RID Hijacking: Maintaining Access on Windows Machines
The RID Hijacking hook, applicable to all Windows versions, allows setting desired privileges to an existent account in a stealthy manner by modifying some security attributes of a user.
By only using OS resources, it is possible to replace the RID of a user right before the access token is created. To automatize the attack, a Metasploit module was developed. It requires a meterpreter session against the victim.
Overview
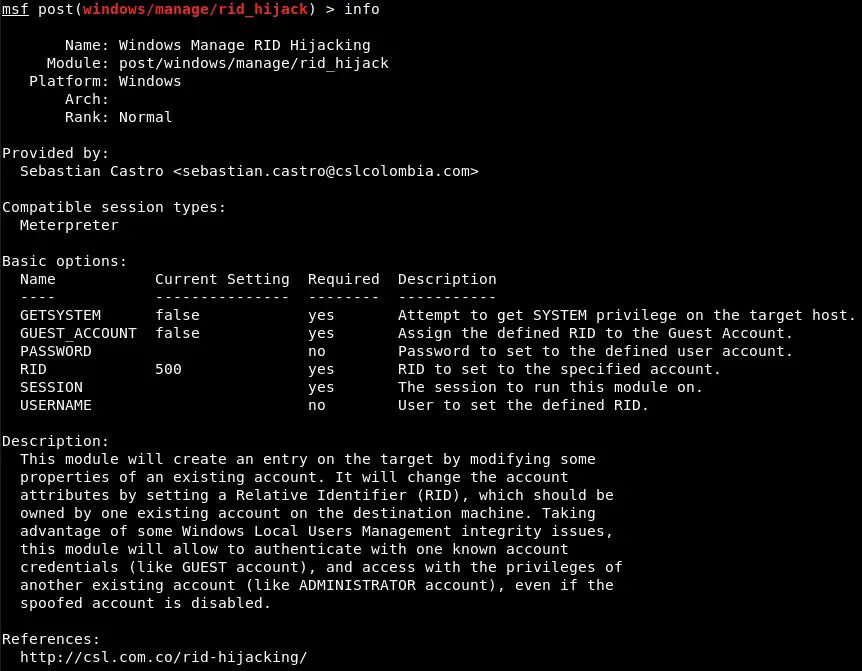
This module will create an entry on the target by modifying some properties of an existing account. It will change the account attributes by setting a Relative Identifier (RID), which should be owned by one existing account on the destination machine.
Taking advantage of some Windows Local Users Management integrity issues, this module will allow to authenticate with one known account credentials (like GUEST account), and access with the privileges of another existing account (like ADMINISTRATOR account), even if the spoofed account is disabled.
By using a meterpreter session against a Windows host, the module will try to acquire SYSTEM privileges if needed, and will modify some attributes to hijack the permissions of an existing local account and set them to another one.
Vulnerable Software
This module has been tested against:
- Windows XP, 2003. (32 bits)
- Windows 8.1 Pro. (64 bits)
- Windows 10. (64 bits)
- Windows Server 2012. (64 bits)
This module was not tested against, but may work on:
- Other versions of windows (x86 and x64).
Download
git clone https://github.com/r4wd3r/RID-Hijacking.git
Use
Options
- GETSYSTEM: Try to get SYSTEM privileges on the victim. Default:
false - GUEST_ACCOUNT: Use the GUEST built-in account as the destination of the privileges to be hijacked. Set this account as the hijacker. Default: false.
- SESSION: The session to run this module on. Default: none.
- USERNAME: Set the user account (SAM Account Name) of the victim host which will be the destination of the privileges to be hijacked. Set this account as the hijacker. If GUEST_ACCOUNT option is set to true, this parameter will be ignored if defined. Default: none.
- PASSWORD: Set or change the password of the account defined as the destination of the privileges to be hijacked, either GUEST account or the user account set in USERNAME option. Set password to the hijacker account. Default: none.
- RID: Specify the RID number in decimal of the victim account. This number should be the RID of an existing account on the target host, no matter if it is disabled (i.e.: The RID of the Administrator built-in account is 500). Set the RID owned by the account that will be hijacked. Default: 500
Scenarios
Assigning Administrator privileges to Guest built-in account.
Results after login in as the Guest account.
Assigning Administrator privileges to local custom account.
Results after login in as the testuser account.
Assigning custom privileges to Guest built-in account and setting new password to Guest.
Assigning custom privileges to local custom account and setting new password to custom account.
Source: https://github.com/r4wd3r/