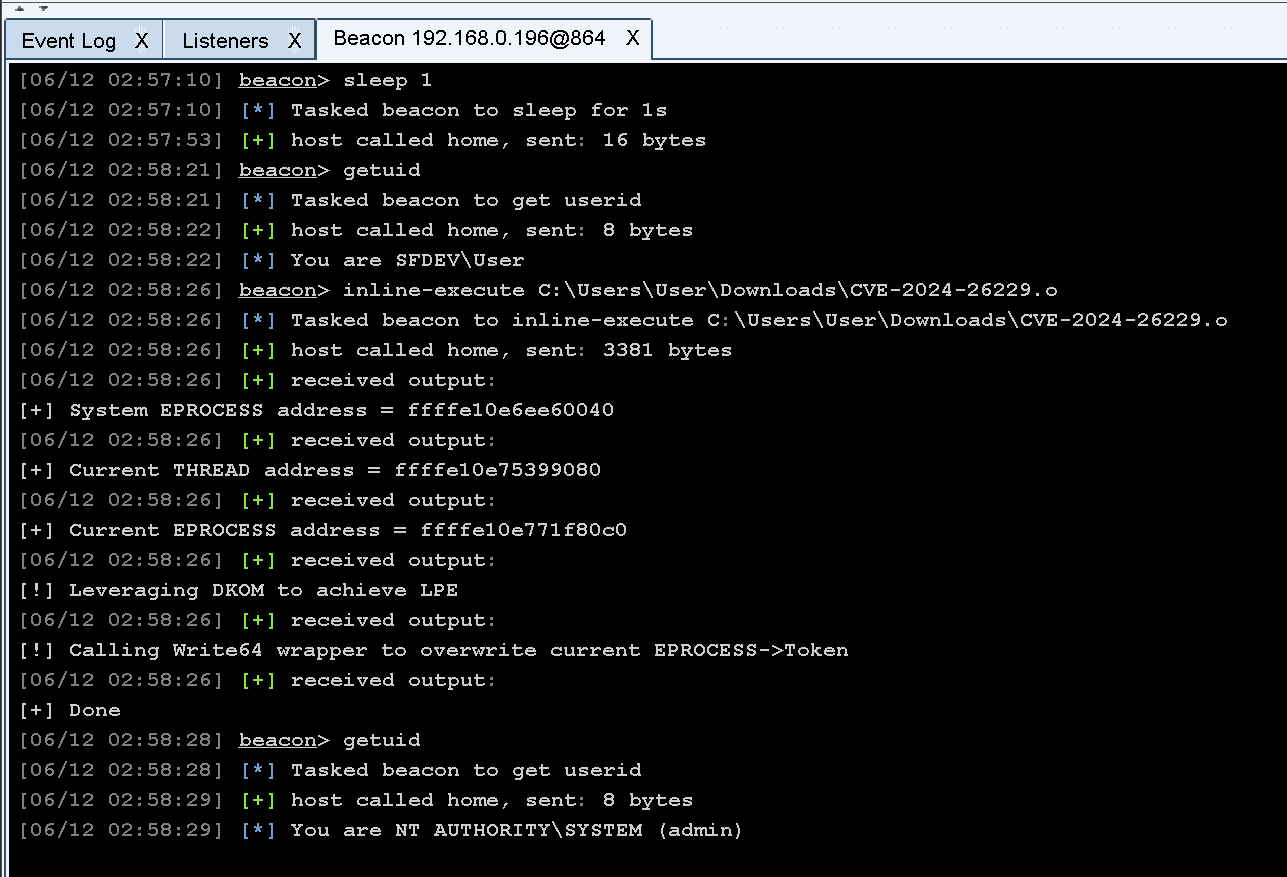
Security researchers are raising the alarm as proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code targeting a recently patched high-severity vulnerability (CVE-2024-26229) in Microsoft Windows has surfaced on GitHub. The vulnerability could allow attackers to gain SYSTEM privileges, the highest level of access on a Windows system. The vulnerability is categorized under CWE-122, specifically a heap-based buffer overflow, a type of defect that can lead to severe security breaches.
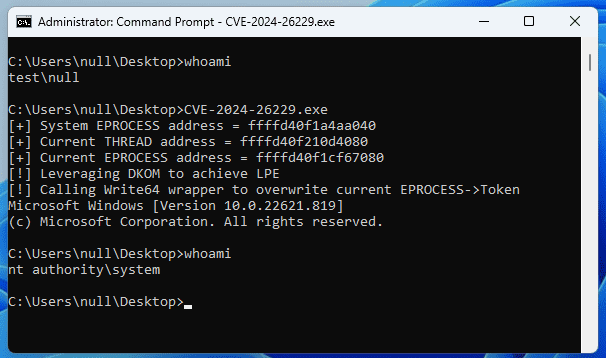
A heap-based buffer overflow occurs when a program writes more data to a buffer than it can handle, causing the excess data to overflow into adjacent memory regions. This overflow can corrupt memory and potentially enable an attacker to execute arbitrary code or gain unauthorized access to a system. Essentially, attackers can craft malicious code or inputs that trigger the overflow, allowing them to gain control over the affected system, execute arbitrary commands, install malware, or access sensitive data.
Microsoft has warned that an attacker who successfully exploits this vulnerability could gain SYSTEM privileges, the highest level of access on a Windows system. This elevates the risk associated with CVE-2024-26229, making it a prime target for malicious actors.
Microsoft originally addressed the vulnerability in its April Patch Tuesday updates, urging users to apply the fix as soon as possible. However, the recent release of PoC exploit code for CVE-2024-26229 on GitHub [1,2] has heightened concerns as it could make it easier for less-skilled attackers to leverage the flaw.
Security experts warn that the availability of PoC code could lead to an increase in attacks targeting unpatched systems. Individuals and organizations must prioritize updating their Windows systems to the latest version, ensuring they are protected from this dangerous vulnerability.